Figure 3 – Cytokine levels in peritoneal lavage fluid from WT and Mye-Cftr−/− Mice.
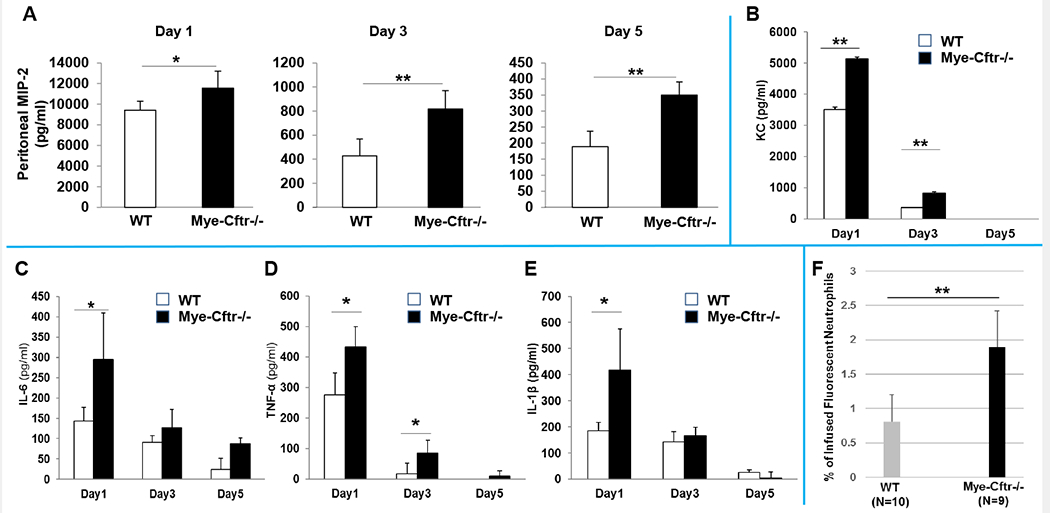
WT and Mye-Cftr−/− mice were challenged with zymosan (0.7g/kg, i.p.). Peritoneal lavage fluid was collected from each assigned animal for Days 1, 3 & 5 post-challenge using 2 ml of PBS. Multiple pro-inflammatory cytokines (A: MIP-2; B: KC; C: IL-6; D: TNF-α; E: IL-1β) were measured using ELISA. Mye-Cftr−/− mouse lungs were more inflamed and produced significantly higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines at different time points after zymosan challenge. F) Neutrophil recruitment assay. Bone marrow nucleated cells (1×107) from Mye-Cftr−/− mice were fluorescently labeled and infused via tail veins into WT or Mye-Cftr−/− mice that had been pre-challenged with intraperitoneal administration of zymosan (0.7 g/kg) for 24 hours. Six hours post cell injection, peritoneal cells were lavaged out and immunostained with the Ly6G antibodyand transfused into either WT or Mye-Cftr−/− mice that had been conditioned by peritoneal zymosan challenge. Fluorescent neutrophils recruited to the peritoneal cavity of each tested animal were determined by flow cytometry. Student’s t-test was used to judge any difference in neutrophil recruitment between the two mice (P<0.05, n=4).
