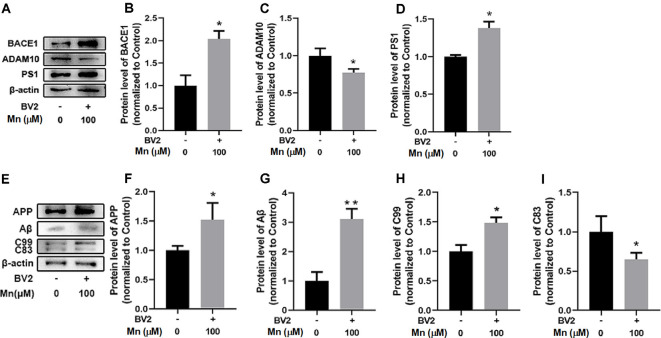
Figure 5.
Mn enhances amyloidogenic APP processing in APPsw-N2a cells cocultured with microglia BV2 cells. (A–D) Western blot analyses of the protein levels of BACE1, ADAM10, and PS1 in APPsw-N2a cells. Example gel images are shown with β-actin as the internal control (A). BACE1 level (B) and PS1 level (D) were increased, but ADAM10 level (C) was decreased, in 100 μM Mn-treated APPsw-N2a cells cocultured with BV2, compared with the control group. (E–I) Western blot analyses were carried out to examine the protein expression levels of APP, C99, C83, and Aβ in APPsw-N2a cells (E). Mn treatment, 100 μM, significantly increased the protein levels of APP (F), Aβ (G), and C99 (H) in APPsw-N2a cells cocultured with BV2, compared with the control group; in contrast, 100 μM Mn treatment significantly decreased in the protein levels of C83 (I) in APPsw-N2a cells cocultured with BV2 compared with the control group. All data are means ± SE. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA, n = 5 for each group.