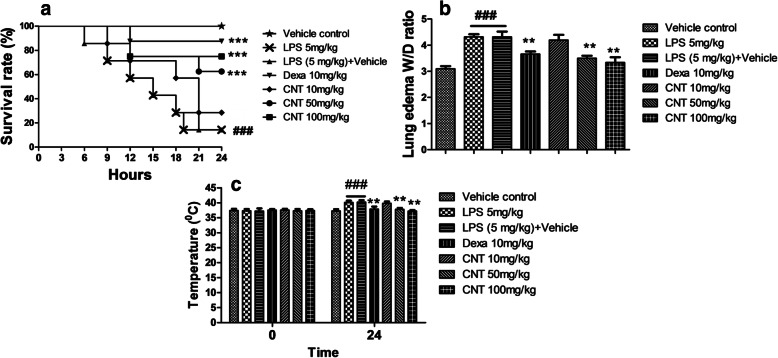
Fig. 1.
Effects of continentalic acid (10, 50 and 100 mg/kg) on LPS-induced mortality (a), lung W/D ratio (b) and temperature changes (c) in mice following LPS-induced lung injury. The survival rate was analysed at different time interval such as 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21 and 24 h following LPS-induced acute lung injury and the effect of the continentalic acid was assessed on the LPS-induced acute lung injury. The continentalic acid dose dependently improved the survival rate and the dose of the 100 mg/kg showed maximum protection. Similarly, the weight to dry ratio of the lung was assessed by dividing the wet weight of the lung on the dry weight. Furthermore, the temperature changes were determined in all the treated groups before the induction of the LPS-induced lung injury and 24 h after the LPS administration. The continentalic acid showed significant improvement in the survival rate, lung W/D ratio and temperature changes. All the data were expressed as mean (n = 8) ± SD. ###p < 0.001 compared to control group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 compared to LPS-treated group