Figure 5.
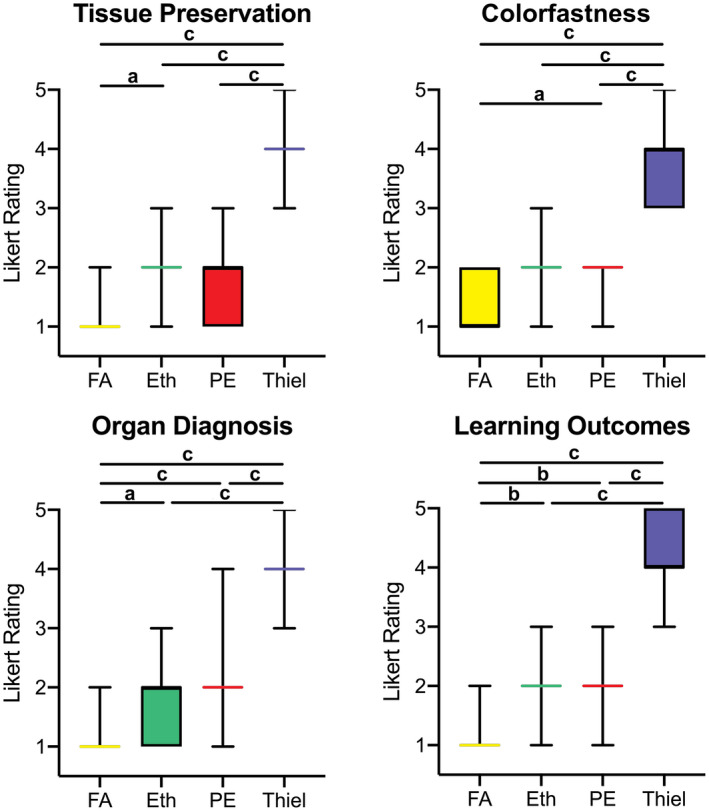
Survey on histological anatomical tissue quality derived from human cadavers embalmed with formaldehyde (FA), ethanol–glycerin (Eth), phenoxyethanol (PE), and Thiel. Tissue preservation, colorfastness, their suitability to make a proper organ diagnosis and their potential to improve student learning outcomes when used as study material were assessed. Significant difference (a P ≤ 0.05, b P < 0.001, c P < 0.0001) was found throughout the different embalming techniques, showing superiority of formaldehyde embalmed compared the other techniques especially for organ diagnosis and student learning outcomes compared to PE, and PE being superior to Thiel yet similar to Eth for most aspects. Likert scale rating: 1 = perfect/well suited/fully agree and 5 = poor/completely unsuitable/fully disagree.
