Figure 3.
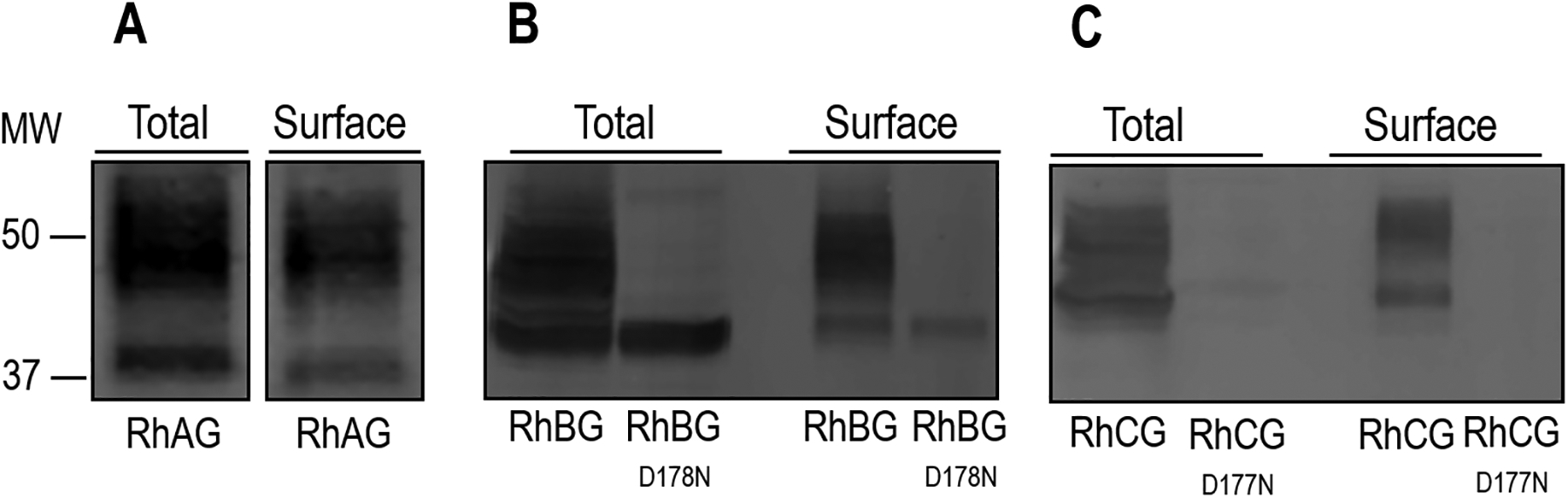
Surface expression of RhAG, RhBG, RhBGD178N, RhCG, and RhCGD177N. We assessed the total and surface expression of RhAG, RhBG, RhBG, RhBGD177N, RhCG, and RhCGD178N by biotinylating 30 intact oocytes injected with cRNA for each protein channel, and used anti-RhAG, anti-RhBG, or anti-RhCG to detect protein abundance. a RhAG. We detect the protein in both the total and surface fractions. There is also a characteristic high molecular weight pattern consistent with mature N-linked glycosylation in both samples. b RhBG. We also detect glycosylated WT RhBG in both total and surface fractions. However, the abundance of RhBGD178N in the total fraction is greatly reduced and lacks any detectable glycoslyation. The abundance of the mutant protein is also greatly reduced at the cell surface. c RhCG. We detect WT protein in the total and surface fractions, but we are unable to detect appreciable amounts of RhCGD177N in either fraction. Molecular weight (MW) markers are displayed to the left.
