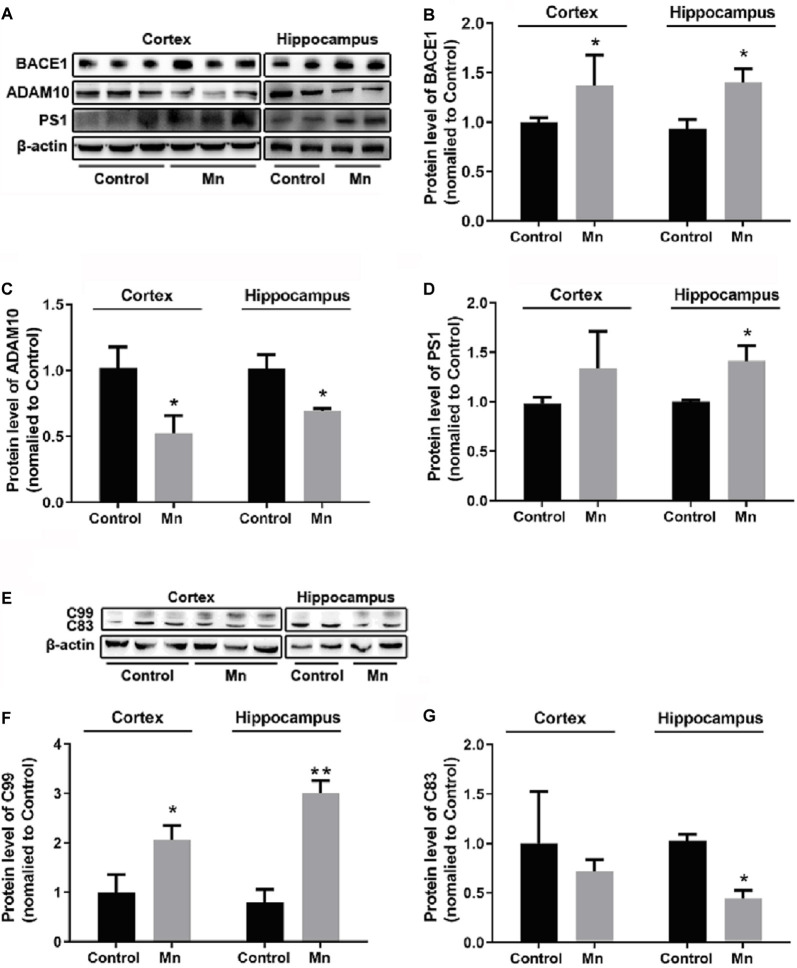
Figure 3.
Mn exposure promoted amyloidogenic APP processing in 3×Tg-AD mouse brains. (A–D) The expression levels of BACE1, ADAM10, and γ-secretase PS1 in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) were examined by Western blot. The protein levels of BACE1 and PS1 were significantly increased (B,D), whereas ADAM10 were markedly decreased (C) in the cortex and hippocampus of Mn-exposure mice. (E–G) Western blot analysis of the expression of intracellular APP cleavage fragments, including C99 and C83, in the brain of AD mice treated with or without Mn. Mn exposure significantly increased the levels of C99 both in the cortex and hippocampus, and reduced the levels of C83 in hippocampus. β-actin served as the internal control. n = 5 mice for each group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, compared with the control group, t-test.