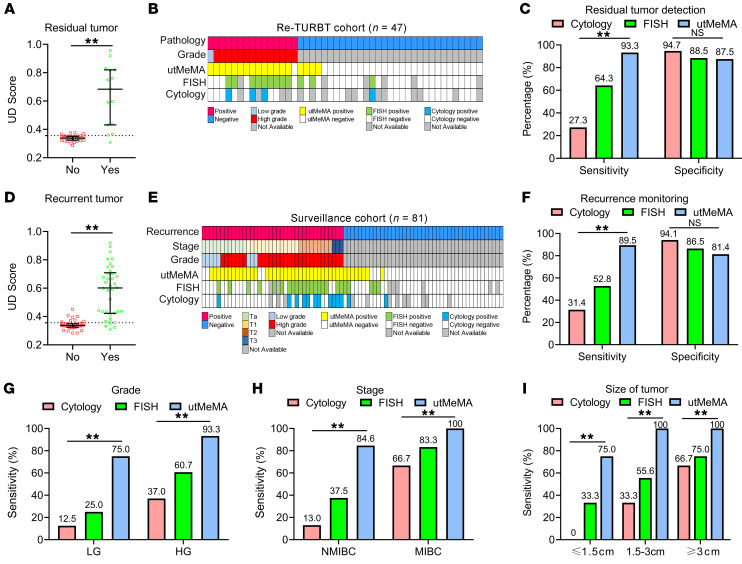
Figure 6. Application of utMeMA to detect residual tumor and monitor the recurrence of BCa.
(A) The distribution of UD score in BCa patients with or without residual tumors (n = 47). Statistical significance was assessed using unpaired t test (2-tailed). The data are shown as median with the interquartile range. (B) The landscape of pathological characters and detection results in re-TURBT cohort, including 15 cases with residual tumor and 32 cases without tumor. (C) The sensitivity and specificity of utMeMA in the detection of residual tumor, in comparison with urine cytology and FISH (n = 47). (D) The distribution of UD score in patients with BCa with or without recurrent tumor. The data are shown as median with the interquartile range. Statistical significance was assessed using unpaired t test (2-tailed). (E) The landscape of pathological characteristics and detection results in surveillance cohort, including 38 cases with tumor recurrence and 43 cases without recurrence (n = 81). (F) The sensitivity and specificity of utMeMA in detection of recurrent tumor, in comparison with urine cytology and FISH (n = 81). (G–I) The sensitivity of utMeMA in patients with recurrent BCa with indicated grade (G), stage (H), and size (I) of tumor, in comparison with urine cytology and FISH (n = 38). Statistical significance was assessed using χ2 test (C, F, G–I). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.