Figure 2.
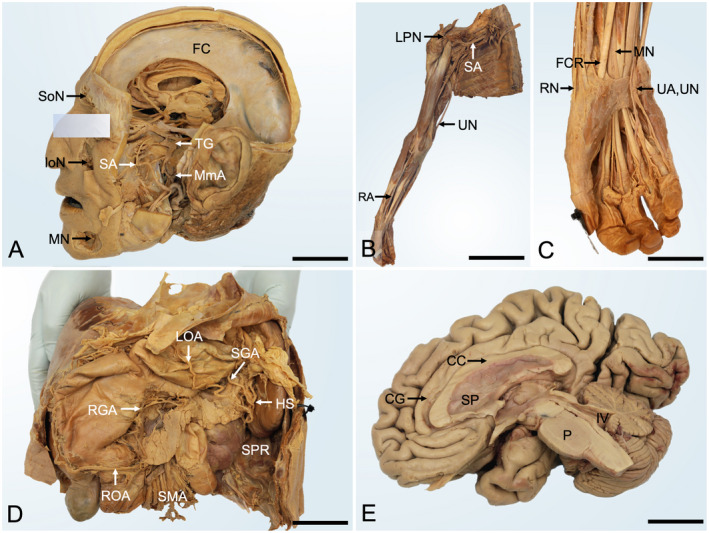
Gross anatomy samples of phenoxyethanol‐based embalming prosections. A, Head dissection from a 91‐year‐old male (5 years postfixation). The neurocranium and parts of the zygomatic bone, mandible, and left cerebral hemisphere were removed to show the trigeminal nerve and its branches. Note the reflected parotid duct. FC, falx cerebri; IoN, infraorbital nerve; MmA, middle meningeal artery; MN, mental nerve; SoN, supraorbital nerve; SA, sphenopalatine artery; TG, trigeminal ganglion; scale bar 45 mm. B, Right upper limb dissection of a 65‐year‐old male (7 years postfixation) shows an overview of the upper limb. LPN, lateral pectoral nerve; RA, radial artery; SA, subclavian artery; UA, ulnar artery; scale bar 280 mm. C, the magnified wrist and hand dissection of the upper limb shown in panel B. FCR, flexor carpi radialis; MN, median nerve; RN, radial nerve; UA, ulnar artery; UN, ulnar nerve; scale bar 45 mm. D, Upper abdominal area prosection from a 78‐year‐old female (4 years postfixation). The liver, stomach pancreas, and spleen are shown to be supplied by branches of the celiac trunk and superior mesenteric artery. HS, hilum of the spleen; LOA, left gastro‐omental artery; RGA, right gastric artery; ROA, right gastro‐omental artery; SGA, short gastric arteries; SMA, superior mesenteric artery; SPR, spleno‐phrenic recess; scale bar 100 mm. E, Right sagittal dissection of the brain from a 98‐year‐old female (2 years postfixation) after removal of the arachnoid layer. CC, corpus callosum; CG, cingulate gyrus; P, pons; SP, septum pellucidum; IV, fourth ventricle; scale bar 30 mm.
