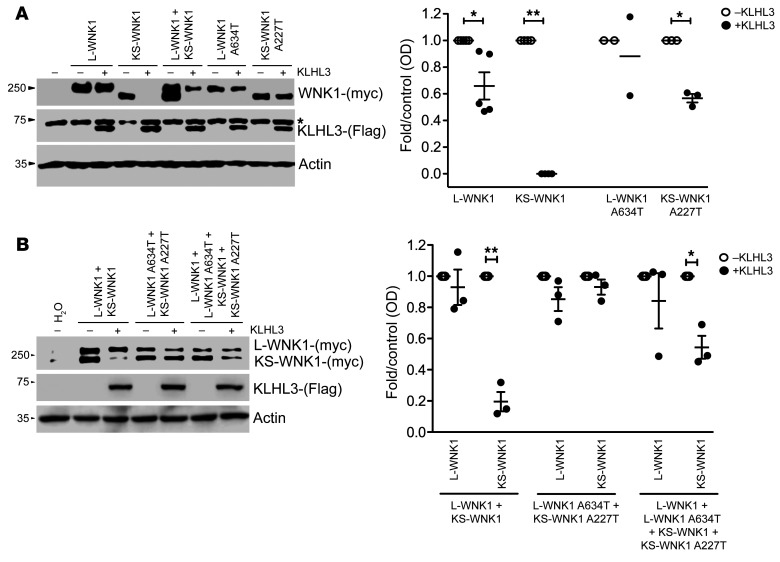
Figure 3. Differential effect of the WNK1 Ex7 G1900A (A634T-L-WNK1; A227T-KS-WNK1) variant on the interaction between KLHL3 and L-WNK1 or KS-WNK1 isoforms.
(A) Representative immunoblot of proteins extracted from X. laevis oocytes (left panel) that were injected with WT or mutant L-WNK1 or KS-WNK1 in the absence or presence of KLHL3 cRNA, as stated. The upper blot shows c-myc–positive bands corresponding to L-WNK1 and KS-WNK1. The middle blot shows unspecific upper band present in all lanes (*), including water-injected oocytes, and a lower band corresponding to KLHL3 only present in KLHL3-injected oocytes. The lower blot shows actin. Densitometry of several (n = 3) blots in which the effect of KLHL3 was tested in L-WNK1 or KS-WNK1 WT or mutants separately (right panel). In the absence of KLHL3, mean values were arbitrarily set to 1.0, and in the presence of KLHL3, values were normalized accordingly. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, unpaired Student’s t test. (B) Representative immunoblot of proteins extracted from X. laevis oocytes (left panel) that were injected with mixture of WT or mutant L-WNK1 and KS-WNK1 in the absence or presence of KLHL3 cRNA in order to analyze the consequences of L-WNK1 and KS-WNK1 coexpression. Immunoblot (left panel) and densitometry analysis of several blots (right panel) are as in Figure 3A.