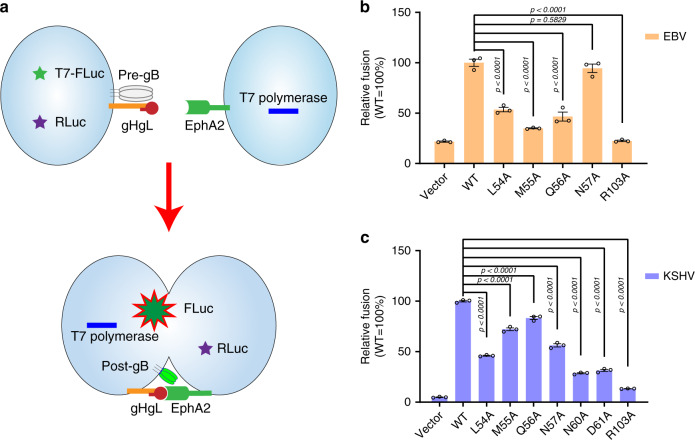
Fig. 4. Key residues in the gHgL-binding site of EphA2 are critical for cell fusion.
a Schematic diagram of the cell-based fusion assay. The cells expressing gB, gH, gL, and firefly luciferase reporter gene under the control of the T7 promoter were co-cultured with other cells expressing T7 polymerase and EphA2 proteins. Receptor EphA2 bound to gHgL, increasing the fusion of the two types of cells. T7 polymerase initiated the expression of firefly luciferase, which was detected using the Dual-Luciferase® Reporter Assay System. Renilla luciferase was used as a transfection control. Pre-gB indicates the pre-fusion state of gB, whereas post-gB indicates the post-fusion state of gB. b, c Cell-based EBV (b) and KSHV (c) fusion assays were performed by co-culturing of HEK-293T cells transfected with plasmids expressing EphA2 and mutants, and HEK-293T cells transfected with plasmids expressing gB and EBV gHgL (b) or KSHV gHgL (c). Representative results from three experiments are shown. Relative fusion was normalized to that of wild type EphA2. The data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent replicates). Statistical significance was analyzed using Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test for multiple groups. The GenBank accession codes for gH, gL, and gB are shown in the Supplementary Table 3. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.