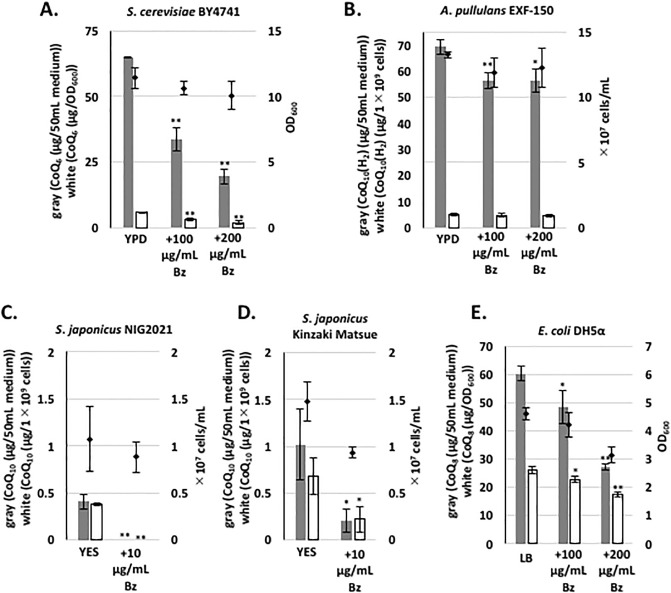
Fig 9. CoQ production in various microorganisms following Bz addition.
For the pre-culture, S. cerevisiae BY4741, A. pullulans EXF-150 [43], S. japonicus NIG2021, S. japonicus isolated from a Kinzaki ancient tomb located in Matsue [38], and E. coli DH5α cells were cultivated in 10 mL of the indicated medium for 1 day. To explore the inhibitory effect of Bz, the indicated amount (μg/mL) of Bz was added to the media. For fungi, the initial cell density was ~1×105 cells/mL and cells were cultivated for 2 days with rotation at 30°C; for E. coli, the initial cell density was OD600 0.1 and cells were cultivated for 12 h with rotation at 37°C. Gray bars show the CoQ10 content per 50 mL of medium, and white bars show CoQ10 normalized against cell number. Diamonds show cell number or optical density. Five micrograms of CoQ6 was used as an internal standard for measuring CoQ8, CoQ10, or CoQ10(H2), which is CoQ10 with a saturated isoprenoid unit in the side chain. Five micrograms of CoQ10 was used as an internal standard for measuring CoQ6. Data are represented as the mean ± SD of three measurements. Asterisks on bars denote statistically significant differences (**p<0.01, *p<0.05) relative to each medium without Bz (Student’s t-test).