Abstract
Objective
Recent efforts to update the definitions and taxonomic structure of concepts related to pain have revealed opportunities to better quantify topics of existing pain research subject areas.
Methods
Here, we apply basic natural language processing (NLP) analyses on a corpus of >200,000 abstracts published on PubMed under the medical subject heading (MeSH) of “pain” to quantify the topics, content, and themes on pain-related research dating back to the 1940s.
Results
The most common stemmed terms included “pain” (601,122 occurrences), “patient” (508,064 occurrences), and “studi-” (208,839 occurrences). Contrarily, terms with the highest term frequency–inverse document frequency included “tmd” (6.21), “qol” (6.01), and “endometriosis” (5.94). Using the vector-embedded model of term definitions available via the “word2vec” technique, the most similar terms to “pain” included “discomfort,” “symptom,” and “pain-related.” For the term “acute,” the most similar terms in the word2vec vector space included “nonspecific,” “vaso-occlusive,” and “subacute”; for the term “chronic,” the most similar terms included “persistent,” “longstanding,” and “long-standing.” Topic modeling via Latent Dirichlet analysis identified peak coherence (0.49) at 40 topics. Network analysis of these topic models identified three topics that were outliers from the core cluster, two of which pertained to women’s health and obstetrics and were closely connected to one another, yet considered distant from the third outlier pertaining to age. A deep learning–based gated recurrent units abstract generation model successfully synthesized several unique abstracts with varying levels of believability, with special attention and some confusion at lower temperatures to the roles of placebo in randomized controlled trials.
Conclusions
Quantitative NLP models of published abstracts pertaining to pain may point to trends and gaps within pain research communities.
Keywords: Pain, Natural Language Processing, Deep Learning, Machine Learning, Biomedical Informatics, word2vec
Introduction
Pain has been an active area of investigation since the dawn of history, and in recent times it has garnered significantly increased attention with the onset of the opioid use disorder crisis in the United States [1,2]. This crisis and its many organizational responses, such as the National Institutes of Health Helping to End Addiction Long-Term (HEAL) initiative, have spurred further examination into the science and clinical therapy of both acute and chronic pain. These studies have revealed multiple opportunities to better refine the definitions and taxonomic structure of concepts related to pain, including initiatives related to both acute (ACTTION-APS-AAPM Pain Taxonomy [AAAPT]) and chronic (ACTTION-American Pain Society Pain Taxonomy [AAPT]) pain [3,4].
To this point, during the evolution of the AAPT and AAAPT tools, it had become apparent that no quantitative evaluation of which aspects of pain had been topics of substantive inquiry had been published [5,6]. For instance, during discussions on domains and conditions related to pain, an empirical approach based on expert consensus was employed, given the absence of any preexisting objective infrastructure. Although such approaches were certainly appropriate and successful, the preceding discussions nevertheless exposed an opportunity to better quantify the domains of research subsumed under the broader definitions of “pain.”
The overarching goal of these analyses was to quantify the topics, content, and themes on pain-related research dating back to the 1940s. Here, we apply basic natural language processing (NLP) analyses on a corpus, or collection of texts, of >200,000 abstracts published on PubMed under the MeSH of “pain” [7]. We began by quantifying general NLP statistics of pain-related abstracts [8,9]. Next, we examined the definitions of pain-related terms using vector-embedded techniques (word2vec) to quantitatively define pain-related terms by their similarity to other terms within the PubMed corpus of pain abstracts [10,11]. To further refine the meanings of research areas pertaining to pain, we then used two topic modeling techniques to determine the count, content, and intertopic relationships of distinct quantified topics under the Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) of pain. Finally, we used deep learning techniques to generate new, synthetic abstracts to offer insights into high-level topic integration in pain research.
Methods
This project was an analysis of existing publicly available PubMed abstracts; thus institutional review board (IRB) requirements were waived by IRB-01 at the University of Florida.
All preparation, analyses, and reporting steps were conducted using Python 3 [12]. For reference, the associated code can be found in the Supplementary Data file and includes a listing of the libraries used for the analyses. The Supplementary Data are given in the form of a Jupyter Notebook and interweave code segments with each segment’s output in an effort to improve the interpretability of the exercises and enhance the reproducibility of the experiments [13,14].
Data Preparation
On June 5, 2017, at 0900, the PubMed repository was queried for Medline entries under the MeSH of “pain” using an English-language filter and the Medline entry for the corpus downloaded. For each entry, the PMID, article title, journal title, publication date, and abstract text were extracted using the Medline.parse function of the Biopython library (version 1.7.1) [15]. The entries were converted to a Pandas (version 0.23) data frame such that each row represented a unique abstract and each column represented one of the variables of the abstract’s Medline entry [16].
Using standard NLP techniques, corpus cleaning was performed on a copy of the original abstract text [17]. Punctuation, numbers, words in all capitals followed by a colon (signifying a section header such as “BACKGROUND:”), and single-letter words were removed from abstract text. Hyphens were excepted from this filtering given their common use in defining certain concepts. The remaining terms were converted to lowercase. Next, stop words (e.g., the, me, you, it, of) referenced from the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK; version 2.3.1) “English” set were removed to minimize focus on those terms found throughout most English-language documents, as they offer little value in differentiating among domain-specific language [18]. Thus, a sample original abstract beginning “BACKGROUND: Despite their huge epidemiological impact…” was converted to “despite huge epidemiological impact…” This version of the abstract text was defined as the “cleaned” abstract.
Next, using a copy of the “cleaned” abstract, words were tokenized, or split into separate terms, using the NLTK RegexpTokenizer with the string “r’\w+’” coding for words comprised of alphanumerics and associated underscores. This tokenization was performed to allow analyses of component terms. Thus, the cleaned abstract containing “despite huge epidemiological impact…” was converted to (despite, huge, epidemiological, impact). This version was defined as the tokenized abstract. Elsewhere in the analyses, token counts were calculated for the original uncleaned abstracts, and such token counts were specified as such.
A fourth copy was then created whereby tokenized terms from cleaned abstracts were “stemmed” or had common suffixes removed using the NLTK PorterStemmer such that the tokens “pain” and “pains” would be considered a single entity. Similar to the tokenization process, this step was performed to enable examination of term distribution in later analyses. This version was defined as the stemmed abstract.
Analyses
Analyses were conducted using the processed corpus. Analyses were organized to first consider simpler constructs including term-level descriptions (Term-Level Descriptions section) and the relationships among terms using word2vec (word2vec Comparisons section). We then turned our attention to higher-order analyses of concepts contained within the corpus via topic modeling (Topic Modeling Data Preparation section) using both latent semantic indexing (LSI; Topic Modeling via LSI section) and latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA; Topic Modeling via LDA section) techniques. Finally, we employed deep learning methods in a text generation exercise (Text Generation Summaries section) to better understand how various terms and topics were organized into sentences and higher-order constructs used in the abstract format.
Term-Level Descriptions
Abstract length as a function of token counts was calculated, and the distribution of abstract lengths was determined for raw abstracts, cleaned abstracts, and the number of unique terms in cleaned abstracts. The most common 100 stemmed terms across all cleaned abstracts were calculated and their distribution across abstracts measured.
We next turned our attention to calculating the term frequency–inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) [19]. The TF-IDF weights each term for each abstract reflecting how important a given term is for that abstract within the context of the corpus as a whole. For instance, a term with a high TF-IDF may be uncommon across the corpus, but perhaps especially common in a particular abstract. Because of computational constraints, we created a TF-IDF matrix with rows equal to the number of abstracts, columns equal to the 1,000 terms with the highest TF-IDF, and cell values representing the TF-IDF statistic for a given abstract–term pair. Additional constraints to the TF-IDF matrix determination included a minimum document frequency of two abstracts and a maximum document frequency of 50% of abstracts. In this TF-IDF application, terms could also be comprised of n-grams, which are sets of consecutive terms in an abstract, with n-gram length ranging from one to three. The n-gram approach allowed us to consider common phrases as entities alongside individual terms, controlling for shared commonalities across all abstracts in the corpus. We identified the distribution of the TF-IDF across the corpus, as well as those terms across the corpus with the greatest TF-IDF values.
word2vec Comparisons
word2vec is a method for vectorizing words from each abstract based on which words they are adjacent to [11,20]. In short, this modeling approach uses a two-layer neural network to assign each word a long list, or vector, of numbers whereby each number roughly represents how often that word is close to all of the other words within the corpus. Through this process, words can be defined according to their vector representations, and words with similar meaning end up with similar vector representations and lying close to each other in an n-dimensional vector space. Writ large, in one canonical example, word2vec can then infer that “king” is to “queen” as “man” is to X, and correctly indicate that x is “woman” despite never receiving an explicit definition, gender assignment, or any other meta-information about the term “woman.”
In this application using GenSim (version 3.4), we used word2vec models based on the corpus of abstracts in an effort to “objectively” define terms related to pain [21]. First, we identified those terms most similar to the key entities “pain,” “acute,” and “chronic.” Taking further advantage of the vector representation of each term, which allows for addition and subtraction of term-related vectors, we then looked for terms similar to the vector concept of “pain minus chronic” and “pain minus acute.” The word2vec model interprets this task as looking for words similar to “pain” but dissimilar to “chronic.” We also used this approach to examine for terms related to the vector concept of “acute minus chronic” and “chronic minus acute.” We then measured the calculated similarity in vector space between the terms “acute” and “chronic,” as well as for “anesthesia” and “surgery.” Finally, those terms with the highest LDA values were plotted to help visualize similar and different terms within the vector space.
Topic Modeling Data Preparation
Topic modeling was performed with latent semantic indexing (LSI) and latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) using GenSim (version 3.4) [21]. Preparatory to the topic modeling analyses, we first created a dictionary to map words to integer labels that represented each separate word by extracting each individual token from the tokenized cleaned abstracts. We then filtered “extreme” terms from the dictionary such that all tokens were present in at least one document but not in >80% of abstracts. This step decreased the number of terms that were necessary to include in each topic modeling strategy, an important step given the considerable computational requirements and times necessary even for this reduced set of features. Additionally, this approach served as a filter that focused on those terms unique to subsets of abstracts from a probabilistic perspective, thus supplementing the supervised, stop words–based approach discussed earlier. Each abstract was then converted to a “bag of words” for further processing.
Topic Modeling via LSI
In LSI, we first created a matrix of words (rows) and abstracts (columns) where the cells indicated the count of a given word in a given abstract [22]. Because some words appear more frequently in general (e.g., “the”), instead of using the actual word count, typically we use the TF-IDF measure, which ensures that we are adjusting the original word count by decreasing the weight of terms that occur very frequently in the abstract set. Because the resulting matrix is sparse (e.g., there are many cells with a value of zero, especially for rare words), we use a dimensionality reduction technique to obtain a smaller set of “topics” that associate co-occurring words (e.g., “chronic” and “pain”). In LSI, the dimensionality reduction technique is called the Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) technique. The SVD technique decomposes the original matrix into new and smaller matrices that associate words with latent topics, and latent topics with abstracts, across the corpus of abstracts. Notably, LSI considers each abstract to be a nonordered bag of words and each topic to be a collection of words that occur together in the same document.
Here, LSI was first performed using tokens from the cleaned abstracts, implemented using the GenSim library (version 3.4) [21]. A topic count of 10 was chosen based upon coherence testing of LSI models with topic counts ranging from 2 to 50 that demonstrated a peak coherence score at ∼10 topics. The resulting terms with corresponding term weights were reported for each topic.
Separately, we performed LSI using the TF-IDF of the cleaned abstracts by directly applying truncated SVD using the scikit-learn package (version 0.17.1) [23]. The truncated SVD provides a more efficient yet approximate decomposition of the TF-IDF document matrix. In our experiment, we used truncated SVD to obtain the two largest singular values. We then plotted a random sample of 200 abstracts where each abstract was plotted with respect to the two corresponding SVD components in an interactive HTML document.
Topic Modeling via LDA
In LDA topic modeling, each abstract is represented as a mixture of topics [24]. After assigning an empiric topic count, as for LSI, the algorithm assigns every word to a topic temporarily using the Dirichlet distribution. The algorithm then checks how prevalent the word is across all topics and how prevalent the topics are for a given abstract. This process is repeated for each word, in every abstract, across the entire corpus several times with iteratively updated assignments. Put another way, LDA pretends that abstracts are written by authors who first decide which mixture of topics will be included in the abstract (e.g., 50% acute pain, 30% chronic pain, 20% aging) and then randomly (but using the Dirichlet distribution) assign words from each topic to the abstract.
