Figure 6.
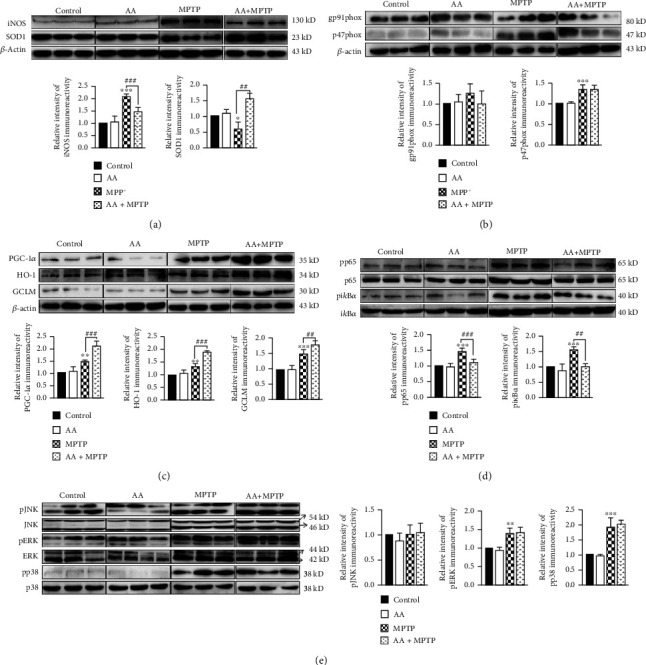
Ascorbic acid enhances antioxidant function and decreases NK-κB activation in the midbrains of MPTP-treated mice. Wild-type mice were intraperitoneally treated with 500 mg/kg of AA for 60 days, following by coinjected with 25 mg/kg of MPTP every 3.5 days for five weeks. After behavioral testing, midbrains were removed and total proteins were extracted. (a) The expression levels of iNOS and SOD1 were detected by Western blotting (n = 3). (b) The expression of gp9phox and p47phox was detected by Western blotting (n = 3). (c) The expression levels of PGC-1α, HO-1, and GCLM were detected by Western blotting (n = 3). (d) The expression levels of phosphorylated p65 and iκBα were detected by Western blotting (n = 3). (e) The expression levels of phosphorylated JNK, ERK, and p38 were detected by Western blotting (n = 3). Data were obtained from three independent experiments. One-way ANOVAs followed by LSD pairwise comparisons were performed. ∗ was considered significant compared to control (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001). # was considered significant compared to MPTP or MPP+ (#P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001).
