Figure 1. Study Design Overview in the PROMIS-HFpEF Derivation Cohort.
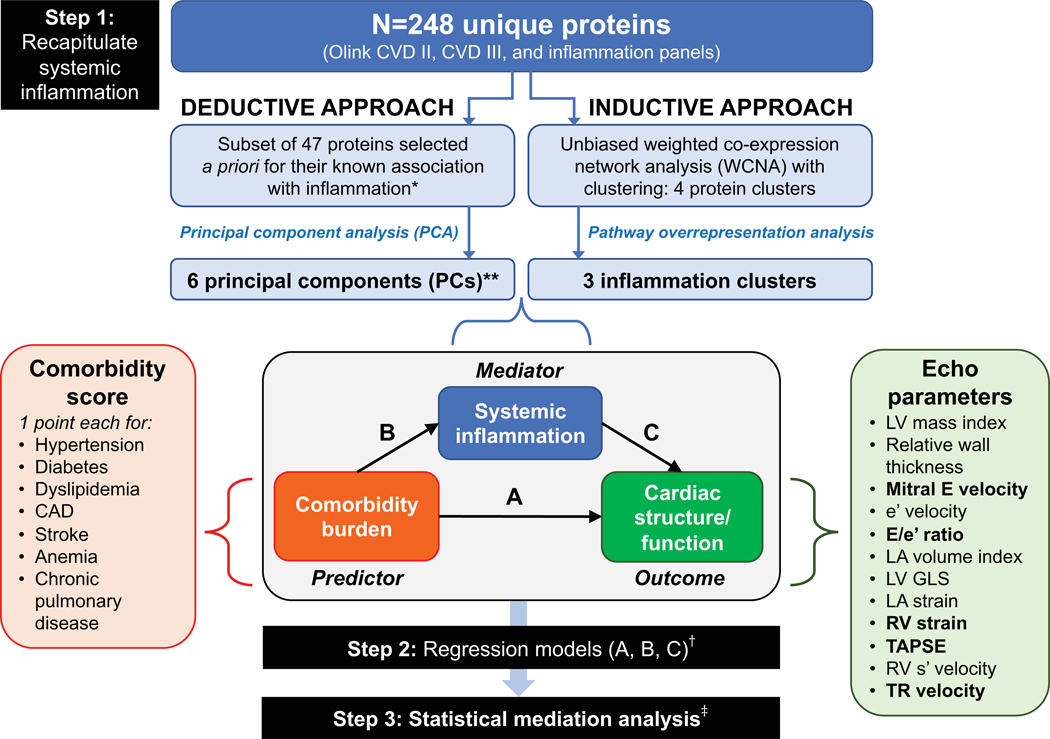
The analytic approach in the PROMIS-HFpEF derivation cohort started with recapitulating (summarizing) systemic inflammation using both inductive and deductive approaches in step 1. The deductive approach used a priori knowledge of proteins associated with inflammation based on functional annotation in the GO, KEGG, and Reactome databases, followed by principal components analysis. The inductive approach used an unbiased weight co-expression network analysis (WCNA) with clustering, followed by pathway overrepresentation analysis. The resulting principal components and inflammation protein clusters were then used as markers of systemic inflammation in subsequent analyses. In step 2, we used 1-way regression models to determine the association between (A) comorbidity burden with cardiac structure/function; (B) comorbidity burden and systemic inflammation; and (C) systemic inflammation and cardiac structure/function. Finally, in step 3, we performed formal statistical mediation analysis to determine whether markers of systemic inflammation (PCs and protein clusters) mediated the association between comorbidity burden and specific indices and cardiac structure/function. *Selected if annotated as inflammation-related in 2 or more of the databases (GO, KEGG, and Reactome).**These 6 PCs captured 57% of the variation in the 47 selected inflammation-related proteins. †All regression models were adjusted for age, sex, GFR, and study site; LA volume index, LA reservoir strain, e’ velocity, and E/e’ ratio were also further adjusted for atrial fibrillation. ‡ Mediation analysis was only performed for protein PCs/clusters and echocardiographic parameters that fulfilled a valid 3-way association in step 2 (i.e., statistically significant associations with a coherent direction had to be present in regression models corresponding to arrows A, B, and C). Echocardiographic parameters that met these criteria for mediation analysis are represented in bold font. Inflammation protein parameters that met these criteria were PC1, PC5, PC6, the turquoise cluster, and the yellow cluster. Abbreviations: CAD = coronary artery disease; Echo = echocardiographic; LV = left ventricle; LA = left atrial; RV = right ventricular; TAPSE = tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion; TR = tricuspid regurgitation; GO = gene ontology; KEGG = Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes ad Genomes.