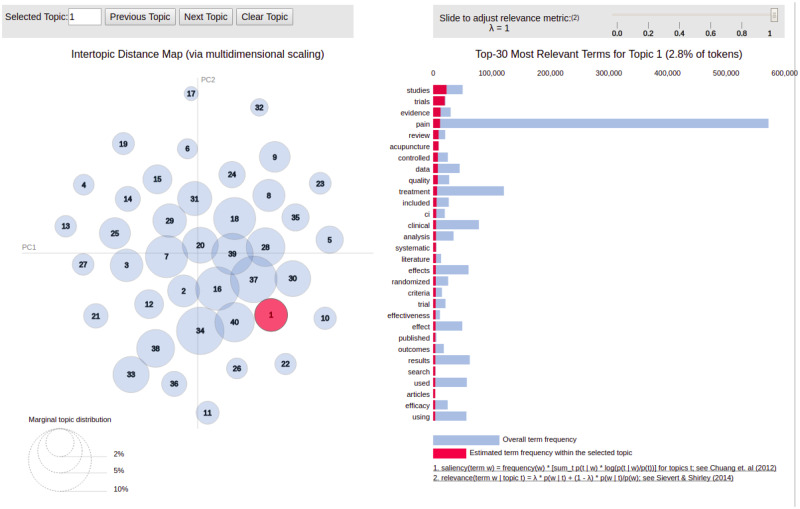
In addition to reporting term weights for each topic, we also implemented the pyLDAvis library to offer an interactive visualization of term assignments across the topics and to plot each topic using Jensen-Shannon divergence and principal coordinate analysis on a Cartesian plane [25,26]. For each topic, we identified those abstracts with the greatest topic contribution to highlight the linkages between topics, key words defining the topic, and the abstract most representative of said topic. We also listed the number and proportion of documents represented by each document.
In this visualization, each topic is represented by a plotted circle; the number inside of the circle identifies the labeled topic. The circle size is proportional to the proportions of topics across all terms in the corpus of abstracts. The red bars that appear when hovering over a topic show the estimated number of times that term was generated by the selected topic, and the blue bars represent the overall frequency of that term in the entire corpus of abstracts (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/LDAvis/vignettes/details.pdf).
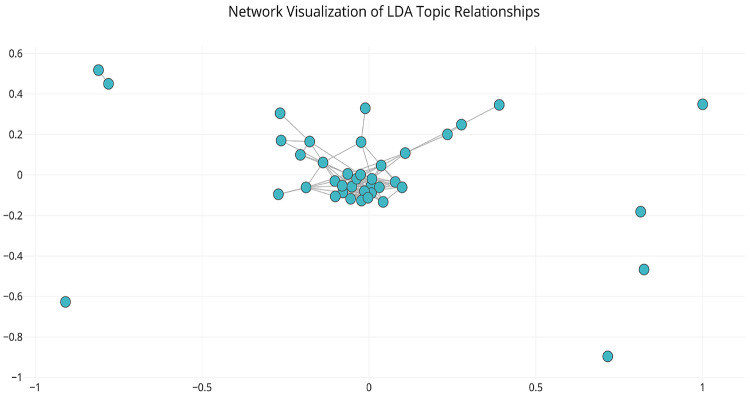
To further aid in visualizing the LDA topics, we constructed an interactive topic network. Briefly, this visualization represents each of the 40 LDA topics as a node on a graph, and the edges, or connections, between nodes highlight the intersecting and differentiating terms of the connected topics. The connectedness among topic-nodes was defined using the Jensen-Shannon distance metric, which considers the relative probability distribution of terms across topics to define the topic similarities [27–29]. In other words, to construct this graph, we measured the Jensen-Shannon distance between each pair of nodes and placed these values into a matrix where each row and column were represented by a topic node (adapted from: https://github.com/RaRe-Technologies/gensim/blob/develop/docs/notebooks/topic_network.ipynb).
Text Generation Summaries
To develop summaries of the corpus of abstracts, we randomly selected 100 abstracts and created 100-word summaries of the subset, along with the 10 key words most representative of the abstract sample. This was performed using the GenSim summarize and key words functions.
In an effort to further summarize the corpus of abstracts and gain additional qualitative insight into the nature of existing pain research, we used deep learning methods to generate new hypothetical abstracts based on our existing corpus. This represented a separate text generation exercise from the above GenSim methods. Specifically, we used an end-to-end, two-layer recurrent neural network with gated recurrent units (GRUs) to learn a pain-oriented language model from our entire corpus of pain-related abstracts [30,31]. The model was trained to predict the next word in an abstract given all preceding words and, similarly, was used to generate new abstracts one word at a time.
Contrary to our previous experiments, for generating abstracts, we did not apply TF-IDF, but rather created a token vocabulary by assigning an identifying integer to each unique word in the corpus. As training progressed, the GRU network jointly learned 100-dimensional embeddings for each word in the vocabulary. For training, we added special <START> and <END> tokens to bookend each abstract in our corpus, and when generating abstracts, we began with the <START> token and continued generating words until the <END> token was generated or a self-imposed limit of 300 words was reached.
Our model consisted of a 100-dimensional embedding layer, two 512-dimensional GRU layers, and a fully connected output layer with softmax activation. We trained our model for 10 epochs. In typical language generation tasks, a scaling parameter known as temperature is often used to control the balance between the conservative and obvious and the experimental and error-prone, and when generating our abstracts, we varied this temperature setting and explored its effects on pain-related text.
Results
There were 202,053 PubMed extracts downloaded and processed with complete abstract text. The oldest abstract originated in June 1949, and there were 5,333 unique journal titles within the cohort. The sum count of all tokens across the corpus of raw, unprocessed abstracts was 42,128,246 terms. This sum count decreased to 24,492,735 terms for cleaned abstracts. In considering only the sum count of unique tokens within each cleaned abstract (e.g., unique to that abstract, but shared across the corpus), there were 16,200,330 terms. Given an average adult reading speed of 300 words per minute, this corpus of raw abstracts would require 140,427.5 minutes, or 2,340.5 hours, or 292.5 eight-hour days to manually review.
Term Distributions
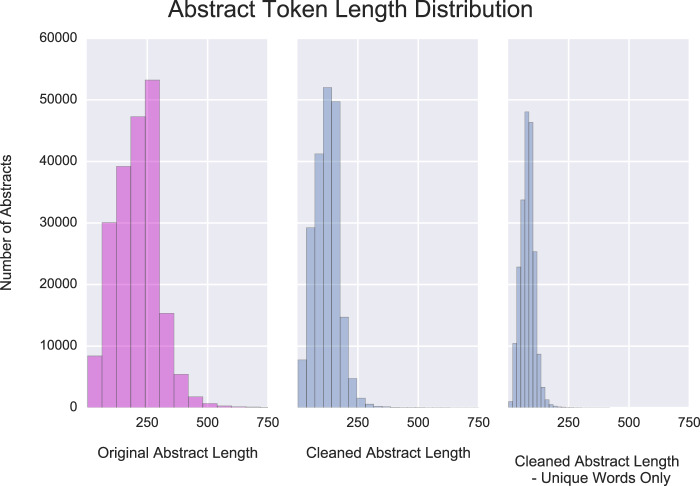
Across the corpus, for raw abstracts the word length ranged from three to 1,495, with a mean word length of 208.5 and a median length of 212 words. Figure 1 highlights the distribution of token lengths for original, cleaned, and unique terms within cleaned abstracts.
Figure 1.
Distribution of abstract token lengths for original, cleaned, and unique terms within cleaned abstracts. This figure is truncated at 750 terms to improve visualization of the skewed distribution. Across the corpus, for raw abstracts the word length ranged from three to 1,495, with a mean word length of 208.5 and a median length of 212 words.
Across the corpus of cleaned abstracts, the most common stemmed terms included “pain” (601,122 occurrences), “patient” (508,064 occurrences), and “studi-” (208,839 occurrences) (Figure 2) .
Figure 2.
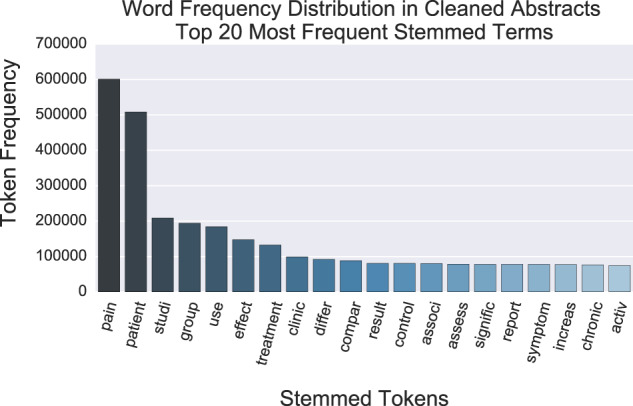
Word frequency distribution for the 20 most common stemmed terms in the corpus of a cleaned abstract. The stemming process removes suffixes such that common root terms can be considered single entities, minimizing the influence of such constructs as plural, tense, and possession.
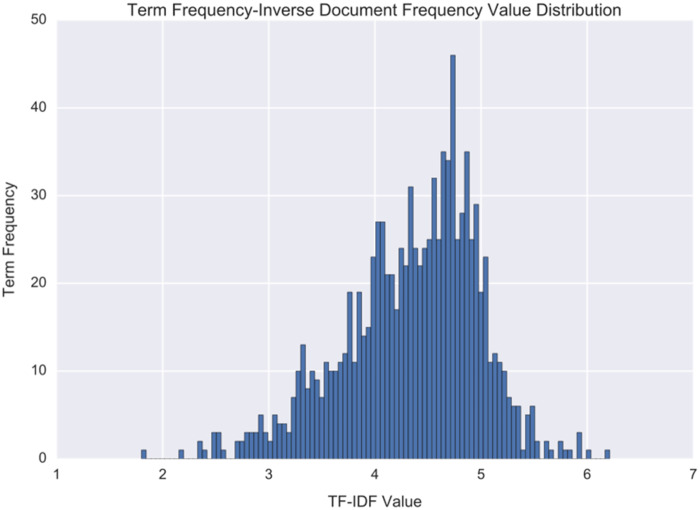
Figure 3 shows the distribution of TF-IDF values for the 1,000 terms with the most common frequency within the corpus of cleaned abstracts. Terms with the highest TF-IDF included “tmd” (TF-IDF = 6.21), “qol” (6.01), “endometriosis” (5.94), “pca” (5.94), “cad” (5.92), “acs” (5.85), “acupuncture” (5.8), “il” (5.73), “capsaicin” (5.72), and “oa” (5.65). Terms with the lowest TF-IDF within the 1,000-term cap included “study” (1.8), “treatment” (2.19), “significant” (2.36), “clinical” (2.36), “patient” (2.39), “significantly” (2.48), “using” (2.49), “results” (2.5), “used” (2.52), and “compared” (2.53).
Figure 3.
Term frequency–inverse document frequency value distribution for the 1,000 terms with the most common frequency within the corpus of cleaned abstracts. Terms with the highest TF-IDF included “tmd” (TFIDF 6.21), “qol” (6.01), “endometriosis” (5.94), “pca” (5.94), and “cad” (5.92). Terms with the lowest TF-IDF within the 1,000-term cap included “study” (1.8), “treatment” (2.19), “significant” (2.36), “clinical” (2.36), and “patient” (2.39).
word2vec Analysis of Term Relationships
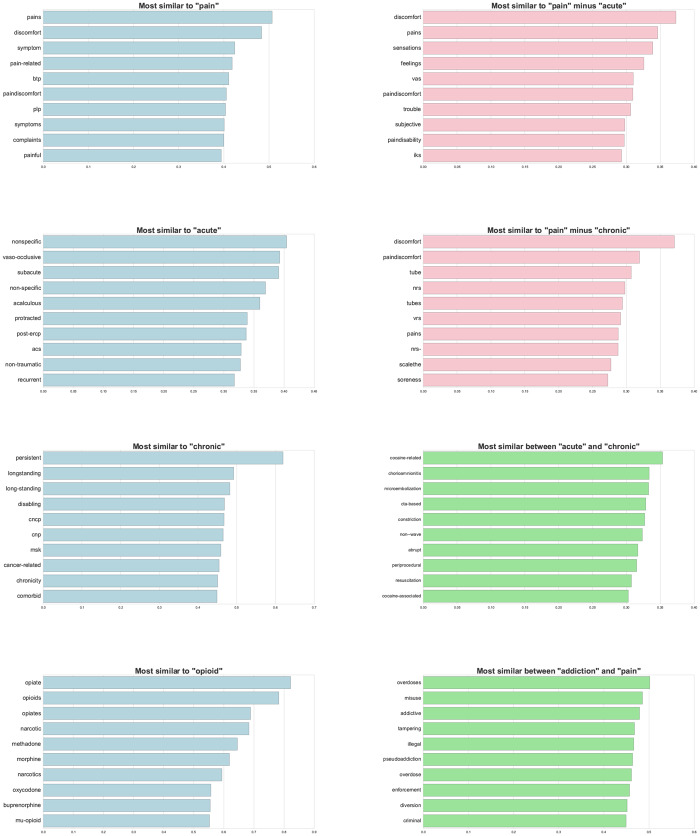
Figure 4 compares the vector–space relationships among key terms, including “pain,” “acute,” and “chronic.” The vector–space model was built using the pain corpus, and thus all comparisons fall under this internal context. Using the vector-embedded model of term definitions available via the “word2vec” technique, the most similar terms to pain included “discomfort,” “symptom,” and “pain-related”; the top 10 list also included the acronyms “btp” and “plp.” For the term “acute,” the most similar terms included “nonspecific,” “vaso-occlusive,” and “subacute”; “post-ERCP,” “ACS,” and “acalculous” were also cited as highly similar. For the term “chronic,” the most similar terms included “persistent,” “longstanding,” and “long-standing.” Additional details listing definitions and comparisons can be found in the Supplementary Data.
