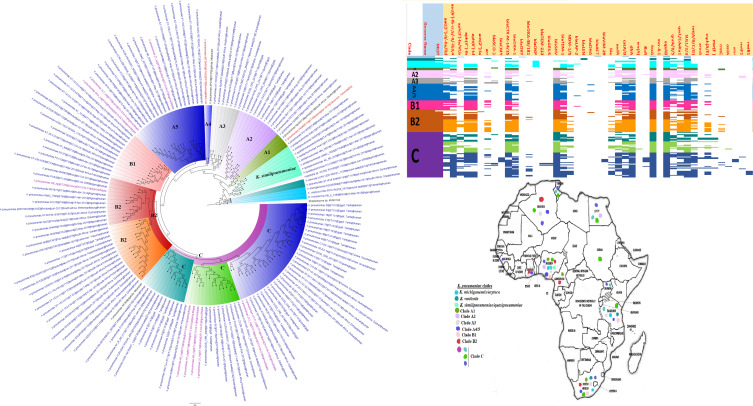
FIG 7.
Geographic distribution of Klebsiella pneumoniae clades (from second 200-genome set) and associated resistomes in Africa. Klebsiella pneumoniae was mainly from humans, with a few strains being isolated from plants and animals. There was a mixture of the clades in South Africa, Tanzania, Uganda, and West and North Africa. Strains from humans shared very close phyletic relationships with strains from animals and plants (Fig. 6 and 7). The clades harbored many conserved ARGs (n = 14): aac(3′)-Ia/IIa, aac(6′)-IIa/Ib-cr, aph(3ʺ)-Ib, aph(6′)-Id, blaCTX-M, blaOXA, blaSHV, blaTEM, aadA, catA/B, dfrA, fosA, oqxAB, and sul1/2. Other ARGs that were substantially found in K. pneumoniae included arr, mph(A/E), qnrA/B/S, qacEΔ1, and blaNDM-1/5. A few genes were restricted to certain clades. Intercountry as well as human-animal dissemination of isolates of the same clade was observed. Isolates from humans, animals, the environment, and plants are colored blue, red, mauve/pink, and green, respectively, on the phylogeny tree.