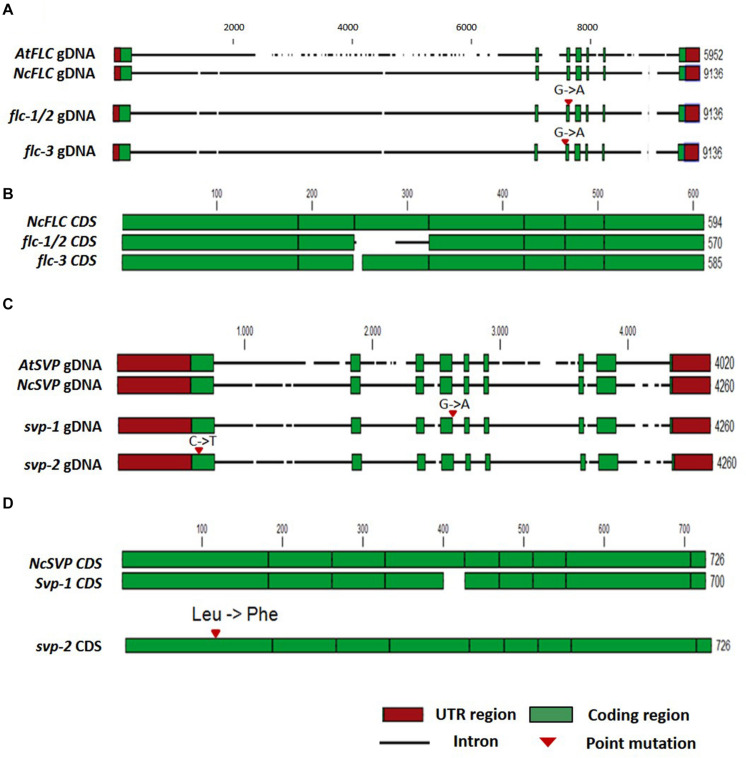
FIGURE 4.
Analysis of the N. caerulescens FLC and SVP DNA sequences in WT and the flc and svp mutants. (A) Schematic representation of the Arabidopsis thaliana FLC genomic DNA (gDNA) sequence (AtFLC) compared to the NcFLC genomic DNA sequence in N. caerulescens WT, flc-1/flc-2, and flc-3 mutants. Numbers indicate total DNA sequence length in base pairs. Intron DNA sequences are indicated with a horizontal black line, with breaks to indicate InDels. 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTR) are indicated with red boxes. Protein coding exons are indicated with green boxes. G to A single base pair mutations are found in all mutants. The mutations in flc-1 and flc-2 are identical, suggesting a common mutation event. The mutation in these mutants locates at the 3′ splice junction of exon 3, while the mutation in flc-3 locates at the 5′ splice junction of exon 3. (B) Schematic representation of NcFLC coding sequences (CDS) of the N. caerulescens WT and flc mutants. The G to A mutation in flc-1/flc-2 causes an in-frame substitution of exon 3 sequence, while the mutation in flc-3 leads to a 9 bp deletion at the start of exon 3. Exons are indicated in green boxes, the alternative exon 3 in the flc-1/flc-2 CDS is indicated with a horizontal black line. (C) The same as (A) for the SVP gene. In the svp-1 mutant, a G to A mutation was found at the 3’ splice junction of exon 4, in the svp-2 mutant, a C to T mutation was found in exon 1. (D) The same as (B) for the NcSVP CDS. The mutation in svp-1 causes an in-frame deletion of part of exon 4, while the mutation in svp-2 leads to a single amino acid change of Leucine to Phenylalanine in exon 1. The numbers at the end of each line indicate the total number of nucleotides, the scale refers to the WT N. caerulescens sequence.