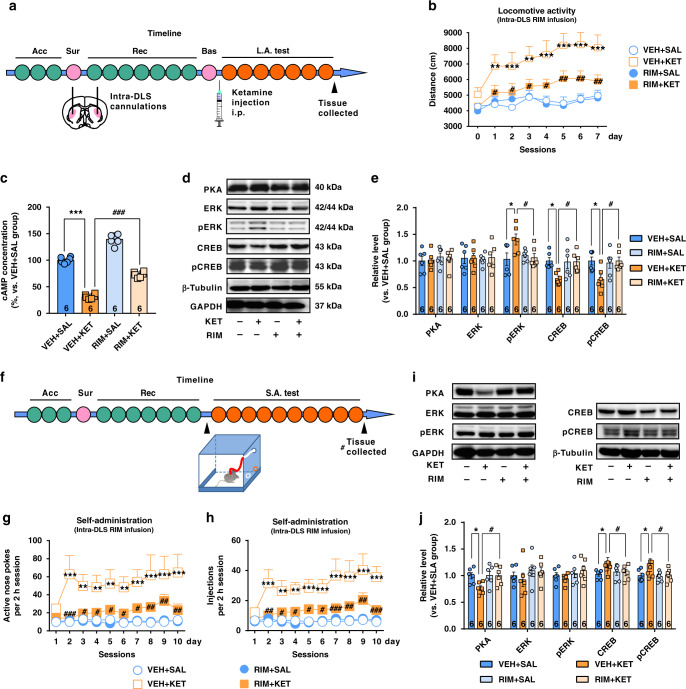
Fig. 2. CB1Rs blockage attenuates the psychostimulant and reinforcing effects of ketamine.
a Experimental time course for locomotor activity detection in the mice receiving intra-DLS infusion of rimonabant (RIM). b Bilateral intra-DLS infusion of RIM (0.6 μg per side) attenuated ketamine-induced hyperactivity (n = 10 mice/group, two-way repeated measured ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, Drug, F(3,36) = 10.22, P < 0.0001; time, F(7,252) = 10.12, P < 0.0001; interaction, F(21,252) = 1.953, P = 0.0088). c Intra-DLS infusion of RIM significantly elevated ketamine-reduced cAMP in hyperlocomotion model. (One-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, F(3,20) = 283.6, P < 0.0001). d Representative immunoblotting of downstream signaling molecules after CB1Rs blockage in ketamine-induced hyperlocomotion. e Statistical analysis of immunoblotting showed that in hyperlocomotion model, ketamine increased pERK expression, but decreased CREB and pCREB expression; these effects were reversed by rimonabant (one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, pERK, F(3,20) = 3.639, P = 0.0304; CREB, F(3,20) = 3.802, P = 0.0263; pCREB, F(3,20) = 3.933, P = 0.0234). The optical densities of the detected proteins are normalized to the mean of GAPDH and α-tubulin. f Experimental time course for self-administration in mice receiving intra-DLS RIM infusion. g Bilateral intra-DLS infusion of RIM (1 μM, 1 μL per side) effectively reduced ketamine-enhanced active nose pokes (n = 7 mice/group, two-way repeated measured ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, treatment, F(3,24) = 7.477, P = 0.0011; time, F(9,216) = 3.383, P = 0.0007; interaction, F(27,216) = 1.901, P = 0.0065). h Bilateral intra-DLS infusion of RIM effectively decreased drug injections (n = 7 mice/group, two-way repeated measured ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, treatment, F(3,24) = 10.86, P = 0.0001; time, F(9,216) = 5.055, P < 0.0001; interaction, F(27,216) = 2.172, P = 0.0012). i Representative immunoblotting of downstream signaling molecules after CB1Rs blockage in ketamine self-administration test. j Statistical analysis for immunoblotting showed that ketamine decreased PKA expression, but increased CREB and pCREB expression; rimonabant counteracted these effects (one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test: PKA, F(3,20) = 3.37, P = 0.0389; CREB, F(3,20) = 3.546, P = 0.0331; pCREB, F(3,20) = 3.656, P = 0.03). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Compared to VEH + SAL group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; Compared to VEH + KET group, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01. SAL saline, KET ketamine, VEH vehicle, RIM rimonabant, Acc acclimation, Sur surgery, Rec recovery, Bas baseline test, L.A. test locomotor activity test, S.A. test self-administration test. One small circle represents for a day. One big circle represents for a week. Source data provided as a Source Data file.