Figure 4.
Term relationships defined using the word2vec vector space model. The top 10 terms associated with pain, acute, chronic, and opioid suggest validation of implicit definitions of each term based upon the vector space methodologies. The vector space methods extend to mathematical functions of the term vectors for “pain minus acute” and “pain minus chronic.” For instance, “paindisability” is related to “pain minus acute” but not to “pain minus chronic.” Similar vector space functions highlight comparisons between “acute and chronic” and “addiction and pain.”
LSI-Based Topic Modeling
Table 1 also shows the 10 topics identified via LSI, along with the top 20 terms representing each topic. Although there was considerable overlap in terms across topics, we attempted to empirically label each topic using the topic’s top terms.
Table 1.
Topics identified by latent semantic indexing
| Nth Best Term | Topic 1: Chronic Pain Patients | Topic 2: Heart Disease Patients | Topic 3: Perioperative Interventions | Topic 4: Perioperative Translational | Topic 5: Back Pain | Topic 6: CAD Interventions | Topic 7: Inpatient Strata | Topic 8: Cardiac Surgery | Topic 9: Low Back Pain | Topic 10: Heart Disease Groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Pain | Patients | Group | Group | Back | Treatment | Treatment | Surgery | Back | Coronary |
| 1 | Patients | Pain | Patients | Pain | Induced | Coronary | Group | Angina | Low | Group |
| 2 | Group | Group | Groups | Treatment | Morphine | Group | Postoperative | Coronary | Symptoms | Study |
| 3 | Study | Coronary | Pain | Patients | Patients | Mg | Morphine | Spinal | Studies | Patient |
| 4 | Treatment | Angina | Significantly | Studies | Low | Back | Analgesia | Postoperative | Evidence | Treatment |
| 5 | Chronic | Disease | Study | Induced | Group | Placebo | Surgery | Back | Headache | Mg |
| 6 | Patient | Study | Postoperative | Study | Spinal | Patient | Back | Treatment | Women | Back |
| 7 | Significant | Chronic | Mg | Spinal | Health | Angina | Chronic | Placebo | Trials | Low |
| 8 | Clinical | Surgery | Morphine | Clinical | Rats | Low | Women | Patient | Chronic | Placebo |
| 9 | Significantly | Myocardial | Effects | Symptoms | Effects | Trials | Mg | Mg | Study | Chronic |
| 10 | Groups | Treatment | Compared | May | Symptoms | Efficacy | Use | Nerve | Morphine | Patients |
| 11 | Compared | Mean | Control | Effects | Women | Myocardial | Spinal | Lumbar | Opioid | Angina |
| 12 | Back | Groups | Analgesia | Postoperative | Treatment | Postoperative | Children | Low | Risk | Management |
| 13 | May | Patient | Placebo | Associated | Receptor | Morphine | Risk | Exercise | Coronary | Disease |
| 14 | Associated | Clinical | Significant | Effect | Nerve | Relief | Coronary | Myocardial | Treatment | Surgery |
| 15 | Two | Years | Effect | Risk | Dose | Subjects | Opioid | Surgical | Children | Artery |
| 16 | Low | Compared | Treatment | Low | Effect | Controlled | Patient | Chronic | Age | Use |
| 17 | Using | Follow | Surgery | Groups | Neuropathic | Levels | Patients | Women | Years | Acute |
| 18 | Surgery | Two | Dose | Rats | Opioid | Risk | Low | Up | Review | Knee |
| 19 | One | Symptoms | Time | Evidence | Care | Dose | Study | Follow | Angina | Myocardial |
CAD = Coronary Artery Disease.
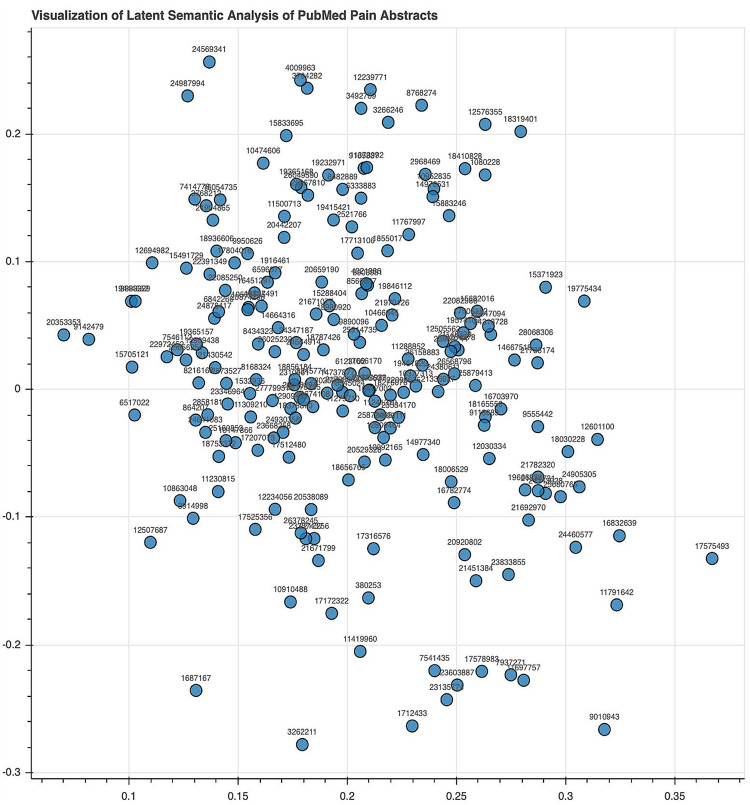
LSI was repeated using the TF-IDF with a two-component SVD (Figure 5). Although this drastically decreased the number of topics considered, this approach enhanced the visualization of LSI’s relationship among abstracts, allowing a different perspective into those themes driving similarities among the sample of abstracts. For instance, abstracts PMID1687167 and PMID3262211 are both outliers located in the left lower quadrant and discuss dopaminergic signaling in pain mechanisms. On the contrary, abstracts PMID24569341 and PMID24987994 in the left upper quadrant discuss clinical pain syndromes of thoracic etiologies and are closely neighbored by PMID4009963 and PMID3794282, which discuss pain related to coronary spasm.
Figure 5.
Latent semantic indexing (LSI) abstract visualization. LSI was repeated on the term frequency–inverse document frequency with a two-component SVD. Although this drastically decreased the number of topics considered, this approach enhanced the visualization of LSI’s relationship among abstracts, allowing a different perspective into those themes driving similarities among the sample of abstracts.
LDA-Based Topic Modeling
Topic Definitions from Topic–Term Relationships
We first identified the optimal LDA topic count by serially testing the coherence values. Topic coherence allows us to identify the coherence of the topic via inspecting the similarity of the top words in a given topic. There are different approaches to measuring coherence, including computing the pairwise mutual information measure among the top words. In this experiment, we use a four-stage coherence pipeline from the GenSim library [32]. We tested across a range of topic counts between two and 100 at intervals of 10. Candidate topic counts were tested using the Gensim LDA multicore model using just five passes of the corpus initially due to computational constraints. After identifying the peak coherence value between 30 and 50, we focused an updated coherence assay between 30 and 50 at intervals of two, which demonstrated peak coherence at 40 topics. We then used the GenSim LDAmulticoremodel function with 100 passes over the corpus, which had a final coherence of 0.49 and a perplexity of −7.62 at 40 topics.
Table 2 highlights the distribution of abstracts across different topics as well as prototypical abstracts that contained the greatest percent topic contribution for each abstract. In other words, these prototype abstracts were predominantly focused on a single one of the 40 identified LDA topics. The dominant topic for each abstract ranged from 19% to 87% in percent contribution. Among the topics, topic 10 was the most common, occurring in 7% of abstracts, whereas topic 2 was the least common, occurring in <1% of abstracts.
Table 2.
Distribution of terms and abstracts across topics identified using latent Dirichlet allocation–based topic modeling
| Topic No. | Topic Key Words | No. of Abstracts with Topic | Percentage of Abstracts with Topic | Prototypical Abstract PMID | Topic Percent Contribution of Prototypical Abstract | Prototypical Abstract Text |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | Pain, stimulation, stimuli, threshold, sensory, responses, response, subjects, thresholds, stimulus | 8,873 | 0.04 | 24276314 | 0.9935 | In healthy participants, high-frequency electrical stimulation of the forearm not only evokes local hyperalgesia but also inhibits sensitivity to pressure-pain in the ipsilateral forehead, possibly due to activation of ipsilateral inhibitory pain modulation processes. The aim of this study was to compare the effects of high- and low-frequency electrical stimulation of the forearm on sensitivity to pressure-pain in the ipsilateral forehead, as inhibitory pain modulation may be stronger after low- than high-frequency electrical stimulation. Before and after high- and low-frequency electrical stimulation, sensitivity to heat and to blunt and sharp stimuli was assessed at and adjacent to the electrically conditioned site in the forearm. In addition, sensitivity to blunt pressure was measured bilaterally in the forehead. Pain was more intense after high- than low-frequency electrical stimulation and was followed by primary and secondary hyperalgesia to mechanical stimulation after high- but not low-frequency electrical stimulation. Nevertheless, sensitivity to pressure-pain decreased to the same extent in the ipsilateral forehead after both forms of electrical stimulation. This decrease was associated with heightened sensitivity to pressure-pain at the electrically conditioned forearm site and with diminished sensitivity to heat around this site. These findings suggest that sensitisation of pressure-sensitive nociceptive afferents at the site of electrical stimulation is associated with generation of an ipsilateral pain-inhibitory process. This ipsilateral pain-inhibitory process may decrease sensitivity to pressure-pain in the ipsilateral forehead and suppress secondary hyperalgesia to heat. |
| 1.0 | Imaging, CT, MRI, magnetic, resonance, patients, lesions, tomography, computed, findings | 1,376 | 0.01 | 21079201 | 0.8152 | PURPOSE: To compare the image quality of water-only images generated from a dual-echo Dixon technique with that of standard fast spin-echo T1-weighted chemical shift fat-suppressed images obtained in patients evaluated for pelvic pain with a 1.5-T magnetic resonance (MR) system. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The ethics board granted approval for this retrospective study; patient consent was not required. Twenty-five women underwent both standard axial T1-weighted fast spin-echo chemical shift fat-suppressed imaging and dual-echo Dixon imaging of the pelvis. Two readers independently scored the acquisitions for image quality, fat suppression quality, and artifact. On the basis of signal intensity measurements, the uniformity of fat suppression, the contrast between fat-suppressed and non-fat-suppressed tissue, and the contrast between pathologic lesions and suppressed fat were calculated. Values obtained with the T1-weighted fat-suppressed and dual-echo Dixon techniques were compared by using the Wilcoxon signed rank test. RESULTS: The images generated with the dual-echo Dixon technique were of higher quality, had better fat suppression, and had less artifact (qualitative scores: 4.4, 4.6, and 4.0, respectively) compared with the standard T1-weighted fat-suppressed images (qualitative scores: 3.4, 3.3, and 3.6, respectively; P < 0.01). Contrast between fat-suppressed and non-fat-suppressed tissue (contrast ratio: 0.86 for dual-echo Dixon technique vs 0.42 for T1-weighted fat-suppressed technique, P < 0.001) and between pathologic lesions and suppressed fat (contrast ratio: 0.88 for dual-echo Dixon technique vs 0.57 for T1-weighted fat-suppressed technique, P = 0.012) was significantly improved with the dual-echo Dixon technique. Twelve pathologic lesions were identified with dual-echo Dixon imaging versus eight that were identified with T1-weighted fat-suppressed imaging. CONCLUSION: Compared with standard T1-weighted fat-suppressed imaging, dual-echo Dixon imaging facilitates improved image quality of fat-suppressed images of the pelvis, enabling better delineation of pathologic lesions. |
| 2.0 | Shoulder, tendon, arm, cuff, athletes, rotator, pain, degrees, motion, thickness | 991 | 0.0 | 15839306 | 0.8569 | STUDY DESIGN: Prospective cohort study. OBJECTIVES: To determine the effect of rotator cuff tear size on shoulder strength and range of motion. BACKGROUND: Patients with rotator cuff pathology typically present with weakness and motion loss in various motions. The extent to which the presence of a rotator cuff tear and the size of the tear affect strength and range of motion is not well understood. METHODS AND MEASURES: Sixty-one patients scheduled for surgery, with a diagnosis of a rotator cuff tear and/or subacromial impingement, underwent examination for shoulder pain, function, range of motion, and strength. The extent of rotator cuff pathology was documented during subsequent surgery (presence of tear, tear size, tear thickness). RESULTS: There were 10 massive tears, 15 large tears, 13 medium tears, 12 small tears, and 11 rotator cuffs without a tear. Patients had marked weakness in abduction strength at 90 degrees and 10 degrees of abduction, in external rotation strength at 90 degrees, and in the “full can test” (all, P < 0.0001). Marked range of motion losses in shoulder flexion and external rotation at 0 degrees and 90 degrees abduction (all, P < 0.001) were also observed. Abduction strength deficit at 10 degrees was affected by rotator cuff tear size (P < 0.0001). Twenty of 25 patients with large or massive tears had deficits greater than 50%, compared with only 1 of 11 patients with no tear, 2 of 12 patients with a small tear, and 5 of 13 patients with a medium tear (P < 0.0001). Other strength and range of motion deficits or indices of pain and function were unaffected by tear size. CONCLUSIONS: Weakness of greater than 50% relative to the contralateral side in shoulder abduction at 10 degrees of abduction was indicative of a large or massive rotator cuff tear. |
| 3.0 | Levels, patients, plasma, serum, concentrations, significantly, blood, concentration, diabetic, level | 2,654 | 0.01 | 21947962 | 0.8062 | The relationship between oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL) and C-reactive protein (CRP) in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is unknown. We, therefore, measured serum levels of Ox-LDL and high-sensitivity (hs)-CRP in 90 ACS patients, 45 stable angina pectoris (SAP) patients, and 66 healthy controls using sandwich ELISA. ACS patients were subdivided into: (1) acute myocardial infarction (AMI; n = 45); (2) unstable angina pectoris (UAP; n = 45) groups. In AMI patients, Ox-LDL (177.5 mmol/l) and hs-CRP (25.40 mg/l) levels were significantly higher (P < 0.01) than in UAP (Ox-LDL : 107.5 mmol/l, hs-CRP : 10.7 mg/l) and SAP (Ox-LDL : 82.3 mmol/l, hs-CRP : 2.10 mg/l) patients as well as controls (Ox-LDL : 41.4 mmol/l, hs-CRP : 1.76 mg/l). Ox-LDL/hs-CRP levels in UAP patients were significantly higher (P < 0.01) than in SAP patients and controls. Importantly, a positive correlation was found between Ox-LDL and CRP (r = 0.622; P < 0.01) levels. Serum levels of total, HDL, and LDL cholesterol did not differ among these patient groups. In conclusion, our data show that Ox-LDL and hs-CRP levels correlate positively in ACS patients, supporting the hypothesis that Ox-LDL and CRP may play a direct role in promoting the inflammatory component of atherosclerosis in these individuals. We suggest that Ox-LDL/CRP elevated levels may serve as markers of the severity of the disease in evaluation and management of ACS patients. |
