Fig. 7. Local mammary immunization establishes resident memory CD4 T cells in the mammary tissue on the contrary to the intramuscular route of immunization.
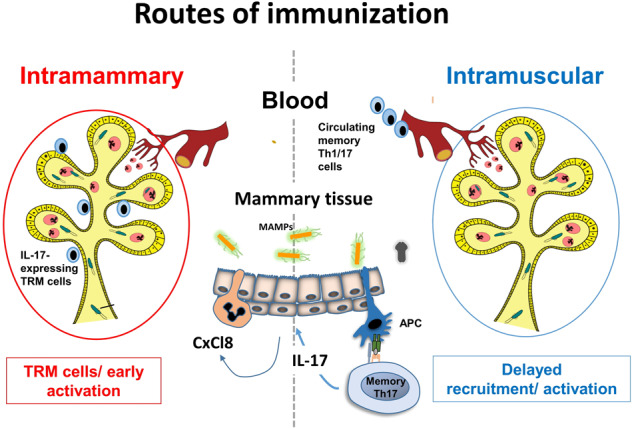
The schematic describes our current view of the beneficial effect of intramammary immunization and compares the two routes of immunization. Systemic injection of killed bacteria in adjuvant produces a pool of Th1/Th17 circulating CD4 T cells. Injection of E. coli culture supernate antigens via the teat ductal route enables settlement of CD4 TRM cells in the mammary tissue that are poised to express IL-17 and mobilize a protective response through neutrophil recruitment early during the course of an E. coli mastitis.
