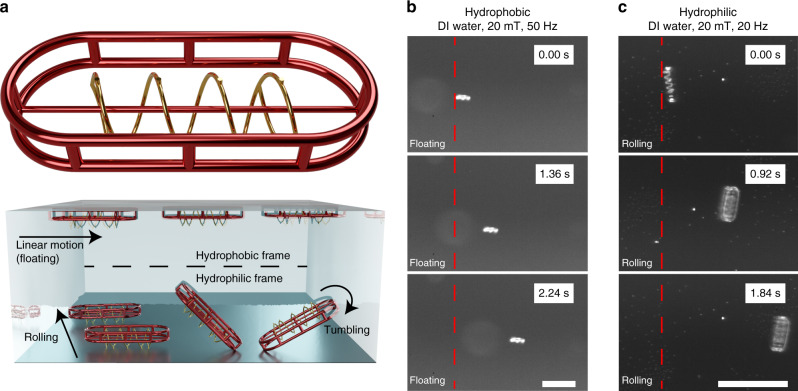
Fig. 3. Mechanically interlocked micromachines with buoyancy control.
a A polymeric frame placed around the long axis of a helical microswimmer can be used to allow metallic structures to fluid in low-density liquids such as DI water and blood. As represented in the schematic, the use of a hydrophobic frame (ecoflex) forces the structure to migrate towards the liquid/air interface, while a hydrophilic frame (PDMS) will cause it to sink and perform the rolling motion. To interlock the metallic and polymeric structures, the helical geometry is terminated by a half-segment with opposed chirality attached to both ends of the helix. By properly designing the pitch angle, an out-of-plane rotating magnetic field will result in a corkscrew motion7, thus resulting in forward motion. b When a hydrophobic frame (ecoflex) is used, hybrid microrobots can float and move forward when actuated using a rotating magnetic field. The round circle behind the structure is due to light reflection on the surface of the underlying substrate. c If a hydrophilic frame (PDMS) is used, the structure will sink towards the substrate and roll along its short axis when the same excitation is used. The scale bars are 150 μm.