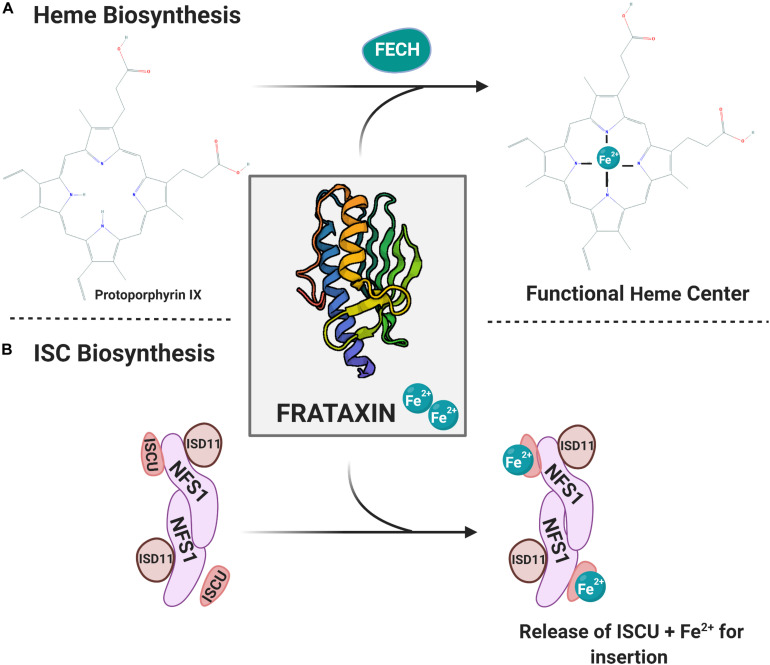
FIGURE 1.
Mitochondrial iron co-factor biosynthetic pathways are reliant on FXN iron chaperone function. (A) Heme biosynthesis. The final step is ferrochelatase (FECH)-mediated Fe2+ insertion into protoporphyrin IX. FXN-Fe2+ serves as the iron source for this heme maturation process. (B) The mitochondrial iron–sulfur cluster (ISC) biosynthetic pathway is depicted. The ISC scaffold includes NFS1, ISD11, and ISCU dimers. Delivery of the Fe2+ by FXN follows sulfur addition by cysteine desulferase (not shown). The final step of the formation before release of ISCU containing ISC centers for addition into an apo-enzyme. Protein structure provided through The Protein Data Bank (Berman et al., 2000; Dhe-Paganon et al., 2000).