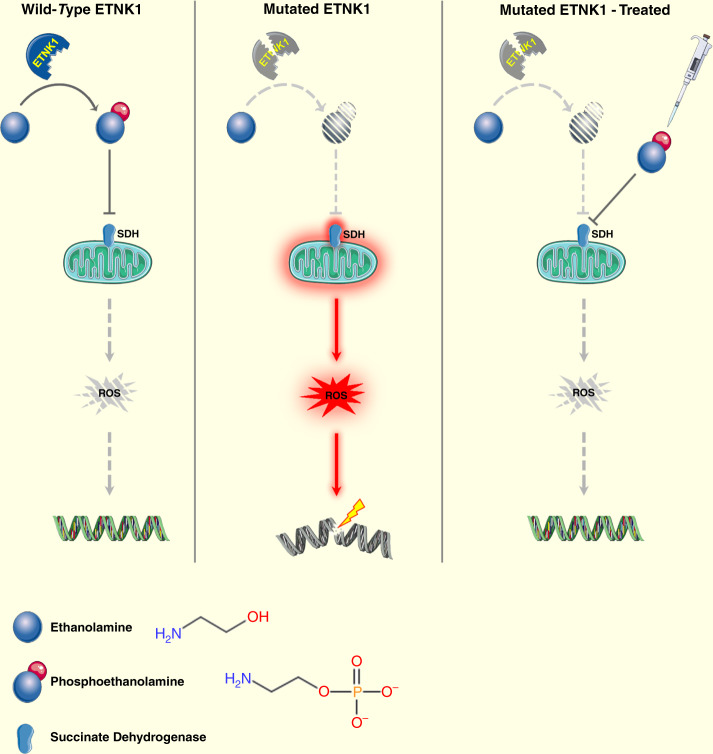
Fig. 7. Diagram showing the proposed model for ETNK1 mutations.
Left panel: wild-type ETNK1 actively phosphorylates Et leading to the accumulation of P-Et, which in turn negatively modulates mitochondrial activity and ROS production through inhibition of SDH. Middle panel: in the presence of mutated ETNK1 the production of P-Et is impaired, which causes abnormal mitochondrial activation, increased ROS production and DNA damage. Right panel: treatment of ETNK1-mutated cells with exogenous P-Et leads to restoration of normal mitochondrial activity through suppression of SDH, normalization of ROS production and protection of DNA from ROS-mediated damage. Elements of the image were obtained from https://smart.servier.com/ under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License.