Figure 8A.
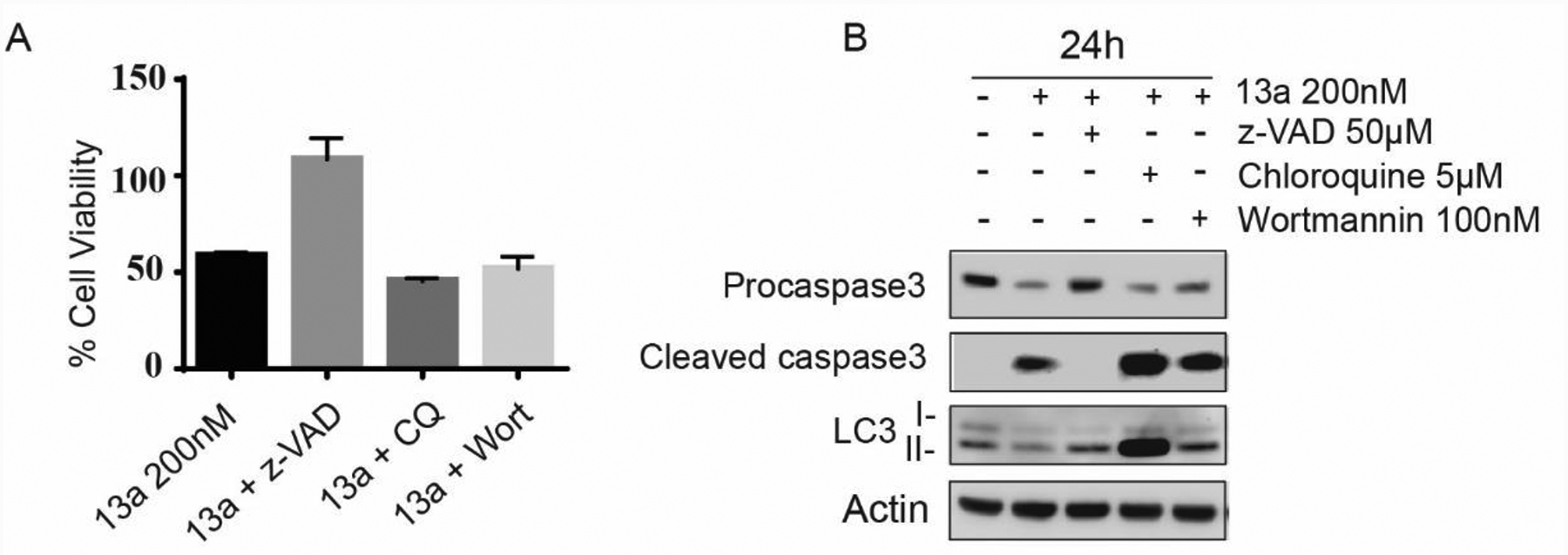
Treatment of 13a (200 nM) with z-VAD (50 μM), chloroquine (CQ 5 μM) or wortmannin (Wort 100 nM) for 24 h incubation (*p < 0.001, n = 3). The pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD is capable of attenuating cell death rather than the autophagy inhibitors wortmannin and chloroquine, suggesting although both of apoptosis and autophagy occur after treatment of 13a, apoptosis is the key factor leading to cell death. 8B. Treatment of 13a (200 nM) with z-VAD (50 μM), chloroquine (CQ 5 μM) or wortmannin (Wort 100 nM) for 24 h incubation (*p < 0.001, n = 3). z-VAD rescues procaspase activation, and chloroquine blocks the degradation of LC3-II in 24 h and prevent the progression of autophagy.