| 4.0 | Pain, scale, scores, patients, score, study, quality, questionnaire, life, VAS | 7,164 | 0.04 | 21814745 | 0.994 | PURPOSE: To investigate the validity of the Neck Pain and Disability Scale Dutch Language Version (NPAD-DLV) and the Neck Disability Index (NDI)-DLV. METHODS: NPAD-DLV, NDI-DLV, Short-Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36)-DLV, visual analog scale (VAS)(pain) and VAS(disability) were administered to 112 patients with non-specific chronic neck pain in an outpatient tertiary rehabilitation setting. Twenty seven hypotheses were formulated regarding validity. NPAD-DLV and NDI-DLV were evaluated for content validity (normal distribution total scores, missing items, floor and ceiling effects), internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha and Spearman Item-total correlations), construct validity (Pearson correlations with SF-36 domains, VAS(pain) and VAS(disability) and Pearson correlation between total scores of NPAD-DLV and NDI-DLV). RESULTS: NPAD-DLV and NDI-DLV scores were distributed normally. Missing items were negligible. Floor and ceiling effects were absent in NPAD-DLV and in NDI-DLV two items had floor effects and one item had a ceiling effect. Cronbach's alpha of NPAD-DLV was 0.93 and of NDI-DLV 0.83. Item-total correlations ranged for NPAD-DLV from 0.45 to 0.73 and for NDI-DLV from 0.40 to 0.64. The correlation between, respectively, NPAD-DLV and NDI-DLV and: SF-36 domains ranged from -0.36 to -0.70 and from -0.34 to -0.63; VAS(pain) was 0.54 and 0.43; VAS(disability) was 0.57 and 0.52. The correlation between the total scores of NPAD-DLV and NDI-DLV was 0.77. Twenty six hypotheses were not rejected and one hypothesis was rejected. CONCLUSION: The NPAD-DLV and NDI-DLV are valid measures of self-reported neck-pain related disability. |
| 5.0 | Women, pregnancy, delivery, section, labor, zoster, PHN, neuralgia, herpes, labor | 969 | 0.0 | 125043 | 0.8622 | Initial clinical trials of a saline-filled IUD were conducted with 697 women (397 nulliparas and 307 multiparas) experiencing 6,672 woman-months of use. The cumulative rates for multiparas were: pregnancy 1.5, expulsion 10.5, medical removal 10.9, continuation 68. For nulliparous women the rates were: pregnancy 4.3, expulsion 19.4, medical removal 14.3, continuation 58. Efforts are being made to modify the geometry and content of this IUD to decrease the expulsion rate and removals for bleeding. |
| 6.0 | Headache, migraine, patients, headaches, type, tension, CSF, cerebral, symptoms, intracranial | 2,769 | 0.01 | 6713523 | 0.9452 | The relationship between headache and epilepsy remains unresolved. We studied 3,600 patients affected by primary headache and 36 epileptic patients with a present or past history of headache. In the first group, no family history of epilepsy nor epileptiform EEG patterns were found. In the second group, there was no chronological relationship between epileptic seizure and headache attack in more than half of the patients; when found (46.1%) the relationship was neither precise nor specific. Taken as a whole, these data suggest the autonomous nature of epilepsy and headache. |
| 7.0 | Muscle, group, subjects, exercise, pain, control, activity, study, training, strength | 6,428 | 0.03 | 20627798 | 0.9822 | The purpose of the current study was to examine how effectively people with and people without low back pain (LBP) modify lumbopelvic motion during a limb movement test. Nineteen subjects with LBP and 20 subjects without LBP participated. Kinematic data were collected while subjects performed active hip lateral rotation (HLR) in prone. Subjects completed trials (1) using their natural method (Natural condition) of performing HLR, and (2) following standardized instructions to modify lumbopelvic motion while performing HLR (Modified condition). Variables of interest included (1) the amount of HLR completed prior to the start of lumbopelvic motion, and (2) the maximum amount of lumbopelvic motion demonstrated during HLR. Compared to the Natural Condition, all subjects improved their performance during the Modified condition by (1) completing a greater amount of HLR prior to the start of lumbopelvic motion, and (2) demonstrating less lumbopelvic motion (P < 0.01 for all comparisons). There was a tendency for people without LBP to demonstrate a greater difference in maximal lumbopelvic rotation between the Natural and Modified conditions (P = 0.07). In conclusion, people are able to modify lumbopelvic motion following instruction. Further study is needed to determine if people without LBP improve lumbopelvic motion following instruction to a greater extent than people with LBP. |
| 8.0 | Lumbar, spinal, back, spine, disc, cervical, pain, low, fusion, l | 3,189 | 0.02 | 10917245 | 0.9183 | This study examined the facet angles of the joint facets of the intervertebral joints, the anterior and posterior heights of the intervertebral disks, and cervical lordosis as possible parameters of olisthesis. Lateral radiographs of the cervical spine in 123 patients were examined, and parameters were correlated to anterolisthesis and retrolisthesis in each segment. Results indicate anterolisthesis is caused by a decrease of the facet angles of the caudal joint facets. This process is favored by loss of anterior height of the intervertebral disks and a flattened position of the cervical spine. Loss of posterior height of the intervertebral disks promotes retrolisthesis. |
| 9.0 | Dental, bone, foot, fracture, fractures, oral, tissue, ankle, teeth, tooth | 1,736 | 0.01 | 22159859 | 0.7464 | Autogenous cancellous bone graft provides an osteoconductive, osteoinductive, and osteogenic substrate for filling bone voids and augmenting fracture-healing.The iliac crest remains the most frequently used site for bone-graft harvest, but the proximal part of the tibia, distal end of the radius, distal aspect of the tibia, and greater trochanter are alternative donor sites that are particularly useful for bone-grafting in the ipsilateral extremity. The most common complication associated with the harvest of autogenous bone graft is pain at the donor site, with less frequent complications including nerve injury, hematoma, infection, and fracture at the donor site. Induced membranes is a method that uses a temporary polymethylmethacrylate cement spacer to create a bone-graft-friendly environment to facilitate graft incorporation, even in large segmental defects. |
| 10.0 | Group, pain, patients, postoperative, groups, surgery, significantly, study, compared, analgesia | 14,035 | 0.07 | 19253247 | 0.9929 | PURPOSE: The authors compared the efficacy of local anesthetics levobupivacaine, bupivacaine, and lidocaine for retrobulbar anesthesia in vitreoretinal surgery. METHODS: A total of 135 patients presenting for vitreoretinal surgery under local anesthesia were included in the study. Patients were randomly allocated to one of three groups. Group LB patients received 5 mL of 0.5% levobupivacaine, Group L patients received 5 mL of 2% lidocaine, and Group B patients received 5 mL of 0.5% bupivacaine for retrobulbar anesthesia via inferotemporal injection. Sensory and motor block durations were recorded. Intraoperative and postoperative pain was assessed by using verbal pain scale. Anesthesia efficiency, patient and surgeon satisfaction, and akinesia were assessed by using point scales. Hemodynamic data and adverse events were recorded. RESULTS: The demographic characteristics of patients, duration of surgery, and hemodynamic data in both groups were similar. The duration of motor and sensory block was longer in levobupivacaine and bupivacaine groups than lidocaine group. Pain on injection was found more frequent in Group L and Group B than Group LB and the difference between the Groups LB and B was significant (P < 0.05). Surgeon and patient satisfaction were also higher and intraoperative pain was less in levobupivacaine group than lidocaine and bupivacaine groups. CONCLUSIONS: Levobupivacaine provides longer motor and sensory block duration and higher surgeon and patient satisfaction than lidocaine and bupivacaine when used for retrobulbar anesthesia in vitreoretinal surgery. |
| 11.0 | Patients, follow, up, months, surgery, years, one, treatment, mean, surgical | 9,941 | 0.05 | 20412671 | 0.9533 | INTRODUCTION: Favourable short-term results, with respect to less postoperative pain and earlier return to physical activity, have been demonstrated with laparoscopic totally extraperitoneal (TEP) hernia repair compared with open mesh repair. However, there is limited data regarding long-term results. PATIENTS AND METHODS: The study cohort consisted of 275 consecutive patients undergoing TEP repair between 1996 and 2002. Patient demographics, details of surgery, postoperative complications, recurrence and chronic pain were collected from patient records and from a prospective database. All patients were seen at 6 weeks and then annually for 5 years following surgery. RESULTS: A total of 430 repairs were performed in the 275 patients (median age, 56 years; range, 20-94 years; men, 97.5%). Bilateral repair was performed in 168 patients (61.1%) and recurrent hernia repair in 79 patients (28.7%). Two patients were converted to an open procedure. Five-year follow-up was achieved in 72% of patients. Eleven patients (4%) died during the follow-up period due to unrelated causes. Hernia recurrence rate at 5 years was 1.1% per patient (three repairs). Recurrences were noted at 7 months, 2 years and 4 years following surgery. Chronic groin pain was reported by 21 patients (7.6%), seven of whom required referral to the pain team. CONCLUSIONS: TEP hernia repair is associated with a recurrence rate of 1% at 5 years in this series. Chronic groin symptoms are also acceptably few. This recurrence rate following TEP repair compares extremely favourably with open mesh repair, particularly as it includes a high proportion of recurrent repairs. As well as the proven early benefits, TEP repair can be considered a safe and durable procedure with excellent long-term results. |
| 12.0 | Pain, patients, chronic, depression, anxiety, symptoms, sleep, related, psychological, reported | 9,626 | 0.05 | 11882770 | 0.9929 | OBJECTIVES: Insomnia and depression are common problems for people with chronic pain, and previous research has found that each is correlated with measures of pain and disability. The goal of this study was to examine the combined impact of major depression and insomnia on individuals with chronic pain. METHODS: The participants were patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain who underwent evaluation at an interdisciplinary treatment center. On the basis of semistructured interviews, participants were classified in three groups depending on whether they: (1) met criteria for major depression with insomnia (n = 38); (2) had insomnia without major depression (n = 58); or (3) had neither insomnia nor major depression (n = 47). The groups were then compared on self-report measures that included the McGill Pain Questionnaire, the Beck Depression Inventory, and the Multidimensional Pain Inventory. RESULTS: Participants with major depression and insomnia reported the most difficulty on measures of affective distress, life control, interference, and pain severity, although the insomniac patients without major depression also had elevated scores on some measures. In regression analyses, insomnia severity ratings did not contribute uniquely to the prediction of psychosocial problems when depression was controlled, but they did contribute to the prediction of pain severity. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that patients with chronic pain and concurrent major depression and insomnia report the highest levels of pain-related impairment, but insomnia in the absence of major depression is also associated with increased pain and distress. |
| 13.0 | Coronary, artery, left, bypass, arteries, spasm, right, aortic, stenosis, vein | 3,109 | 0.02 | 12082197 | 0.9783 | We describe a case of successful direct coronary stenting of two tight lesions, one at the site of the left internal mammary artery (LIMA) graft anastomosis with left anterior descending coronary artery and the other at the site of the anastomosis between the right internal mammary artery (RIMA) graft and the right coronary artery. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of successful direct stent implantation through the LIMA and RIMA. |
| 14.0 | Topical, MS, application, lidocaine, used, water, acid, patch, using, gel | 623 | 0.0 | 17193331 | 0.7546 | Seven benzophenanthridine alkaloids, 1-7, were isolated from the roots of Zanthoxylum nitidum. Among them, two novel alkaloids, named (R)-8-[(R)-1-hydroxyethyl]dihydrochelerythrine (1) and 8-methoxynorchelerythrine (2), were structurally identified as new compounds on the basis of the spectroscopic analysis. Bioactivity evaluation showed that nitidine (3), dihydrochelerythrine (4), oxyavicine (5), 8-methoxychelerythrine (6), and 8-hydroxydihydrochelerythrine (7) exhibit comparable analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects as hydrocortisone. |
| 15.0 | Women, pelvic, endometriosis, symptoms, menstrual, dysmenorrhea, sexual, uterine, men, cycle | 986 | 0.0 | 20883987 | 0.6218 | Dysmenorrhea as a reason to initiate estroprogestins is significantly more common in women with endometriosis than in women without the disease. This might explain the previously reported mild association between endometriosis and past use of oral contraceptives. |
| 16.0 | Pain, patient, experience, research, may, information, factors, important, approach, model | 6,991 | 0.03 | 20505617 | 0.9383 | This article illustrates a process of knowledge development and the interrelationship between knowledge and practice using Carper's fundamental patterns of knowing. It explores two kinds of knowledge, theoretical knowledge and practical knowledge, using postoperative pain assessment as an illustration. By using their theoretical knowledge and their practical experience, nurses can maintain and develop their professional knowledge and competence. |
