Figure 4. ESC clone picking.
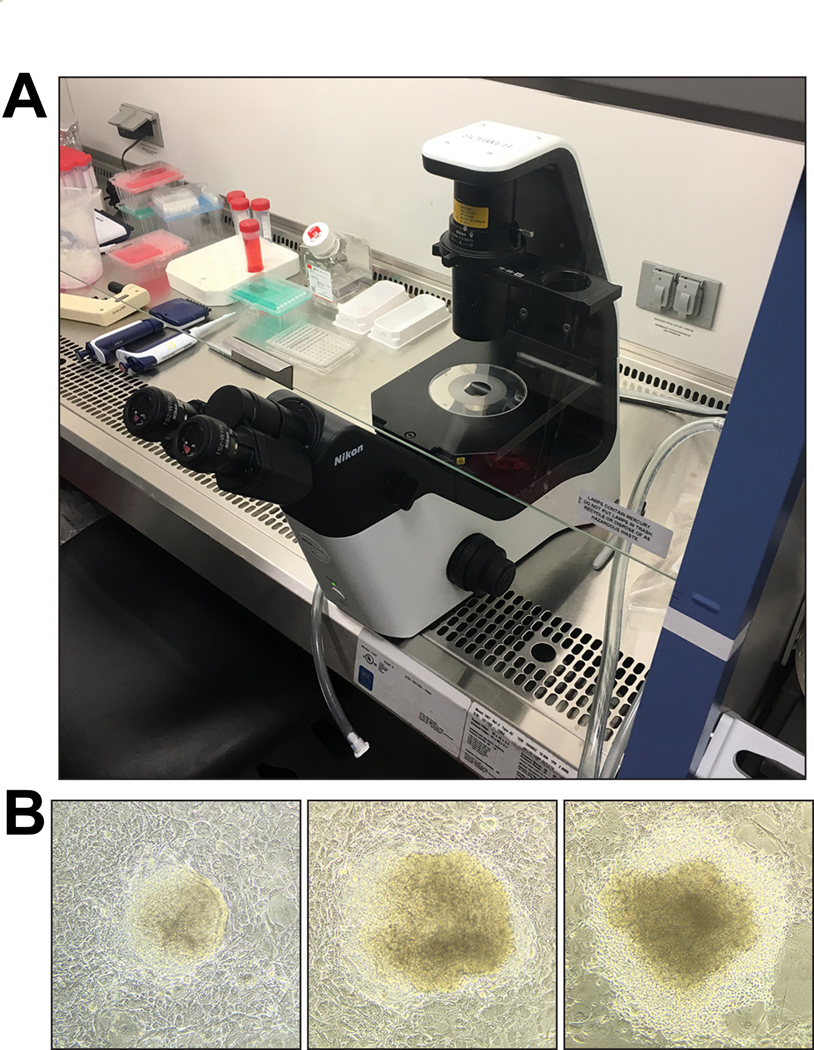
(A) Example of setup for picking ESC clones under a microscope inside a biosafety cabinet. An inverted routine microscope (for example, Nikon TS2 Eclipse with plain stage) can easily be moved into a biosafety cabinet for clone picking. ESC clones are picked with sterile, P20 filter pipette tips under a 10× objective. (B) When picking, domed clones with clear, distinct borders should be preferred over clones with flattened appearance and signs of differentiation. Three clones—ordered from better (left) to worse (right) morphology—are shown as examples. Approximate sizes of ESC clones shown are 200 μm (left), 360 μm (middle), and 400 μm (right). Images were acquired with an Apple iPhone 6S attached to a Nikon Eclipse TS2 inverted routine microscope.
