Fig. 2. Fabricated mechanically interlocked metal-organic microstructures.
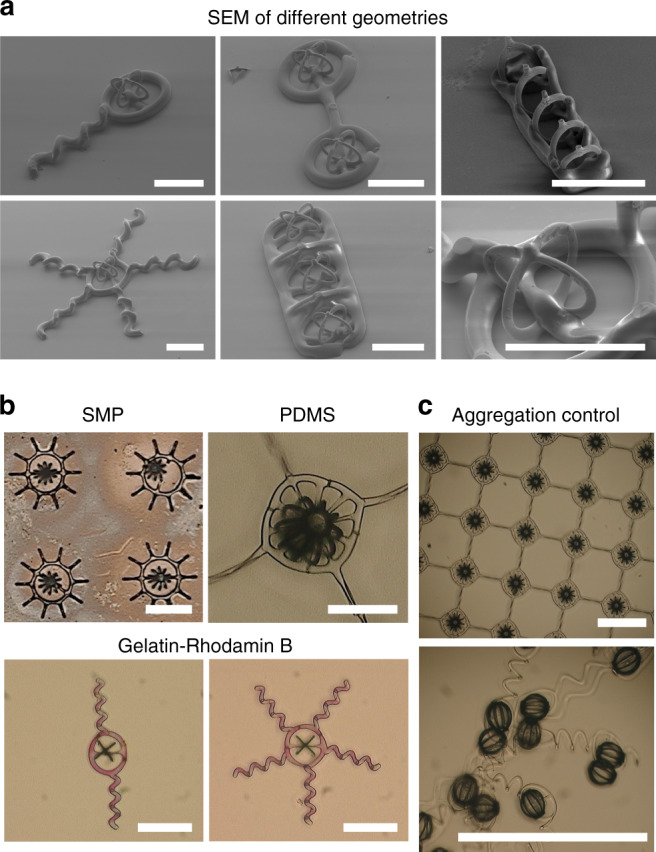
a SEM images of 3D mechanically interlocked structures comprised of fully metallic Fe and PDMS components, highlighting the high-resolution features and possibility of designing completely independent shapes. The scale bar is 50 μm. b Optical images of structures comprised of different polymeric materials. The possibility of using different materials such as shape-memory polymers (SMPs), PDMS, and pure gelatin, possibly loaded with drugs, enables the fabrication of structures suitable for advanced functionalities, such as drug delivery and pre-programmable shape transformation. The use of an interlocking strategy guarantees process compatibility between metal and polymer deposition. As a result, the enhanced magnetic responsiveness and biocompatibility characteristic of fully metallic Fe structures can be harnessed in parallel. The scale bar is 80 μm. c In addition, hybrid microstructures can be mechanically stitched along the X-Y plane to prepare large meshes or filaments. This strategy is suitable to control the agglomeration of magnetic microparticles. The scale bar is 500 μm.
