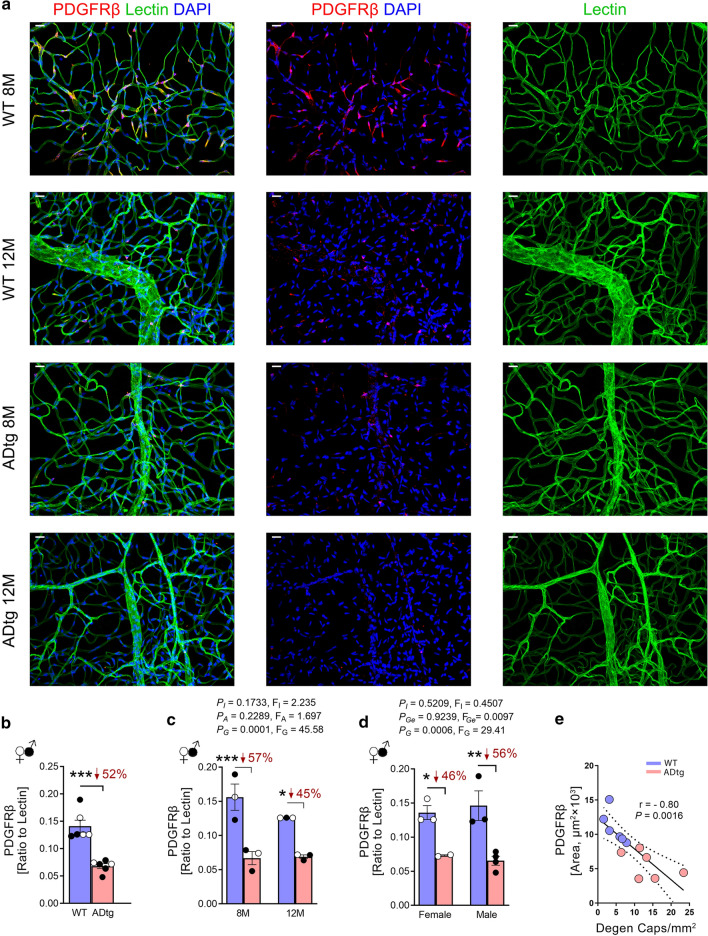
Fig. 2.
Retinal vascular PDGFRβ deficiency in APPSWE/PS1ΔE9 (ADtg) mice. A subset of the mouse cohort described in Fig. 1 of age- and sex-matched ADtg and wild type (WT) mice were analyzed at the age of 8 (n = 6; ADtg = 3 and WT = 3) and 12 (n = 6; ADtg = 3 and WT = 3) months. a. Representative fluorescence images of isolated retinal microvasculature stained for pericytes (PDGFRβ, red), blood vessels (lectin, green), and nuclei (DAPI, blue) in ADtg and WT littermates. Scale bars = 20 µm. b. A quantitative analysis of ratio between PDGFRβ-immunoreactive (IR) area and lectin-IR area in each microscopic field of isolated retinal microvasculature when mice are stratified by genotype of ADtg and WT. c–d Ratio of PDGFRβ-IR area to lectin-IR area in each microscopic field in the same mouse cohort when mice are stratified by genotypes of WT vs. ADtg and c age of mice by 8 month and 12 month or d sex of mice. e Pearson’s coefficient (r) correlation between retinal PDGFRβ-IR area and degenerated capillary count in the same mice cohort (n = 12). Data from individual mice (circles) as well as group means ± SEMs are shown. Black-filled circles represent males and clear circles represent females; blue-filled circles represent WT mice and pink-filled circles represent ADtg mice. Percentage decreases are shown in red. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc multiple comparison test. Two group statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired 2-tailed Student t-test. P and F values of two-way ANOVA refer to comparisons of age groups (PA, FA), ADtg versus WT genotype groups (PG, FG), gender groups (PGe, FGe), and overall interactions (PI, FI)