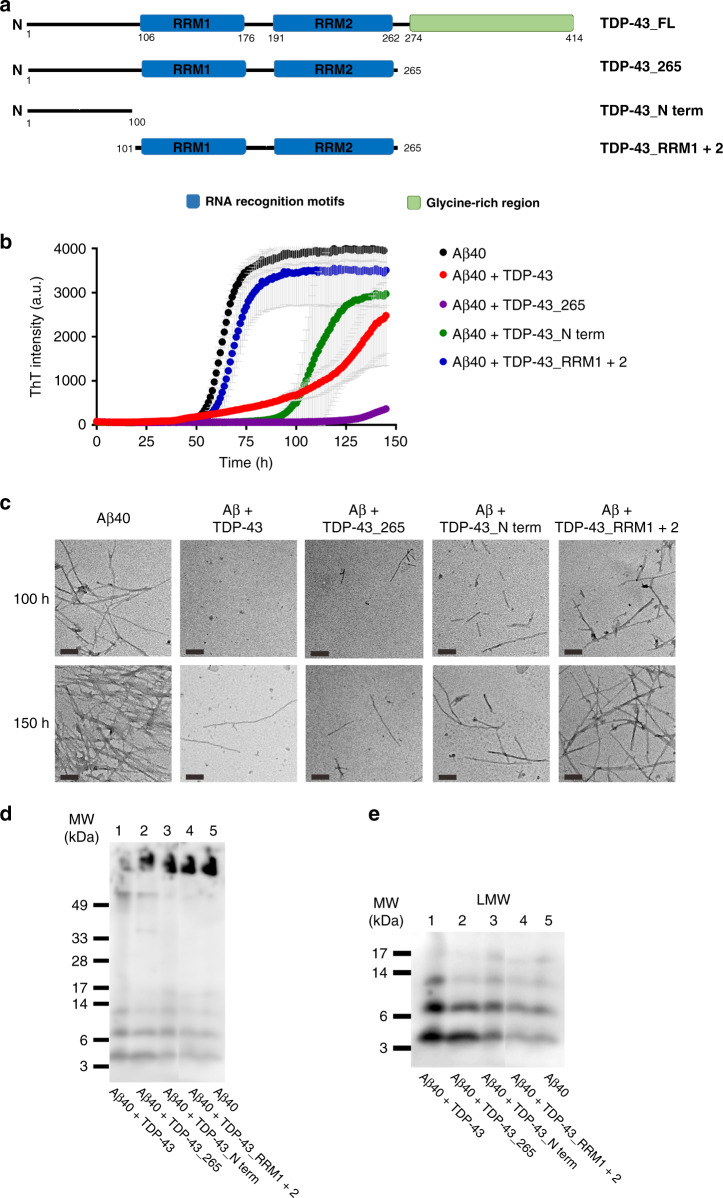
Fig. 2. Truncated TDP-43 variants inhibit Aβ fibrillization.
a Illustration of the structural motifs of TDP-43. Full-length TDP-43 contains an N-terminal domain, two RNA recognition motifs (RRM1 and RRM2), and a glycine-rich region in its C-terminus. The constructs used in the study are shown. They are full-length TDP-43, TDP-43 aa 1–265 (TDP-43_265), TDP-43 aa 101-265 (TDP-43_RRM1 + 2), and TDP-43 aa 1–100 (TDP-43_N-term). b ThT assays of Aβ fibrillization (black) and with TDP-43 variants (TDP-43_FL, red; TDP-43_265, purple; TDP-43_N-term, green; TDP-43_RRM1 + 2, blue) in 10 mM Tris buffer, pH 8.0. Aβ40 concentration was 25 μM, and TDP-43 concentration was 0.25 μM. The averaged data from three replicates and standard deviations are plotted. c TEM images of Aβ species with and without TDP-43 proteins. Two incubation time points, 100 h and 150 h were chosen for examination. The samples were loaded on SDS-PAGE d and then probed by anti-Aβ antibody, 6E10 to show the relative amounts of Aβ40 amyloid fibrils. Two times of independent experiments were performed. e The enlarged area of Fig. 2d shows a clear band distribution of low-molecular-weight Aβ species. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.