Figure 4. Using isoTarget to Identify the Subcellular Localizations of Endogenous Dscam Isoforms.
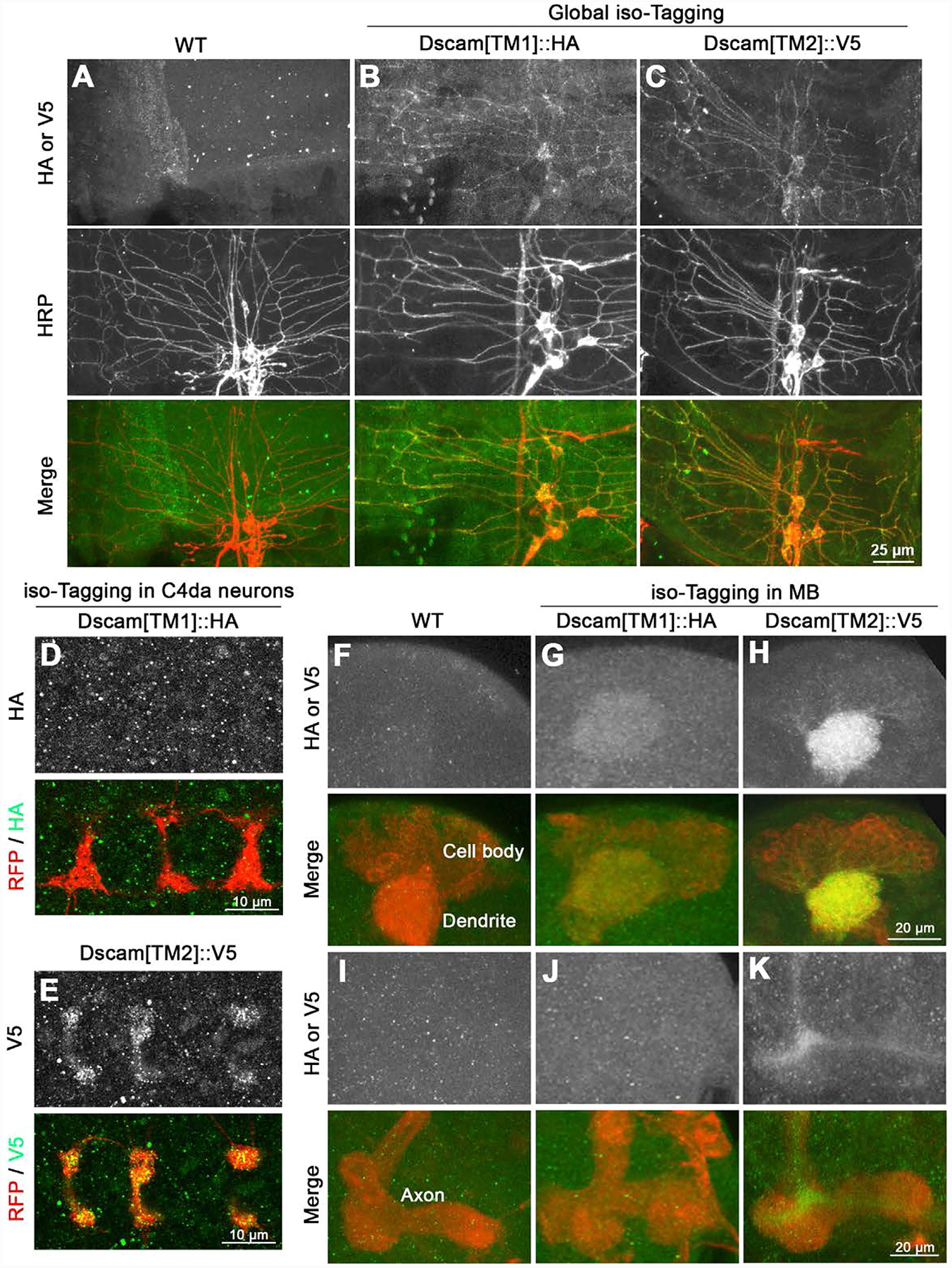
(A–C) Both Dscam[TM1] and [TM2] are localized in the dendrites of larval PNS neurons. At early second-instar stage, compared with control (A), global iso-tagging reveals the localization of endogenous [TM1] and [TM2] in the dendrites of PNS da neurons, which is double-labeled by the PNS neuron marker anti-HRP.
(D and E) Iso-tagging shows that endogenous Dscam[TM2], but not [TM1], is in the axon terminals of C4 da neurons in early second-instar larvae. The C4 da-specific driver ppk-Gal4 was used to tag endogenous Dscam[TM1] or [TM2] by driving the expression of UAS-R-recombinase and to label C4 da axon terminals by driving the expression of UAS-mCD8::RFP.
(F–H) Both Dscam[TM1] and [TM2] are localized in the dendrites of CNS neurons. Iso-tagging in mushroom body (MB) neurons shows that both endogenous [TM1] and [TM2] are present in the MB calyx, which is a cluster of dendrites in third-instar larvae. The MB driver OK107-Gal4 was used to drive the expression of R recombinase for tagging endogenous Dscam[TM1] or [TM2] and the expression of mCD8::RFP for labeling MB morphology.
(I–K) Dscam[TM2], but not [TM1], is localized in MB axons. Compared with the WT control, endogenous Dscam[TM2], but not [TM1], is detected in the axon peduncles of MB in third-instar larvae.
See also Figure S5.