| 17.0 | Morphine, dose, analgesia, opioid, mg, effects, analgesic, administration, infusion, doses | 3,724 | 0.02 | 1424423 | 0.8841 | The single-dose and steady-state pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oxycodone have been determined in patients with moderate to severe cancer pain. The mean +/- SD elimination half-life after single-dose administration of intravenous (4.6 mg to 9.1 mg) and oral (9.1 mg) oxycodone was 3.01 +/- 1.37 hours and 3.51 +/- 1.43 hours, respectively. After intravenous administration, the mean +/- SD volume of distribution was 211.9 +/- 186.6 L, and the mean +/- SD total plasma clearance was 48.6 +/- 26.5 L/hr. The mean absolute oral bioavailability of oxycodone was 87%, and the mean +/- SD volume of distribution after oral administration was 249.1 +/- 204.3 L. When administered orally as 10 mg oxycodone hydrochloride every 4 hours, there was no accumulation of oxycodone at steady state and the mean +/- SD steady-state concentration was 34.6 +/- 10.3 micrograms/L. Intravenous oxycodone produced a faster onset of pain relief than oxycodone tablets, but the duration of analgesia was approximately the same (4 hours). However, the incidence of side effects and their severity were significantly higher (P < 0.05) for intravenous oxycodone than for oxycodone tablets. The marked interindividual variation observed in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oxycodone in this study supports the need for individualized dosing regimens. |
| 18.0 | Children, pain, pediatric, child, adolescents, age, parents, infants, adults, years | 1,440 | 0.01 | 16082239 | 0.8015 | The purpose of the study was to compare a heel stick conducted during Kangaroo Care (skin-to-skin contact) with the mother to a heel stick in a warmer in reducing premature infant physiologic and behavioral pain responses. Twenty-four premature infants in a university-based neonatal intensive care unit were recruited and randomized to 2 sequences: sequence A group received 3 hours of Kangaroo Care (with a heel stick in Kangaroo Care) followed by 3 hours in a warmer (with a heel stick in the warmer). Sequence B group had warmer care and a heel stick (in the warmer) before Kangaroo Care and a heel stick (in Kangaroo Care). Heart rate, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, crying time, and behavioral state were measured before, during, and after heel stick. Repeated measures ANOVA and Mann Whitney U statistics were performed. Heart rate and length of crying in response to pain were significantly reduced during Kangaroo Care and the Kangaroo Care heel stick as compared to when infants were in the warmer and had a heel stick in the warmer. Three infants did not cry at all during the Kangaroo Care heel stick; infants slept more during Kangaroo Care than in the warmer. Kangaroo Care positioning before and during heel stick is a simple and inexpensive analgesic intervention to ameliorate pain in stable premature infants. |
| 19.0 | Pain, care, patients, management, use, patient, health, treatment, medical, practice | 9,978 | 0.05 | 23991536 | 0.9721 | This article presents the results of a collaborative project between the British Pain Society and British Geriatric Society to produce guidelines on the management of pain in older adults. The guidelines are the first of their kind in the UK and aim to provide best practice for the management of pain to all health professionals working with older adults in any care setting. |
| 20.0 | Pain, acupuncture, muscle, treatment, group, points, TENS, sham, stimulation, muscles | 791 | <0.01 | 3494257 | 0.7682 | This study compared the effects of unilateral and bilateral auricular transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on cutaneous pain threshold. Auricular acupuncture points were stimulated with low frequency, high intensity TENS for 45 seconds. Sixty healthy, adult subjects were assigned randomly to one of two treatment groups or to a control group. The two treatment groups received low frequency, high intensity TENS either unilaterally or bilaterally. The control group did not receive auricular stimulation. Experimental pain threshold at the left wrist was determined with a painful stimulus before and after auricular stimulation. Both unilateral and bilateral auricular stimulation groups exhibited a significant increase (P less than 0.05) in experimental pain threshold, but the control group did not. The mean change values between the unilateral and bilateral stimulation groups were not statistically different. These results suggest that both unilateral and bilateral auricular TENS can increase pain threshold. |
| 21.0 | Pain, chronic, treatment, may, neuropathic, clinical, studies, mechanisms, system, drugs | 10,473 | 0.05 | 17080201 | 0.9838 | Pain is a multidimensional sensory experience, and multiple mechanisms are involved in the generation of pathophysiological nociceptive pain. Identification of the mechanisms and molecular components responsible for pain generation has not only advanced our understanding of pain and its control, but has also led to the selection of new targets for designing novel analgesic drugs. The high selectivity and specificity of animal toxins have enabled their use as potential therapeutics in the treatment of pain and candidates for the development of new analgesic drugs. This review focuses on the use of animal toxins for pain control and examines the possible analgesic mechanisms of these molecules. |
| 22.0 | Exercise, pressure, blood, rate, heart, less, angina, increased, increase, beta | 3,216 | 0.02 | 6160338 | 0.945 | The hemodynamic effects of 0.1 mg/kg verapamil given intravenously to 7 patients with angina pectoris were studied at rest and during exercise in the supine position. Cardiac output was measured with the thermodilution technique, which permitted measurements every 30 sec during exercise. Maximal exercise tolerance increased significantly after verapamil. Verapamil had no effect on heart rate at rest, but significantly increased it at the end of the exercise. Left ventricular systolic pressure was reduced by verapamil at rest and during submaximal exercise. Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure was not influenced by verapamil at rest, but was significantly lowered during submaximal exercise. Stroke work index and left ventricular power index were not influenced by verapamil. Rate pressure product was lowered by verapamil during submaximal exercise but had a tendency to be increased at the breaking point. Verapamil had no negative inotropic effect as judged from the left ventricular function curve. It is suggested that the beneficial effect of verapamil relates mainly to a reduction of left ventricular pre- and after-load. The slightly higher rate pressure product after verapamil may also suggest a slight improvement of myocardial perfusion. |
| 23.0 | Patients, disease, symptoms, infection, clinical, renal, cases, associated, fever, one | 4,699 | 0.02 | 21077037 | 0.9293 | Primary Sjogren's Syndrome (pSS) is a chronic, slowly progressive inflammatory autoimmune disorder, characterised by lymphocytic infiltration of the exocrine glands, leading to decrease of glandular secretion. In 40-60% of pSS patients, extraglandular disease develops. We present the case of a patient with two extraglandular sites involvement in the course of pSS manifesting with progressive respiratory and gastrointestinal symptoms. |
| 24.0 | Abdominal, case, year, patient, old, diagnosis, acute, pain, cases, presented | 9,146 | 0.05 | 19223375 | 0.9868 | An unusual case of acute abdomen was caused by the inflammation of ectopic pancreatic tissue in a Meckel's diverticulum. A 49-year-old man presented with acute abdominal pain, and the clinical diagnosis of acute appendicitis was established. During laparotomy, a normal appendix of unusual localization near the gallbladder and a Meckel's diverticulum with an inflamed tip were found. Histological examination showed acute inflammation of heterotopic pancreatic tissue along with normal ectopic gastric and duodenal mucosa within the wall of the diverticulum. Fat necrosis was also ascertained. The authors believe that this is the first report of acute inflammation of ectopic pancreatic tissue and the presence of normal ectopic gastric and duodenal tissue in the same Meckel's diverticulum. |
| 25.0 | IL, beta, alpha, expression, inflammatory, cells, factor, gene, cell, TNF | 1,200 | 0.01 | 26067582 | 0.8444 | A functional allele of the mouse catechol-O-methyltransferase (Comt) gene is defined by the insertion of a B2 short interspersed repeat element in its 3'-untranslated region (UTR). This allele has been associated with a number of phenotypes, such as pain and anxiety. In comparison with mice carrying the ancestral allele (Comt+), Comt B2i mice show higher Comt mRNA and enzymatic activity levels. Here, we investigated the molecular genetic mechanisms underlying this allelic specific regulation of Comt expression. Insertion of the B2 element introduces an early polyadenylation signal generating a shorter Comt transcript, in addition to the longer ancestral mRNA. Comparative analysis and in silico prediction of Comt mRNA potential targets within the transcript 3' to the B2 element was performed and allowed choosing microRNA (miRNA) candidates for experimental screening: mmu-miR-3470a, mmu-miR-3470b, and mmu-miR-667. Cell transfection with each miRNA downregulated the expression of the ancestral transcript and COMT enzymatic activity. Our in vivo experiments showed that mmu-miR-667-3p is strongly correlated with decreasing amounts of Comt mRNA in the brain, and lentiviral injections of mmu-miR-3470a, mmu-miR-3470b, and mmu-miR-667 increase hypersensitivity in the mouse formalin model, consistent with reduced COMT activity. In summary, our data demonstrate that the Comt+ transcript contains regulatory miRNA signals in its 3'-untranslated region leading to mRNA degradation; these signals, however, are absent in the shorter transcript, resulting in higher mRNA expression and activity levels. |
| 26.0 | Cancer, patients, pain, bone, breast, treatment, therapy, disease, survival, metastases | 2,536 | 0.01 | 6938017 | 0.9289 | Ninety patients with poorly differentiated prostatic carcinoma have been treated with Estramustine phosphate (Estracyt). Seventeen of them had clinically metastases and had had no previous therapy. Seventy-three were initially given oestrogens and/or irradiation. Objective response was observed in 59%. The best effect was seen in patients primarily untreated. |
| 27.0 | Injection, pain, epidural, technique, nerve, procedure, injections, local, patients, relief | 2,862 | 0.01 | 2969118 | 0.9025 | Epidural injection of steroid and local anesthesia can be used to treat low back pain. The injection is best performed with fluoroscopic control, with needle placement documented by means of a limited epidurogram. The technique was used in 116 patients; there were only three failures (2.5%) and one complication. |
| 28.0 | Patients, abdominal, laparoscopic, bowel, IBS, symptoms, gastrointestinal, endoscopic, gastric, visceral | 1,852 | 0.01 | 12556774 | 0.7783 | BACKGROUND: Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation may be an alternative to endoscopic sphincterotomy in the treatment of bile duct stones. However, there is a controversy as to the effectiveness and safety of endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation. METHODS: Two hundred eighty-two patients with bile duct stones were enrolled and randomized to an endoscopic sphincterotomy or endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation group. The success rate for duct clearance as well as the frequency and types of complications were evaluated prospectively. Endoscopic sphincterotomy was performed in a standard manner. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation was carried out with gradual inflation of a 4-, 6-, or 8-mm diameter balloon. RESULTS: Complete duct clearance was achieved in 100% in the endoscopic sphincterotomy group and 99.3% in the endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation group (not significant). Complications occurred in 11.8% of patients in the endoscopic sphincterotomy group and 14.5% of those in the endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation group (not significant). No complication was severe; there was no mortality. The frequency of acute pancreatitis was higher in the endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation group than the endoscopic sphincterotomy group (respectively, 10.9% vs. 2.8%; P < 0.045). Hemorrhage occurred only in the endoscopic sphincterotomy group. CONCLUSIONS: Endoscopic sphincterotomy and endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation were approximately equal in terms of successful clearance of bile duct stones. They were also similar with respect to overall complications. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation is an alternative to endoscopic sphincterotomy as a treatment of bile duct stones. |
| 29.0 | Pain, syndrome, patient, case, diagnosis, cases, symptoms, treatment, may, nerve | 10,421 | 0.05 | 12457088 | 0.975 | Elongation of the styloid process and calcification of the stylohyoid ligament as pathological entities described by Eagle are often reported in the literature. The properly called Eagle's syndrome or stylalgia is characterized by a definite symptoms and etiology, that distinguish it from pathologies with partially overlapping symptoms depending on adjacent anatomical structures. A corrected differential diagnosis is paramount for choosing the most adequate treatment. |
| 30.0 | Knee, joint, hip, pain, arthritis, osteoarthritis, OA, arthroplasty, joints, rheumatoid | 2,130 | 0.01 | 14629939 | 0.8365 | The incidence and the causes of provoked anterior knee pain in medial osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee were investigated clinically and radiographically. A retrospective study was performed in 179 primary osteoarthritic knees of 129 patients. Provocative tests were conducted on the patellofemoral (PF) joint to induce retropatellar crepitation, grating pain, tenderness around the patella, and pain on deviating the patella. The femorotibial angle (FTA) was measured on standing anteroposterior radiographs as a parameter of limb alignment. The widths of the medial and lateral joint space of the PF joint were measured on skyline views of standing or 30, 60 or 90 degrees knee flexion. The angle of flexion contracture was measured on lateral radiographs of knees with maximum extension. The lateral shift and tilt of the patella were measured on standing skyline views. Retropatellar crepitation was found in 70% of knees, while provoked anterior knee pain was observed in 35-45% of knees with medial OA of the knee. Standing FTA was significantly greater in knees with tenderness around the patella and pain on deviating the patella than in those without these symptoms (P < 0.05). The angle of flexion contracture was significantly greater in knees with provoked symptoms in the PF joint than in those without symptoms (P < 0.05). The degree of lateral shift was greater in knees with provoked symptoms (P < 0.05). Flexion contracture and varus deformity of the knee with lateralization of the patella may be factors aggravating provoked PF symptoms in medial OA of the knee. The radiographic assessment in this series failed to show a significant relationship between the width of the PF joint space and the incidence of provoked PF symptoms. |
