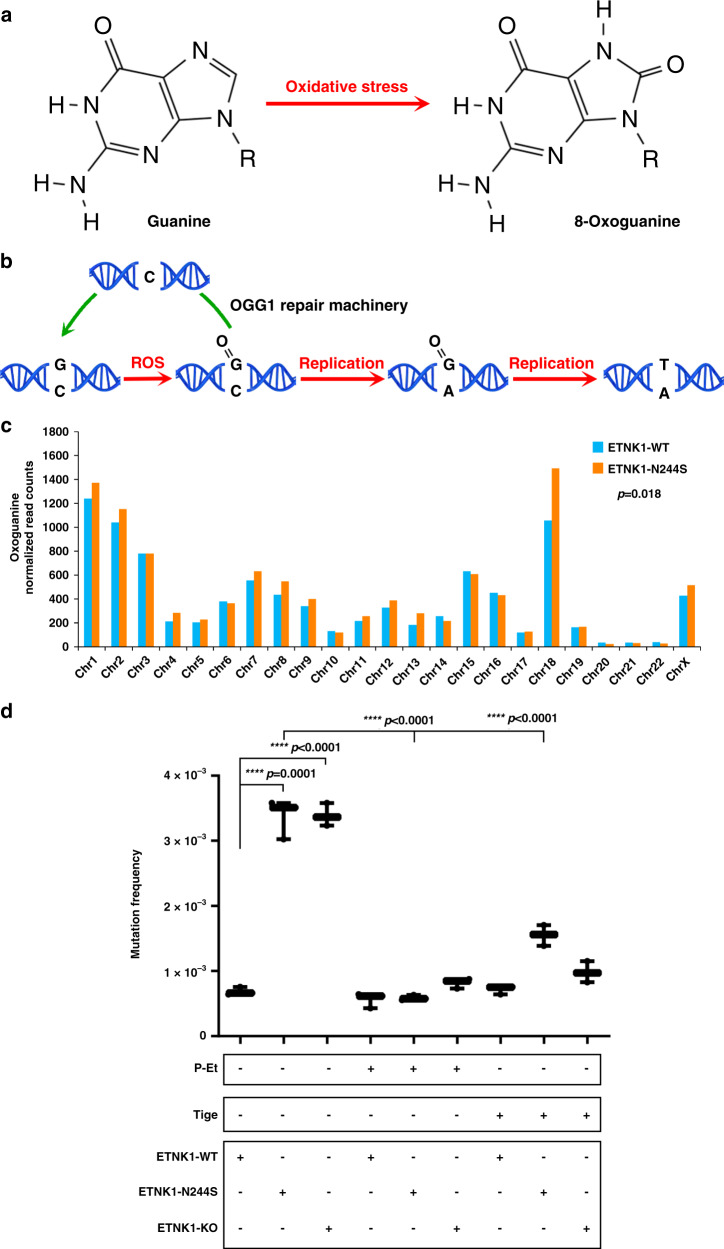
Fig. 4. Oxoguanine analysis and 6-thioguanine resistance.
a Diagram showing the chemical reaction responsible for the generation of oxoG from G after exposure of gDNA to reactive oxygen species. b Scheme of the oxoG-mediated DNA damage. In the presence of the modified base, the gDNA may undergo two different destinies: either the base is excised, owing to the recruitment of the oxoG DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1) repair machinery before the onset of a new replication cycle, or it causes the misincorporation of an adenine in the complementary strand, eventually leading to a G:C to T:A transversion. c Per-chromosome quantification of oxoG binned read counts in ETNK1-WT and N244S CRISPR lines following total read counts normalization; (n = 2). Statistical analysis was performed using a Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. d Mutation frequency assessed by 6-thioguanine assays in ETNK1-WT, N244S, and KO CRISPR lines in the absence or presence of 1 mM P-Et or 2.5 µM tigecycline (cell were pretreated for 15 days; 1 million of cells was plated and exposed to 30 μM of 6-TG for 15 days, while 1500 cells were plated for 15 days, as control). The boxplots delimit the interquartile range; the central bar represents the median; the whiskers extend from minimum to maximum (n = 3 independent experiments). Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc correction. Source data are provided as a Source data file.