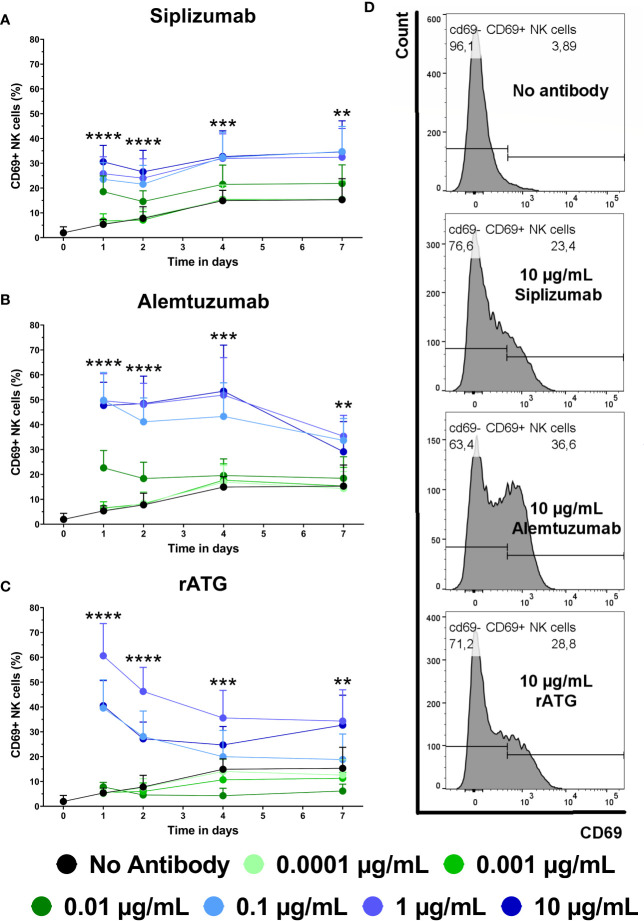
Figure 8.
The effect of siplizumab (A), Alemtuzumab (B), and rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (rATG) (C) and on CD69 expression on NK cells in allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR). Expression of CD69 was analyzed at baseline (day zero) and on days 1, 2, 4, and 7. Data is displayed as the mean of all data points (N = 9 donor pairs) ± SD. NK cells were identified as CD3− CD56+. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test with untreated controls (no antibody) serving as the comparison data set (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). (A) Siplizumab significantly increased CD69+ NK cells at 0.001–10 µg/ml (p ≤ 0.0284) on day 1 and at 0.01–10 µg/ml (p ≤ 0.0010; p ≤ 0.0377; p ≤ 0.0248) on days 2, 4, and 7 of allogeneic MLR. (B) Alemtuzumab significantly increased CD69 expression on NK cells on day 1 at 0.001–10 µg/ml (p ≤ 0.0248), on day 2 at 0.01–10 µg/ml (p ≤ 0.0024), on day 4 at 0.1–10 µg/ml (p ≤ 0.0007), and on day 7 at 0.1 µg/ml (p = 0.0003) and 1 µg/ml (p = 0.0076). (C) rATG significantly increased CD69+ NK cells at 0.01–10 µg/ml (p ≤ 0.0102) on day 1, 0.1–10 µg/ml (p ≤ 0.0022) on day 2, 1 µg/ml (p = 0.0022) and 10 µg/ml (p = 0.0266) on day 4, as well as 1 µg/ml (0.0017) and 10 µg/ml (p = 0.0038) on day 7 of allogeneic MLR. rATG inhibited CD69 expression on NK cells on day 4 at 0.001 µg/ml (0.0034) and 0.01 µg/ml (p = 0.0001). (D) Representative histograms showing CD69 expression on NK cells after 1 day of MLR in samples treated with 10 µg/ml siplizumab or 10 µg/ml rATG.