| 31.0 | Discomfort, laser, co, eye, cm, eyes, air, la, energy, GP | 135 | <0.01 | 26488155 | 0.5681 | OBJECTIVES: The purpose of this study was to determine the clinical impact of using SYSTANE BALANCE Lubricant Eye Drops (Alcon, Fort Worth, TX), an oil-in-water emulsion, as a rewetting eye drop in symptomatic contact lens wearers. METHODS: Subjects who had previously experienced contact lens discomfort (CLD), with a mean lens wearing history of 18.6+/-12.8 years, were randomly assigned to use a Test (SYSTANE BALANCE Lubricant Eye Drops; n=76) or control (habitual nonlipid contact lens rewetting eye drop; n=30) drop over their contact lenses within 5 min of lens insertion and then subsequently at 2 hr intervals up to a maximum of 4 drops per eye daily for a 1-month period. Assessments of subjective comfort, comfortable wearing time, lid wiper epitheliopathy (LWE), and corneal staining were conducted at baseline and after 1 month, after 6 hr of lens wear. RESULTS: Comfort, wearing time, LWE, and corneal staining all showed statistically significant improvements in the test group using SYSTANE BALANCE Lubricant Eye Drops at the 1-month visit compared with baseline data (all P < 0.01) and compared with the control group at the 1-month visit (P < 0.01, P = 0.01, P < 0.01, and P = 0.03, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: The use of SYSTANE BALANCE Lubricant Eye Drops as a rewetting drop in a group of wearers who experienced symptoms of CLD improved subjective comfort scores, increased comfortable wearing time, and reduced signs of LWE and corneal staining, when compared with the use of non-lipid-containing contact lens rewetting eye drops. |
| 32.0 | Pain, back, low, work, health, LBP, reported, prevalence, study, physical | 6,201 | 0.03 | 16685722 | 0.951 | BACKGROUND: Farming continues to rank as one of the most dangerous occupations in the United States. The purpose of this study was to determine the prevalence of low back pain and other musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) among the farmers and to examine the factors associated with occupational back pain. Farmers in a predominately corn and soybean growing region of Kansas served as the study sample. METHODS: Questionnaires were mailed out to 499 active farmers of a Farmers' Cooperative in Southeast Kansas. The self-administered questionnaire was used to determine the prevalence of self-reported symptoms of back pain and other MSDs and to determine the strength of associations between back pain and work factors. RESULTS: The participation rate was 57.2%. The low back was the anatomical area with the highest prevalence of self-reported work-related pain (37.5%), followed by the shoulders (25.9%), knees (23.6%), and neck (22.4%). Close to 60% of the farmers reported that they experienced farm work-related MSD symptoms in at least one of the nine body areas in the previous year. Nearly one quarter of the farmers reported seeing a physician for their low back symptoms, and one in five farmers had to modify their work habits due to low back symptoms during the previous year. CONCLUSIONS: Low back pain and other musculoskeletal conditions are a significant problem for Kansas farmers. This group of Kansas farmers experienced low back pain at a much higher rate than the general working population and higher than other groups of farmers previously studied. |
| 33.0 | Spinal, pain, neurons, nerve, rats, mechanical, cord, dorsal, injury, neuropathic | 10,358 | 0.05 | 15456823 | 0.9948 | Peripheral nerve injury induces upregulation of the calcium channel alpha2delta-1 structural subunit in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and dorsal spinal cord of spinal nerve-ligated rats with neuropathic pain, suggesting a role of the calcium channel alpha2delta-1 subunit in central sensitization. To investigate whether spinal dorsal horn alpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation derives from increased DRG alpha2delta-1 subunit and plays a causal role in neuropathic pain development, we examined spinal dorsal hornalpha2delta-1 subunit expression with or without dorsal rhizotomy in spinal nerve-ligated rats and its correlation with tactile allodynia, a neuropathic pain state defined as reduced thresholds to non-noxious tactile stimulation. We also examined the effects of intrathecal alpha2delta-1 antisense oligonucleotides on alpha2delta-1 subunit expression and neuropathic allodynia in the nerve-ligated rats. Our data indicated that spinal nerve injury resulted in time-dependentalpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation in the spinal dorsal horn that correlated temporally with neuropathic allodynia development and maintenance. Dorsal rhizotomy diminished basal level expression and blocked injury-induced expression of the spinal dorsal hornalpha2delta-1 subunit and reversed injury-induced tactile allodynia. In addition, intrathecal alpha2delta-1 antisense oligonucleotides blocked injury-induced dorsal horn alpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation and diminished tactile allodynia. These findings indicate that alpha2delta-1 subunit basal expression occurs presynaptically and postsynaptically in spinal dorsal horn. Nerve injury induces mainly presynaptic alpha2delta-1 subunit expression that derives from increased alpha2delta-1 subunit in injured DRG neurons. Thus, changes in presynaptic alpha2delta-1 subunit expression contribute to injury-induced spinal neuroplasticity and central sensitization that underlies neuropathic pain development and maintenance. |
| 34.0 | Patients, coronary, angina, myocardial, infarction, disease, cardiac, unstable, group, acute | 8,328 | 0.04 | 9591890 | 0.9946 | There is little information on how previous angina influences in-hospital deaths secondary to acute myocardial infarction (MI). This study evaluated the causes of in-hospital deaths in MI patients with and without previous angina. A total of 2,264 consecutive patients were admitted to our hospital due to acute MI. These patients were divided into 2 groups according to the presence or absence of prior MI. Both groups were further divided according to the presence or absence of previous angina. The causes of in-hospital deaths were classified into 4 categories: (1) cardiogenic shock or congestive heart failure, (2) cardiac rupture, (3) arrhythmia, and (4) other causes. In patients with a first MI, the in-hospital mortality rate was lower in patients with previous angina than those without (6.9% vs 11.4%, P < 0.01). There was no significant difference between these patients with and without previous angina in in-hospital deaths due to cardiogenic shock or congestive heart failure, arrhythmia, or other causes. Death due to cardiac rupture was less frequent in patients with previous angina (1.4% vs 5.0%, P < 0.01). In patients with prior MI, the in-hospital mortality rate was lower in patients with than without previous angina (17.7% vs 25.3%, P < 0.05). In contrast to patients with their first MI, there was a trend toward a lower incidence of in-hospital death due to cardiogenic shock or congestive heart failure in patients with previous angina (12.8% vs 19.0%, P = 0.05). There were no significant differences in in-hospital deaths due to cardiac rupture, arrhythmia, and other causes between the 2 subgroups. In multivariate analysis, previous angina was an independent predictor of in-hospital death. Thus, in-hospital deaths after acute MI in patients with previous angina were less because of less cardiac rupture in patients with a first MI and less cardiogenic shock or congestive heart failure in patients with prior MI. |
| 35.0 | Patients, pain, diagnostic, chest, diagnosis, clinical, acute, test, positive, study | 5,273 | 0.03 | 26013480 | 0.9162 | CLINICAL QUESTION: Can an accelerated 2-hour diagnostic protocol using the cardiac troponin I (cTnI) measurement as the only biomarker be implemented to allow an earlier and safe discharge of low-risk chest pain patients? ARTICLE CHOSEN: Than M, Cullen L, Aldous S, et al. 2-Hour accelerated diagnostic protocol to assess patients with chest pain symptoms using contemporary troponins as the only biomarker: the ADAPT trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012; 59(23):2091-8. OBJECTIVE: To determine whether an accelerated diagnostic protocol (ADP) for possible cardiac chest pain could identify low-risk patients suitable for early discharge using cTnI as the sole biomarker. |
| 36.0 | Patients, treatment, placebo, pain, mg, study, efficacy, effects, double, blind | 9,093 | 0.05 | 6348714 | 0.9888 | Our purpose was to evaluate the analgesic efficacy and safety of single oral doses of flurbiprofen 25, 50 and 100 mg, aspirin 600 mg, and placebo in the relief of moderate to severe post-episiotomy pain. One hundred and fifty-two evaluable patients completed a randomized, double-blind, stratified, parallel groups study. They were observed over a six hour period by one nurse-observer. Based upon each of the summary efficacy measures SPID, TOTAL and PEAK % and most of the hourly direct measures of pain intensity and pain relief, each of the four active treatments were statistically superior to placebo. Flurbiprofen 25 mg appeared to be slightly less effective than aspirin 600 mg, but the differences were not statistically significant. Flurbiprofen 50 and 100 mg were quite similar and were significantly more effective than aspirin 600 mg and flurbiprofen 25 mg. There were no observed or reported adverse effects. |
| 37.0 | Studies, trials, evidence, pain, review, controlled, data, quality, treatment, included | 4,491 | 0.02 | 26679894 | 0.9233 | STUDY DESIGN: Systematic review. OBJECTIVE: To determine the effects of the Pilates method for patients with nonspecific acute, subacute, or chronic low back pain. SUMMARY OF BACKGROUND DATA: The Pilates method is one of the most common forms of intervention based on exercise used for treating patients with low back pain. However, its effectiveness is not well established. METHODS: We conducted searches on CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, PEDro, and SPORTDiscus up to March 2014. We included randomized controlled trials examining the effectiveness of Pilates in patients with acute, subacute, or chronic nonspecific low back pain. The outcomes evaluated were pain, disability, function, and global impression of recovery. Two independent reviewers screened for potentially eligible studies, assessed risk of bias, and extracted the data. We evaluated the overall quality of evidence using the GRADE approach and treatment effect sizes were described using mean differences and 95% confidence intervals. RESULTS: Searches retrieved 126 trials, of which 10 were included in the review (n = 510 participants). Seven studies were considered to have low risk of bias, and three were considered at high risk of bias. When compared to minimal intervention, Pilates reduces pain at short and intermediate term with low- to moderate-quality evidence and medium effect sizes. For disability, there is also a significant difference in favor to Pilates with low- to moderate-quality evidence and small effect size for short term and medium effect size for intermediate term compared with minimal intervention. It is unclear whether Pilates is better than other exercises for short-term pain, but there is low-quality evidence that Pilates reduces pain at intermediate term. For disability, there is moderate-quality evidence that there is no significant difference between Pilates and other exercises in either the short term or the intermediate term. CONCLUSION: There is low- to moderate-quality evidence that Pilates is more effective than minimal intervention with most of the effect sizes being considered medium. However, there is no conclusive evidence that Pilates is superior to other forms of exercises. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE: 1. |
| 38.0 | Induced, effect, effects, receptor, mgkg, rats, test, antinociceptive, mice, activity | 7,888 | 0.04 | 11714902 | 0.9927 | Development of tolerance in mice pretreated intracerebroventricularly with mu-opioid receptor agonist endomorphin-1, endomorphin-2, or [D-Ala(2),N-Me-Phe(4),Gly-ol(5)]-enkephalin (DAMGO) was compared between endomorphin-1- and endomorphin-2-induced antinociception with the tail-flick test. A 2-h pretreatment with endomorphin-1 (30 nmol) produced a 3-fold shift to the right in the dose-response curve for endomorphin-1. Similarly, a 1-h pretreatment with endomorphin-2 (70 nmol) caused a 3.9-fold shift to the right for endomorphin-2. In cross-tolerance experiments, pretreatment with endomorphin-2 (70 nmol) caused a 2.3-fold shift of the dose-response curve for endomorphin-1, whereas pretreatment with endomorphin-1 (30 nmol) caused no change of the endomorphin-2 dose-response curve. Thus, mice acutely tolerant to endomorphin-1 were not cross-tolerant to endomorphin-2, although mice made tolerant to endomorphin-2 were partially cross-tolerant to endomorphin-1; an asymmetric cross-tolerance occurred. Pretreatment with DAMGO 3 h before intracerebroventricular injection of endomorphin-1, endomorphin-2, or DAMGO attenuated markedly the antinociception induced by endomorphin-1 and DAMGO but not endomorphin-2. It is proposed that two separate subtypes of mu-opioid receptors are involved in antinociceptive effects induced by endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2. One subtype of opioid mu-receptors is stimulated by DAMGO, endomorphin-1, and endomorphin-2, and another subtype of mu-opioid receptors is stimulated solely by endomorphin-2. |
