Figure 3.
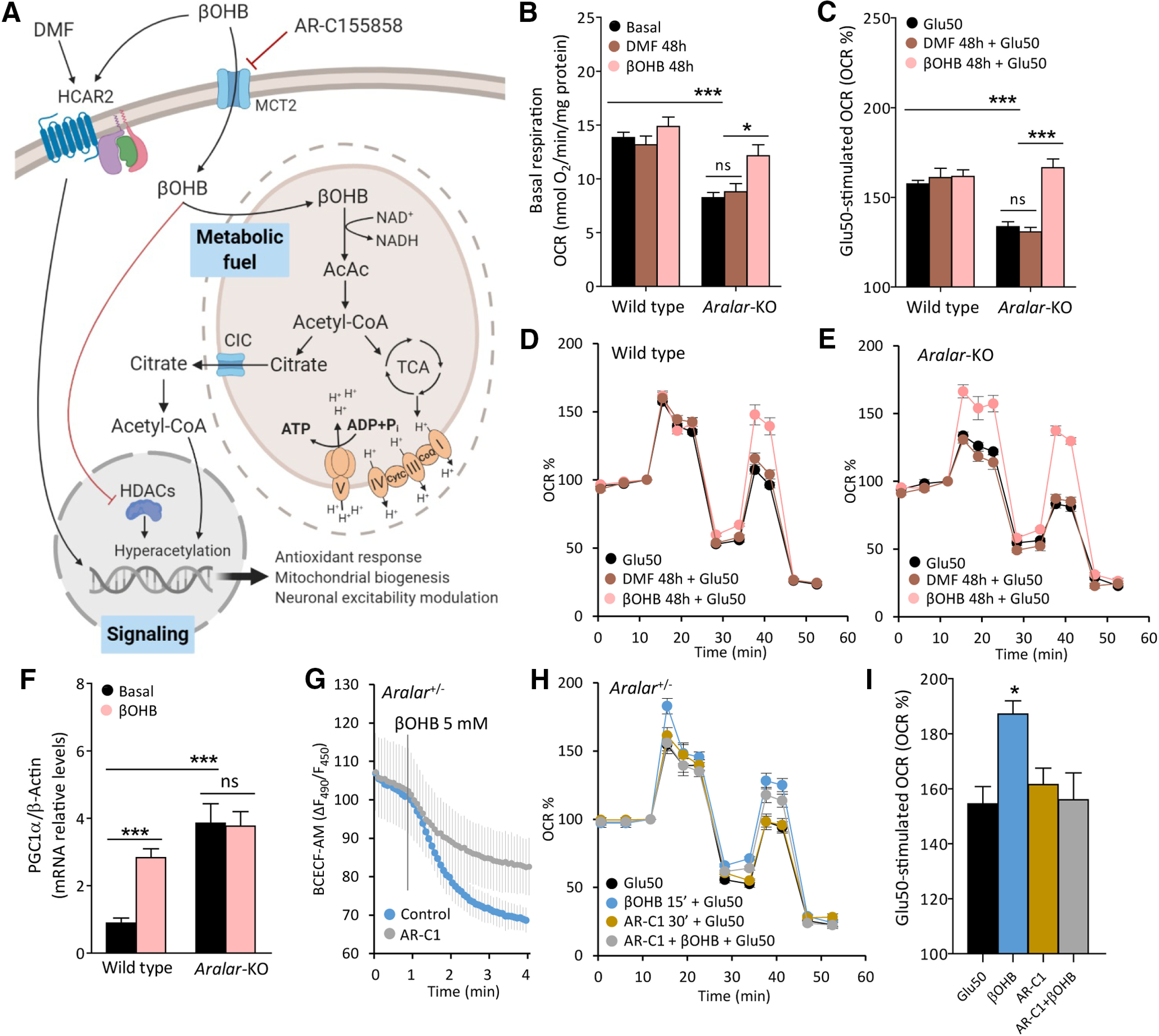
Molecular pathways involved in the effects of βOHB on neuronal respiration. A, Representative scheme of βOHB actions in neurons as a fuel and as a signaling molecule. Image created with BioRender.com. B, Effects of 20 μm DMF and 5 mm βOHB on basal respiration expressed as OCR (nmol O2/min/mg protein). C–E, Effects of DMF and βOHB on Glu50-stimulated respiration expressed as % of basal values (C), in WT (D), and aralar-KO (E) neurons. Mean ± SEM from three to seven embryos measured in triplicate; ***p ≤ 0.001, *p ≤ 0.05 (two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni-corrected t test). F, PGC1α mRNA levels in WT and aralar-KO neurons under basal conditions and after 96-h treatment with 5 mm βOHB. β-Actin used as a housekeeping gene. Mean ± SEM from 6–12 embryos measured in triplicate; ***p ≤ 0.001, versus WT basal (two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni-corrected t test). G, Intracellular pH variations of aralar+/− BCECF-AM loaded neurons expressed as variation in fluorescence ratio (ΔF490/F450), after 5 mm βOHB acute addition with or without a 30-min preincubation with 1 mm MCT2 inhibitor AR-C155858 (AR-C1). H, Effects of 1 mm AR-C1 30-min preincubation on Glu50-stimulated respiration, with or without a 5 mm βOHB 15-min preincubation in aralar+/− neurons. I, Glu50-stimulated respiration expressed as % of basal OCR. Mean ± SEM from one to two embryos in triplicates; *p ≤ 0.05 (one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls multiple comparison t test). Mitochondrial function determined in 2.5 mm glucose and 2 mm Ca2+ DMEM as indicated in Figure 1B. AcAc, acetoacetate; AcCoA, acetyl-CoA; CoQ, coenzyme Q; CytC, cytochrome C; DMF, dimethylfumarate; HCAR2, hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2; HDACs, histone deacetylases; MCT2, monocarboxylate transporter 2; TCA, trycarboxylic acid cycle; βOHB, β-hydroxybutyrate. ns, not significant.
