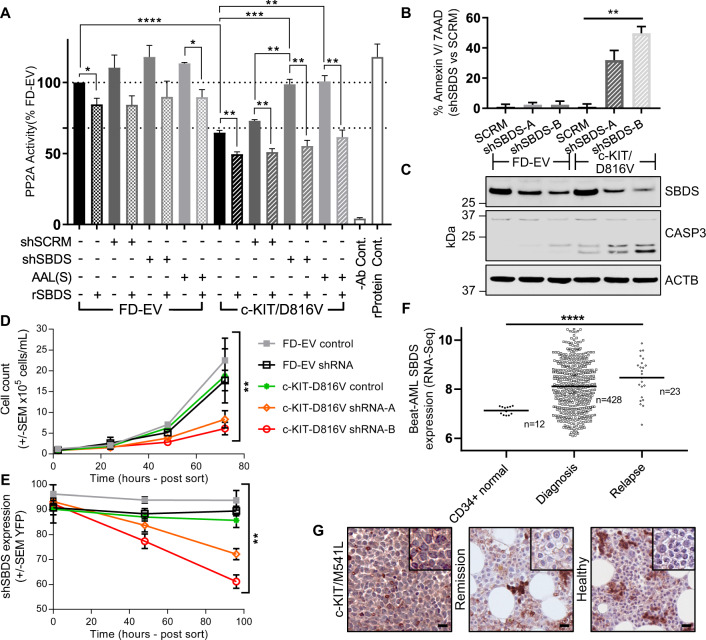
Fig. 2. SBDS inhibits PP2A activity and is essential for the survival of c-KIT/D816V mutant cells.
a PP2A activity was assessed following molecular inhibition of SBDS using SBDS shRNA, or treatment of FD-EV and c-KIT/D816V cells for 12 h with 250 nM AAL(S). FD-EV and c-KIT/D816V cells were transiently transfected with YFP-tagged scrambled shRNA controls or two different YFP-tagged SBDS shRNA constructs for 24 h, and then sorted for populations of cells expressing high YFP. b Cells were then stained 24 h post sort with Annexin V, quantitation of dead cells post sort was measured by Annexin V+ and 7AAD+ cells as a percent of scrambled controls. c Western blot for caspase 3 following transient SBDS knockdown. d c-KIT/D816V cells harbouring the knockdown of SBDS (shSBDS-A, orange; shSBDS-B, red) showed significantly reduced proliferation compared with scrambled shRNA controls (FD-EV, grey; c-KIT/D816V, green) and FD-EV SBDS knockdown (shSBDS, black) determined by the Trypan blue exclusion assay, and e reduced YFP+ cells as determined via flow cytometry (**p < 0.01, Two-way ANOVA). f SBDS RNA-sequencing data from primary AML blast samples from 428 AML patients at diagnosis, 23 patients following AML relapse, and SBDS expression in normal bone marrow CD34+ cells from 12 healthy controls. Data extracted from the Beat AML® cohort and were analysed using www.vizome.org. g Trephine biopsies from an AML patient harbouring a c-KIT mutation at diagnosis and following successful treatment with standard of care chemotherapies, and a trephine biopsy from a healthy control immunostained for SBDS.