| 39.0 | Age, years, risk, study, associated, women, factors, men, CI, higher | 4,358 | 0.02 | 25047683 | 0.9018 | OBJECTIVE: To investigate the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and foot joint pain (FJP) over a 5-year period in a community-based cohort. METHODS: We examined a subset of women from the Chingford Women's Study, a community cohort followed up for 20 years. From a baseline of 1,003 female participants, we reviewed data from 639 women (64%) for whom complete data sets for FJP and BMI were obtained over a 5-year period between year 10 (Y10) and year 15 (Y15). Descriptive statistics, binary regression modeling, and odds ratios (ORs) were used to examine the longitudinal relationship between BMI and FJP. RESULTS: For Y10 and Y15, the median age was 61 years (interquartile range [IQR] 57-67) and 66 years (IQR 62-72), respectively, and the mean +/- SD BMI was 26.7 +/- 4.6 kg/m(2) and 27.2 +/- 4.8 kg/m(2), respectively. FJP prevalence was 21.6% at Y10 and 26.6% at Y15. Longitudinal analyses showed that both BMI and FJP increased significantly from Y10 to Y15 (P < 0.001). The odds of having FJP after a 5-year period increased by 4.9% for each BMI unit increase 5 years earlier (OR 1.049 [95% confidence interval (95% CI) 1.011-1.089], P = 0.012). This remained significant when adjusted for age, diabetes mellitus, and rheumatoid arthritis (OR 1.051 [95% CI 1.011-1.091], P = 0.012). CONCLUSION: This is the first large longitudinal cohort study demonstrating that, in middle-aged women, a high BMI precedes and is predictive of FJP independent of age. Evidence from our findings can be used to identify those individuals at risk of developing FJP. |
ACS = acute coronary syndrome; AMI = acute myocardial infarction; BMI = body mass index; CI = confidence interval; CLD = contact lens discomfort; CRP = C-reactive protein; CSF = cerebrospinal fluid; CT = computed tomography; DRG = dorsal root ganglia; ELISA = enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; FJP = foot joint pain; GP = general practitioner; HDL = high-density lipoprotein; HLR = hip lateral rotation; hs = high-sensitivity; IBS = irritable bowel syndrome; IL = interleukin; IUD = intrauterine device; LBP = low back pain; LDL = low-density lipoprotein; MRI = magnetic resonance imaging; MS = multiple sclerosis; NDI-DLV = Neck Disability Index Dutch Language Version; NPAD-DLV = Neck Pain and Disability Scale Dutch Language Version; OA = osteoarthritis; OR = odds ratio; Ox = oxidized; PHN = ; SAP = stable angina pectoris; SF-36 = Short-Form-36 Health Survey; TENS = Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation; TEP = totally extraperitoneal; TNF = tumor necrosis factor; UAP = unstable angina pectoris; UTR = untranslated region; VAS = visual analog scale.
Relationships Among Topics
Although our LDA results demonstrated ∼40 topics across the pain abstract corpus, this statistic does not offer insight into the relationship among those 40 topics. The intertopic distance map (Figure 6) shows, across two principal components serving as x- and y-axes, several regions of overlapping topics. These principal components are based on Jensen-Shannon divergence, which measures the similarities between multiple probability distributions. For instance, many topics related to pain outcomes are represented in the upper right quadrant, whereas topics pertaining to nonclinical research are predominantly found in the upper left quadrant. The left lower quadrant of this distance map focuses on perioperative topics, showing overlap in conditions related to bone, joint, and muscle, with coronary-related topics serving as a more extreme outlier in this quadrant. The lower right quadrant appears focused on outpatient, nonsurgical pain conditions including headache and abdominal pain, which may be areas of poorer specificity.
Figure 6.
pyLDAvis using Jensen-Shannon divergence and principal coordinate analysis. The intertopic distance map shows, across two principal components serving as x- and y-axes, several regions of overlapping topics. For instance, many topics related to pain outcomes are represented in the upper right quadrant, whereas topics pertaining to nonclinical research are predominantly found in the upper left quadrant. The left lower quadrant of this distance map focuses on perioperative topics, showing overlap in conditions related to bone, joint, and muscle, with coronary-related topics serving as a more extreme outlier in this quadrant. The lower right quadrant appears focused on outpatient, nonsurgical pain conditions including headache and abdominal pain that also suggest areas of poorer specificity.
Further insights into the relationships among LDA topics are shown in Figure 7. The network visualization identified several outlier topics such as topic 19, which contains many terms related to age such as “infant,” “old,” “adult,” “children,” “years,” and “dementia.” The network also identified two topics that were outliers from the core cluster but that were closely connected to one another. These two topic nodes (6: perineal, neuralgia, pregnancy, obstetric, risk; and 16: menstruation, estrogen, bleeding, pelvic, chronic) contained many terms directly related to women’s health but were considered quite distant from topic 19, which focused on age.
Figure 7.
Latent Dirichlet allocation topic network visualization. The network visualization identified several outlier topics such as topic 19, which contains many terms related to age such as “infant,” “old,” “adult,” “children,” “years,” and “dementia.” The network also identified two topics that were outliers from the core cluster but that were closely connected to one another. These two topic nodes (6: perineal, neuralgia, pregnancy, obstetric, risk; and 16: menstruation, estrogen, bleeding, pelvic, chronic) contained many terms directly related to women’s health but were considered quite distant from topic 19, which focused on age.
Automated Summaries: GRU-Based Text Generation
Using our deep learning–based GRU abstract generation model, we explored the effects of various temperature settings on the resulting hypothetical abstracts. Figure 8 highlights examples of fully generated pain abstracts across a range of temperatures. In general, synthetic abstracts at lower temperature values qualitatively offered more consistent and highly organized abstract constructions compared with those at greater temperatures, which appeared to exhibit greater creativity in content and construct. Interestingly, the first example of a synthetic abstract offered an understandable and plausible study aim but appeared to confuse the concepts of placebo and treatment in a study of patients with chronic pain.
Figure 8.
Examples of artificial, synthesized PubMed abstracts generated using a gated recurrent unit-based deep learning network. These results highlight the common patterns of content and organization found in human-published abstracts pertaining to pain. A scaling factor known as temperature adjusted the balance between the conservative and obvious vs the experimental and error-prone.
Figure 8.
Continued
Discussion
Our results demonstrate that NLP methods can identify implicit topics, definitions, and summaries of pain-related research. Although prior efforts in deriving pain definitions and taxonomies have relied on a qualitative gestalt of expert opinion and consensus, NLP approaches serve as a quantitative tool that can complement and support existing taxonomic infrastructures [5,33]. This approach detected several topics and themes involving the term “pain” that are not commonly found in many pain-centric meetings, panels, discussions, and publications. Additionally, this approach allowed for the consideration and comparison of topics with respect to “closeness” of related topics, composition of topics, and temporal evolution of topics.
The need for this type of quantitative review became evident during discussions on acute pain conditions during the AAAPT process. In deliberations on lead acute pain conditions that would serve as prototypical topics for an initial round of characterization, several strong opinions were expressed on the relative importance of specific pain types. Ischemic pain was one such condition that garnered considerable debate [34–37]. Interestingly, while of questionable priority in the pain research community, our NLP analyses of pain-related terms under the MeSH of “pain” showed that ischemic pain, as related to cardiac sources, was indeed a lead topic that has received considerable research attention. This may be due to the important public health concern of heart disease and the accordant attention paid to cardiac ischemic pain by funding agencies in the United States. Given this discrepancy between perceived vs actual presence of certain pain topics in the research abstract literature, we felt it important to consider a more formal, robust quantification of content across a range of organizational scales ranging from common terms to higher-level consideration of topics and directions.
Our term-level investigations found that abstract sizes were generally constrained to narrow ranges, likely due to word restrictions by publishers and abstracts. The distribution of the word frequency of word stems shows that common terms were related to overall experimental design but were general and did not highlight specific topics. The stem terms “pain,” “patient,” “studi-,” “group,” and “use” all point toward clinical and experimental methodologic constructs, but their insight ends there. This is a well-recognized phenomenon that has driven the use of TF-IDF, LSI, and LSA methodologies to discover more meaningful content within corpora. Indeed, TF-IDF analyses did reveal several terms that appeared focused on individual pain-related topics such as temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD), acute coronary syndrome (ACS), and endometriosis. While providing some insight into distinctive terms involved in pain research, our methods relied on topic modeling via LDA to offer the greatest insights into pain research topics and their content.
During the process of investigating topic models, we iterated through several approaches and found that, although LSI failed to identify coherent themes, LDA identified upward of 40 distinct topics, as indicated by the peak coherence score. Most abstracts comprised multiple topics rather than a single one, emphasizing the interdisciplinary nature of pain research. The observed network distances between topics identified a strong cohesion in the clinical and perioperative domains. Those topics focusing on terms related to women’s health were close to one another in network analysis, but were relatively distant from all other identified topics. Topics related to geriatrics and pediatrics also followed this pattern of relative isolation. Of particular note, LDA identified several topic domains related to cardiac etiologies. This is perhaps unsurprising given the important public health concern of “chest pain” and myocardial infarction, as well as research resource allocations that have led to remarkable improvements in therapies for cardiac conditions over the last several decades. Nevertheless, our experience with discussions during the AAAPT initiative suggested considerable disagreement with the relative importance of “ischemic pain” among all other domains of pain research, to the extent that this entity was excluded from the initial list of AAAPT conditions! In comparison with the public health concern and research expenditure in cardiac topics, we found it interesting that cancer pain, which carries a similar public health impact and concordant research expenditures, was a relatively infrequent topic in the LDA analysis. This is particularly striking given recent investigations examining the linkage between cancer pain, anesthetic and analgesic therapies, immunosuppression, and potential modulation of metastasis and survival [38–41].
The above topic modeling descriptions were attempts to quantifiably characterize one of the more challenging facets of modern medicine: pain. Although the specification of topics according to the distributions of terms, and abstracts according to the distribution of topics, is quantifiable, understanding these relationships in a human-interpretable format challenges even the most advanced visualization tools. Here, we relied on common dimensionality reduction techniques to “simplify” the potential term–topic–abstract relationships into two axes that could be plotted and explored offline. Although we attempted to report on a miniscule fraction of example cases, we strongly encourage readers to explore this content to get a better sense of the remarkable relationships among topics that these methods can uncover.
Although topic modeling allowed for review and consideration of topic models across the corpora, our investigations using word2vec considered the definitions of the key terms themselves based on the vector embeddings originating from the PubMed corpus. Notably, this approach of using the PubMed corpus may offer different “definitions” of each term given that the examined terms are likely to be in proximity to different terms in comparison with a corpus targeting different audiences, such as one originating from newspapers or Wikipedia. The approach identified certain key terms deemed more similar than others. For instance, in reference to “acute,” a wide range of clinical conditions were highlighted, including vascular (“vaso-occlusive”), pancreatic/biliary (“acalculous,” “post-ERCP”), and cardiac (“acs”). Notable absences here included terms directly related to orthopedics, trauma, or the broader category of surgical. On the other hand, terms related to “chronic” were often synonyms for the term itself (“persistent,” “longstanding,” “chronicity”), although ties to function (“disabling”) and cancer (“cancer-related”) were identified. Despite the common use of certain surgical models for investigating perioperative pain (e.g., total joint arthroplasty, thoracotomy), the only specific procedure with a vector embedding close to postoperative was “post-tonsillectomy.” Contrast this with terms similar to “surgery” that included several procedures, including “hysterectomy,” “cholecystectomy,” “thyroidectomy,” and “appendectomy,” several of which are not considered common procedures for modeling of perioperative pain yet support clinical concerns of perioperative pain management.
