Figure 1.
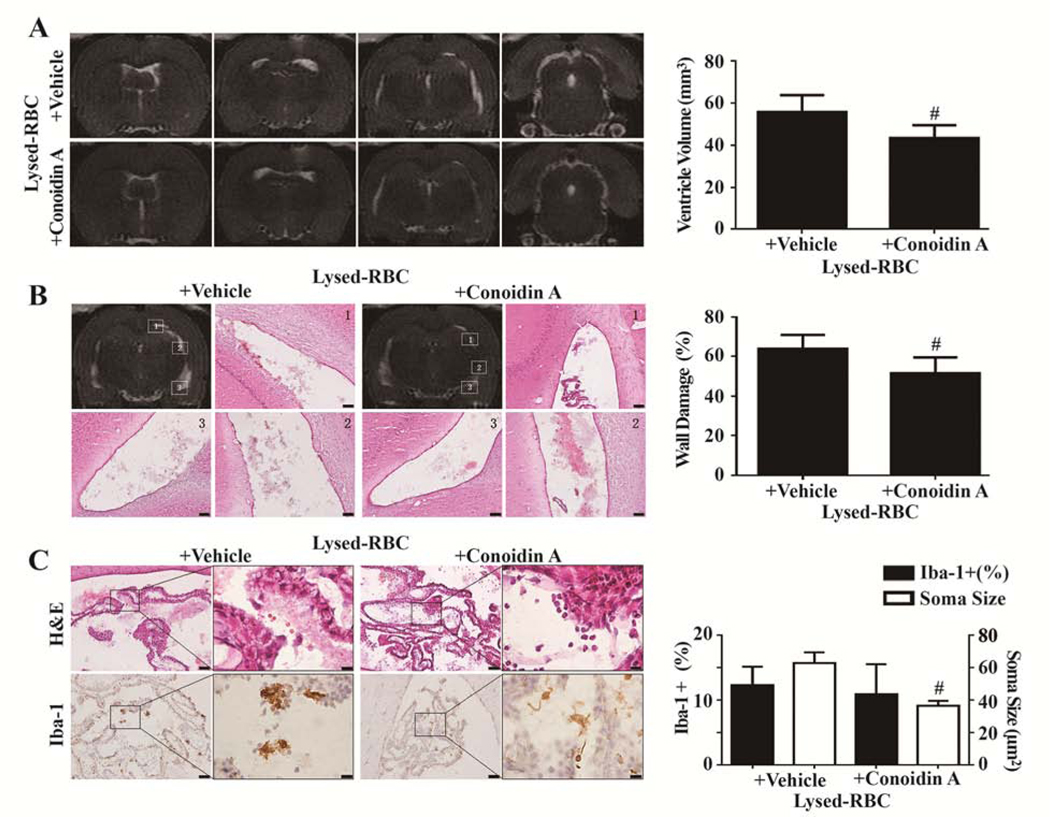
Effects of conoidin A on lysed red blood cell (RBC)–induced hydrocephalus, ventricular wall damage, and choroid plexus inflammation. (A) T2 MRIs 1 d after intraventricular injection of 30 μL lysed RBC with vehicle or conoidin A and quantification of ventricle volume. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining in the same 2 groups showing ventricular wall damage and quantification of that damage. (C) Ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1) immunohistochemistry at the choroid plexus and corresponding H&E sections 1 d after intraventricular injection of 30 μL lysed RBC with vehicle or conoidin A. The number of Iba-1–positive cells and soma size were quantified. Values are mean±SD; n=8; #P<0.01 vs lysed RBC+vehicle group. Scale bar=50 μm at low magnification, 10 μm at high magnification. (Reproduced with permission, Tan et al. Stroke, 2020;51:1578–1586)
