Figure 1.
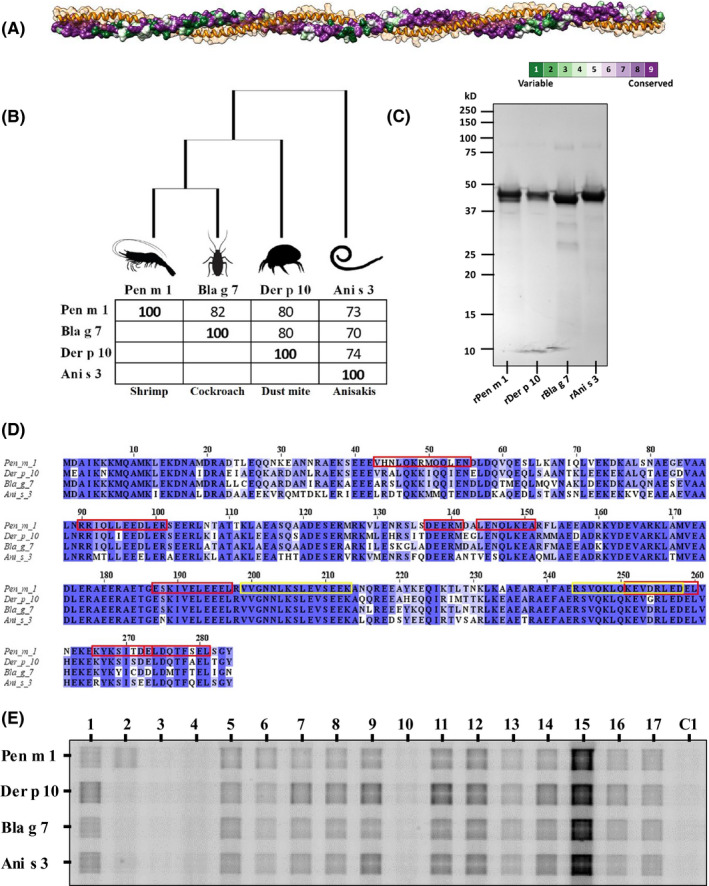
Invertebrate tropomyosins investigated in this study. A, A homology model of tropomyosin displaying the alpha‐helical coiled‐coil structure using a ribbon/space‐fill model (orange) and the patterns of sequence conservation shown using ConSurf model. B, A phylogenetic tree and percent identity grid for invertebrate tropomyosins investigated in this study. C, SDS‐PAGE Coomassie‐stained gel profile of purified tropomyosins. D, Multiple sequence alignment using Clustal Omega algorithm of Pen m 1, Der p 10, Bla g 7, and Ani s 3 showing conserved amino acid residues. Pen m 1 IgE‐binding epitopes are denoted by red boxes. 15 Yellow boxes indicate Pen m 1 peptides 67 and 82 selected for T‐cell cross‐reactivity experiments. E, IgE grid immunoblotting using serum from shrimp‐allergic patients (1‐17) and one healthy donor (C1) to demonstrate presence or absence of IgE co‐sensitization to invertebrate tropomyosins
