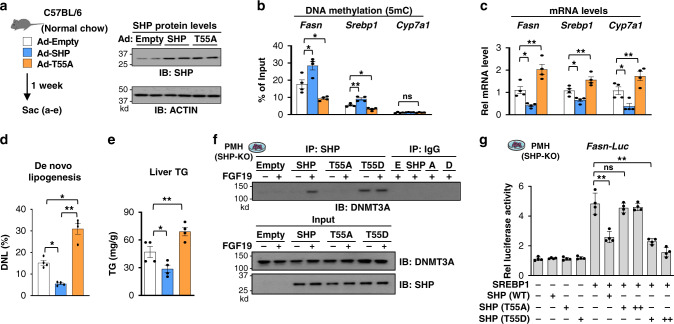
Fig. 6. FGF15/19-induced phosphorylation of SHP is required for its interaction with DNMT3A in repression of hepatic lipogenesis.
a–e C57BL/6 mice were infected by adenoviruses that express SHP-WT or T55A or by empty adenoviruses, and one week later the mice were sacrificed. a Experimental outline (left). Levels of SHP protein determined by IB (right). b DNA methylation at the promoters of the indicated genes measured by MeDIP. c Levels of mRNA of the indicated genes measured by RT-qPCR. d For 2 days prior to brief fasting and sacrifice, drinking water for the mice was 4% deuterated water. Hepatic DNL was measured as described in Methods. e Liver triglyceride (TG) levels. f–g PMHs were prepared from SHP-KO mice and cultured for 48 h. The PMHs were transfected with plasmids expressing control, SHP-WT, a phosphorylation-defective SHP-T55A mutant, or a phosphorylation-mimic SHP-T55D mutant. Seventy two hours later, cells were cultured in serum-free media overnight and then treated with vehicle or FGF19 for 2 h (f) or 6 h (g). f Interaction of SHP and DNMT3A determined by CoIP assays. Four culture plates were pooled for each sample. The experiment was repeated two times with similar results. g Luciferase activities normalized to β-galactosidase activities in PMH transfected with the indicated plasmids. b–e, g The mean values ± SD are plotted (b–e, n = 4 mice; g, n = 4 PMH culture dishes). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with the Tukey post-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ns, statistically not significant.