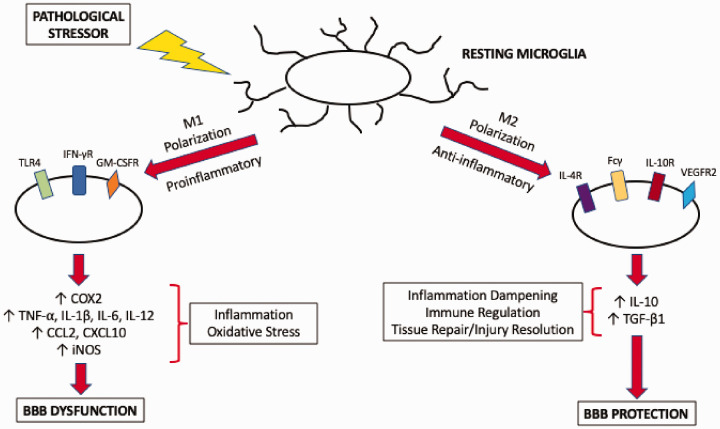
Figure 2.
Polarization of microglia in response to pathological stressors. In the absence of pathological mediators, microglia maintain a resting phenotype where they perform surveillance of the brain extracellular milieu. In the presence of a stressor, microglia are activated and can assume one of two activation states. Polarization to an M1 state is mediated by TLR4, IFN-γ receptors, or GM-CSF receptors and leads to increased production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines as well as increased expression of COX2 and iNOS. This results in increased inflammation and oxidative stress, processes that cause dysfunction of the BBB. In contrast, M2 microglia perform inflammation dampening, immune regulation, and tissue repair/injury resolution functions. Polarization of microglia to a M2 activation state involves IL-4 receptors, Fcγ, IL-10 receptors, or VEGFR2. M2 microglia secrete anti-inflammatory mediators such as IL-10 and TGF-β1 and help to protect the BBB in the setting of neurological disease.