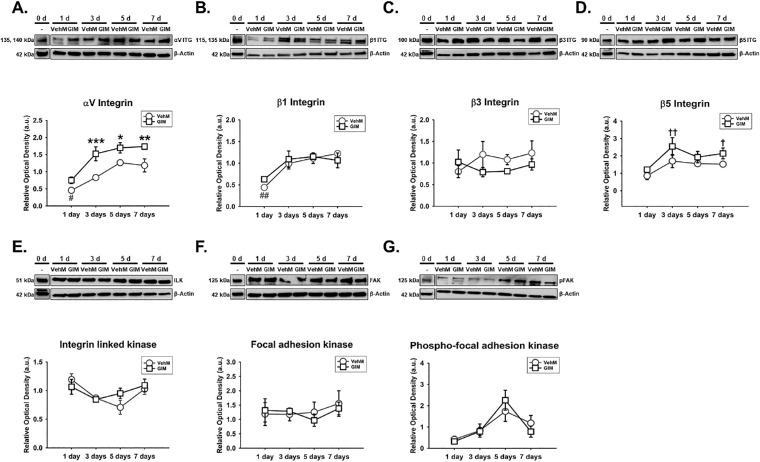
Figure 6.
GIM or VehM temporally and differentially modulated specific integrin subunits and integrin adhesomes in hTM cells. Primary hTM cells were treated with vehicle control (Veh) or 100 nM dexamethasone (DEX) in complete growth media for 4 weeks and decellularized to obtain VehMs and GIMs. New hTM cells from the same donor used to generate these matrices were subsequently cultured on VehMs and GIMs in 1% fetal bovine serum (FBS) growth media for 1, 3, 5, and 7 day(s). Protein was extracted for Western blot analysis. VehM and GIM were respectively normalized to baseline protein levels (time point 0 days). β-Actin was used as an internal control. Respective representative blot (top) and densitometric analysis (bottom) of (A) αV integrin, (B) β1 integrin, (C) β3 integrin, (D) β5 integrin, (E) integrin linked kinase, (F) focal adhesion kinase, (G) phospho-focal adhesion kinase. Columns and error bars; means and standard error of mean (SEM). Two-way ANOVA with the Holm Sidak pairwise comparisons post hoc test was used for statistical analysis (n = 5 biological replicates). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 for GIM versus VehM, given significant treatment and time interaction. †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01 for GIM versus baseline protein, given significant main effect of treatment. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 for VehM versus baseline protein. VehM, vehicle control matrix; GIM, glucocorticoid-induced matrix; hTM, human trabecular meshwork.