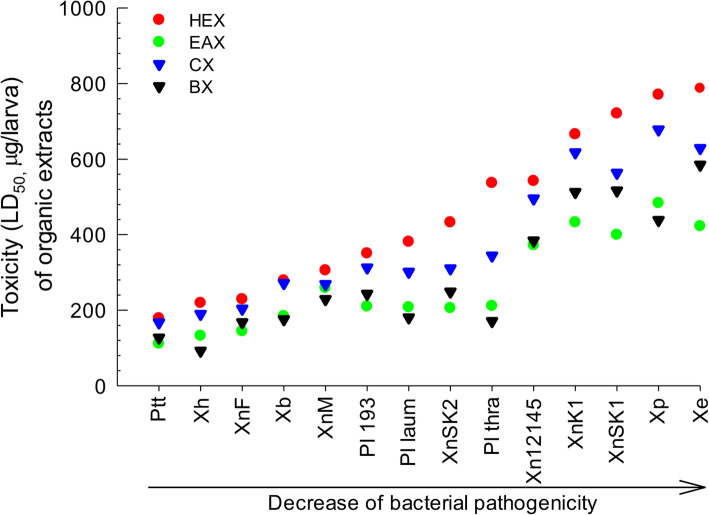
Fig. 1.
Correlations between insecticidal activities of bacteria and their organic extracts. Bacteria used in this assay were: Photorhabdus temperata Subsp. temperata ANU101 (‘Ptt’), Xenorhabdus hominickii ANU101 (‘Xh’), X. nematophila K1 (‘XnK1’), X. ehlersii KSY (‘Xe’),, X. nematophila SK1 (‘XnSK1’), X. nematophila SK2 (‘XnSK2’), Photorhabdus luminescens KACC12123 (‘Pl 193’), P. luminescens subsp. laumondii KACC12283 (‘Pl laum’), P. luminescens subsp. thracensis KACC12284 (‘Pl thra’), X. nematophila KACC12145 (‘Xn12145’), X. nematophila Mexico (‘XnM’), X. nematophila France (‘XnF’), X. bovienii (‘Xb’), and X. poinarii (‘Xp’). Bacterial pathogenicity is presented in Table 1. Their cultured broths were fractionated with four different organic solvents: hexane (‘HEX’), ethyl acetate (‘EAX’), chloroform (‘CX’), and butanol (‘BX’). For each treatment, three replications were performed using 10 larvae per replication