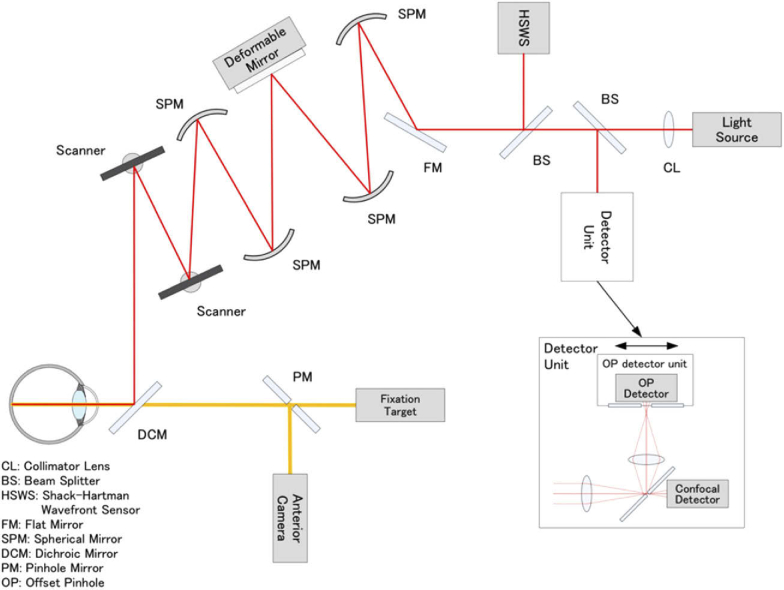
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of the optical structure of adaptive optics scanning light ophthalmoscope. Collimated near-infrared light from the light source propagates through the spherical mirrors, beam splitters, and dichroic mirror to the subject’s eye. Two scanners are used to scan the imaging light two-dimensionally on the retina. Ninety-seven-actuator deformable mirror is used to compensate the eye’s aberration, which is measured by the Shack-Hartman wavefront sensor. The confocal light is detected by the confocal detector of the detector unit through the pinhole, and the light outside the pinhole is reflected to the offset pinhole detector. The light for the fixation target and the anterior camera are combined by the dichroic mirror. The pinhole size of the confocal imaging was 48 μm, which equaled the airy disk diameter (1 ADD) of the system. The pinhole size of the offset pinhole imaging was 344 μm (7 ADD). The pinholes were offset by 180 μm (3.75 ADD) in opposite directions in the plane horizontal to the retina.