Three of the comparisons of terms using mathematical operations between term vectors deserve specific attention. First, the terms most similar between acute and chronic drew inferences to substance use disorder (“cocaine-related,” “resuscitation,” “cocaine-associated”). Second, the terms most similar between addiction and pain heavily emphasized addiction and law enforcement (“overdoses,” “tampering,” “illegal,” “enforcement,” “criminal”) but did not include any terms related to mechanisms linking pain and addiction, a notable finding given the research domain of the corpora. Last, the terms most similar between opioid and pain emphasized specific chemical moieties and targets (“mu-opioid,” “delta-opioid,” “imidazoline”) as well as agents of particular concern regarding opioid use disorder (“heroin,” “benzodiazepine”).
We concluded our analyses using text-generating approaches. The GRU-based deep learning approaches to automated abstract generation herald a new horizon in our understanding of how we communicate pain research. Our intent in this exercise was to show readers how an algorithmic, domain-naïve approach to writing PubMed abstracts could still yield content that may soon approach human-level details in content and organization. As expected, lower temperatures (0.25) were associated with more standard approaches on common topics. For instance, the first sentence of the first example typified this conservative approach: “The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between the characteristics of the pain and the quality of life (QoL) in patients with chronic pain.” This is indeed a rather generic statement that could be applied to a wide range of pain research experiments. On the other hand, at temperatures of 0.75, we see “higher-risk” statements such as, “The primary objective of this study was to examine the long-term effect of supported spine treatment with physical versus psychological treatment for back pain” and “The use of a newly developed form of intravenous (i.v.) infusion of glutamate (B) was used to treat pain in the presence of applied to the spinal cord.” We find it interesting that increasing GRU temperature leads not only to increased risk in sentence construction but also to increases in the audacity of proposed experiments. Additionally, the synthetic abstracts were challenged by the roles of placebos in clinical trials, perhaps in recognition of increasing attention to placebo-related effects on pain intensity. Critically, we reiterate that the GRU-based methods do not contain any explicit instructions on pain, abstract formatting, or even sentence construction; they are instead instructed to train themselves based on the corpus of documents at hand.
It is worth noting that the approaches used here are similar in methodology to the conceptual approaches used to generate “DeepFakes” and so have been carefully listed as synthesized and algorithmically generated to avoid confusion [42]. More recent extensions of natural text generation using Generalized Pretrained Transformer 2 (GPT-2) and Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) may offer even more realistic text generation content, potentially posing new challenges for readers, writers, and reviewers of manuscripts and grants in the domains of pain medicine [43,44]. For perspective, GPT-1 was initially considered “The AI That’s Too Dangerous to Release” [45,46].
Limitations
Many of the limitations of this project center on the scale of content available for perusal. With >42 million terms for review, robust quantitative abstraction of material that crosses many biological, psychological, social, and clinical domains is considerably challenging. Given the motivations of our manuscript, we applied a broad information retrieval strategy and applied only general implementations of stop words rather than clinically oriented stop word dictionaries [47,48]. To highlight the tradeoffs inherent to this approach, including search filters for human subjects research would have biased the results away from topics involving animal experiments; the use of clinical stop words such as “patient” would likewise have skewed topic modeling and vector-based comparisons by removing these important constructs from the analyzed corpus.
Although our work examined abstract length distribution and TF-IDF measures, these analyses only partially account for the heterogeneity in abstract formats. Our approach began with relatively simple summative approaches that were easy to understand and led to easily interpretable results; unfortunately, these results failed to yield much insight into the methods at hand. More complex approaches involving LSI and LDA led to progressively more refined and agreeable topic models, and yet the transparency and interpretability of the methods used to generate these models admittedly become more and more convoluted. Nevertheless, the methods are replicable with fixed seeds and resulted in topic models that seem reasonable to researchers with both basic science and clinical backgrounds. Our approach was intended as a survey of findings; much future work is necessary to investigate topic relationships, and the gaps therein, among pain-related investigations.
Conclusions
The current investigation has both clinical and research ramifications related to the efficiency provided by NLP methodology and analytic output. Clinically, such methods may play a role in topic surveillance and implementation practices. It is well known that a large time gap exists in relation to the creation of diagnostic or treatment evidence and its integration into the health care system, an average of 17 years. This methodology, when conducted periodically, may offer weighted information on emerging topics or therapies that allow health systems to optimize time spent conducting exhaustive literature searches on many topics. By significantly optimizing time spent searching for emerging themes/topics, health systems can possibly leverage such techniques to focus implementation efforts to update diagnostic procedures and/or institute comprehensive treatment regimens based on topics identified with the above methodology.
In addition to clinical applicability, such NLP methods may play a significant role in identifying knowledge gaps within research areas. With a rapidly growing compendium of literature, the future evolution of such NLP methods may assist researchers and funders to identify much-needed pathways of investigation by assessing what has not been published regarding a certain topic. A large set of articles and materials may be searched in a rapid and analytic fashion, reducing or removing a significant human burden. As a complement to this, funders may find opportunities to promote certain topics to assess the amount of funding needed in certain areas. Additionally, funders may assess the discordance between the amount of funding provided and the amount of literature representing certain topics. This may allow funders to assess the quality of research being conducted with such funds and provide opportunities to assist investigators to develop efficient strategies.
Supplementary Data
Supplementary data are available at Pain Medicine online.
Supplementary Material
Funding sources: This project was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant No. R01 GM114290-03 to Patrick J. Tighe, MD, MS).
Conflicts of interest: None.
References
- 1. Dowell D, Haegerich TM, Chou R. CDC guideline for prescribing opioids for chronic pain—United States, 2016. JAMA 2016;315(15):1624–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Howard R, Waljee J, Brummett C, Englesbe M, Lee J. Reduction in opioid prescribing through evidence-based prescribing guidelines. JAMA Surg 2018;153(3):285–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pain Terms: A List with Definitions and Notes on Usage. Recommended by the IASP Subcommittee on Taxonomy. Pain 1979;6(3):249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Treede R-D, Rief W, Barke A, et al. A classification of chronic pain for ICD-11. Pain 2015;156(6):1003–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kent ML, Tighe PJ, Belfer I, et al. The ACTTION-APS-AAPM Pain Taxonomy (AAAPT) multidimensional approach to classifying acute pain conditions. Pain Med 2017;18(5):947–58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Dworkin RH, Bruehl S, Fillingim RB, Loeser JD, Terman GW, Turk DC. Multidimensional diagnostic criteria for chronic pain: Introduction to the ACTTION-American Pain Society Pain Taxonomy (AAPT). J Pain 2016;17(9):T1–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Nadkarni PM, Ohno-Machado L, Chapman WW. Natural language processing: An introduction. J Am Med Inform Assoc 2011;18(5):544–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Collobert R, Weston J, Bottou L, Karlen M, Kavukcuoglu K, Kuksa P. Natural language processing (almost) from scratch. J Mach Learn Res 2011;12:2493–537. [Google Scholar]
- 9. Jones KS. Natural Language Processing: A Historical Review. In: Zampolli A, Calzolari N, Palmer M, eds. Current Issues in Computational Linguistics: In Honour of Don Walker. Linguistica Computazionale, vol 9. Dordrecht: Springer; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality In: Burges CJC, Bottou L, Welling M, Ghahramani Z, Weinberger KQ, eds. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 26. Curran Associates Inc.: 2013;3111–9. [Google Scholar]
- 11. Goldberg Y, Levy O. word2vec Explained: Deriving Mikolov et al.’s negative-sampling word-embedding method. 2014. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1402.3722 (accessed March 9, 2020).
- 12. Van Rossum G, Drake FL Jr. Python Reference Manual. Amsterdam: Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica; 1995.
- 13. Perez F, Granger BE. Project Jupyter: Computational narratives as the engine of collaborative data science. 2015. Available at: http://archive.ipython.org/JupyterGrantNarrative-2015.pdf (accessed March 9, 2020).
- 14. Perkel JM. Why Jupyter is data scientists’ computational notebook of choice. Nature 2018;563(7729):145–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Cock PJ, Antao T, Chang JT, et al. Biopython: Freely available Python tools for computational molecular biology and bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 2009;25(11):1422–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. McKinney W. pandas: A foundational Python library for data analysis and statistics. Python for High Performance and Scientific Computing. 2011;14(9). Available at: http://archive.ipython.org/JupyterGrantNarrative-2015.pdf (accessed March 9, 2020).
- 17. Perkins J. Python 3 Text Processing with NLTK 3 Cookbook. Packt Publishing Ltd; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bird S, Loper E, Klein E. Natural Language Processing with Python. Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly Media Inc.; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 19. Ramos J. Using TF-IDF to determine word relevance in document queries. In: Proceedings of the First Instructional Conference on Machine Learning. 2003;133–42.
- 20. Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781. 2013. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1301.3781 (accessed March 9, 2020).
- 21. Radim Rehurek PS. Software framework for topic modelling with large corpora. In: Proceedings of the LREC 2010 Workshop on New Challenges for NLP Frameworks. 2010.
- 22. Deerwester S, Dumais ST, Furnas GW, Landauer TK, Harshman R. Indexing by latent semantic analysis. J Am Soc Inf Sci 1990;41(6):391–407. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python. J Mach Learn Res 2011;12:2825–30. [Google Scholar]
- 24. Blei DM, Lafferty JD. . Dynamic topic model In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM; 2006:113–20. Available at: https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/1143844.1143859 (accessed March 9, 2020). [Google Scholar]
- 25. Sievert C, Shirley K. LDAvis: A method for visualizing and interpreting topics. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Interactive Language Learning, Visualization, and Interfaces. 2014:63–70.
- 26. Lin J. Divergence measures based on the Shannon entropy. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 1991;37(1):145–51. [Google Scholar]
- 27. Fuglede B, Topsoe F. Jensen-Shannon divergence and Hilbert space embedding. In: International Symposium on Information Theory, 2004 ISIT 2004. Proceedings. IEEE; 2004: 31.
- 28. Cha S-H. Comprehensive survey on distance/similarity measures between probability density functions. Cityscape 2007;1(2):300–7. [Google Scholar]
- 29. Endres DM, Schindelin JE. A new metric for probability distributions. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 2003;49(7):1858–60. [Google Scholar]
- 30. Chung J, Gulcehre C, Cho K, Bengio Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.3555. 2014. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3555 (accessed March 9, 2020).
- 31. Chung J, Gulcehre C, Cho K, Bengio Y, eds. Gated feedback recurrent neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. 2015:. 2067–75.
- 32. Röder M, Both A, Hinneburg A. Exploring the space of topic coherence measures. In: Proceedings of the Eighth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. 2015:399–408. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Fillingim RB, Bruehl S, Dworkin RH, et al. The ACTTION-American Pain Society Pain Taxonomy (AAPT): An evidence-based and multidimensional approach to classifying chronic pain conditions. J Pain 2014;15(3):241–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Segerdahl M, Ekblom A, Sollevi A. The influence of adenosine, ketamine, and morphine on experimentally induced ischemic pain in healthy volunteers. Anesth Analg 1994;79(4):787–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Pertovaara A, Kemppainen P, Johansson G, Karonen S-L. Ischemic pain nonsegmentally produces a predominant reduction of pain and thermal sensitivity in man: A selective role for endogenous opioids. Brain Res 1982;251(1):83–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Maseri A, Crea F, Kaski JC, Davies G. Mechanisms and significance of cardiac ischemic pain. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 1992;35(1):1–18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Maseri A, Chierchia S, Davies G, Glazier J. Mechanisms of ischemic cardiac pain and silent myocardial ischemia. Am J Med 1985;79(3):7–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Exadaktylos AK, Buggy DJ, Moriarty DC, Mascha E, Sessler DI. Can anesthetic technique for primary breast cancer surgery affect recurrence or metastasis? Anesthesiology 2006;105(4):660–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Gottschalk A, Sharma S, Ford J, Durieux ME, Tiouririne M. Review article: The role of the perioperative period in recurrence after cancer surgery. Anesth Analg 2010;110(6):1636–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Hasegawa T, Oguri T, Osawa T, et al. Opioid dose and survival of patients with incurable nonsmall cell lung cancer: A prospective cohort study. J Palliat Med 2018;21(10):1436–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Nguyen J, Luk K, Vang D, et al. Morphine stimulates cancer progression and mast cell activation and impairs survival in transgenic mice with breast cancer. Br J Anaesth 2014;113(Suppl 1):i4–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Floridi L. Artificial intelligence, deepfakes and a future of ectypes. Philos Technol 2018;31(3):317–21. [Google Scholar]
- 43. Budzianowski P., VI Hello It’s GPT-2–How can i help you? Towards the use of pretrained language models for task-oriented dialogue systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.05774. 2019. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.05774 (accessed March 9, 2020).
- 44. Devlin J, Chang M-W, Lee K, Toutanova K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805. 2018. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805 (accessed March 9, 2020).
- 45. Simonite T. OpenAI said its code was risky. Two grads re-created it anyway. Wired. August 26, 2019.
- 46. Griffin A. AI deemed ‘too dangerous to release’ makes it out into the world.The Independent. November 7, 2019.
- 47. Dolamic L, Savoy J. When stopword lists make the difference. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 2010;61(1):200–3. [Google Scholar]
- 48. Pergola G, He Y, Lowe D, eds. Topical phrase extraction from clinical reports by incorporating both local and global context. In: Workshops at the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2018.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.