FIGURE 4.
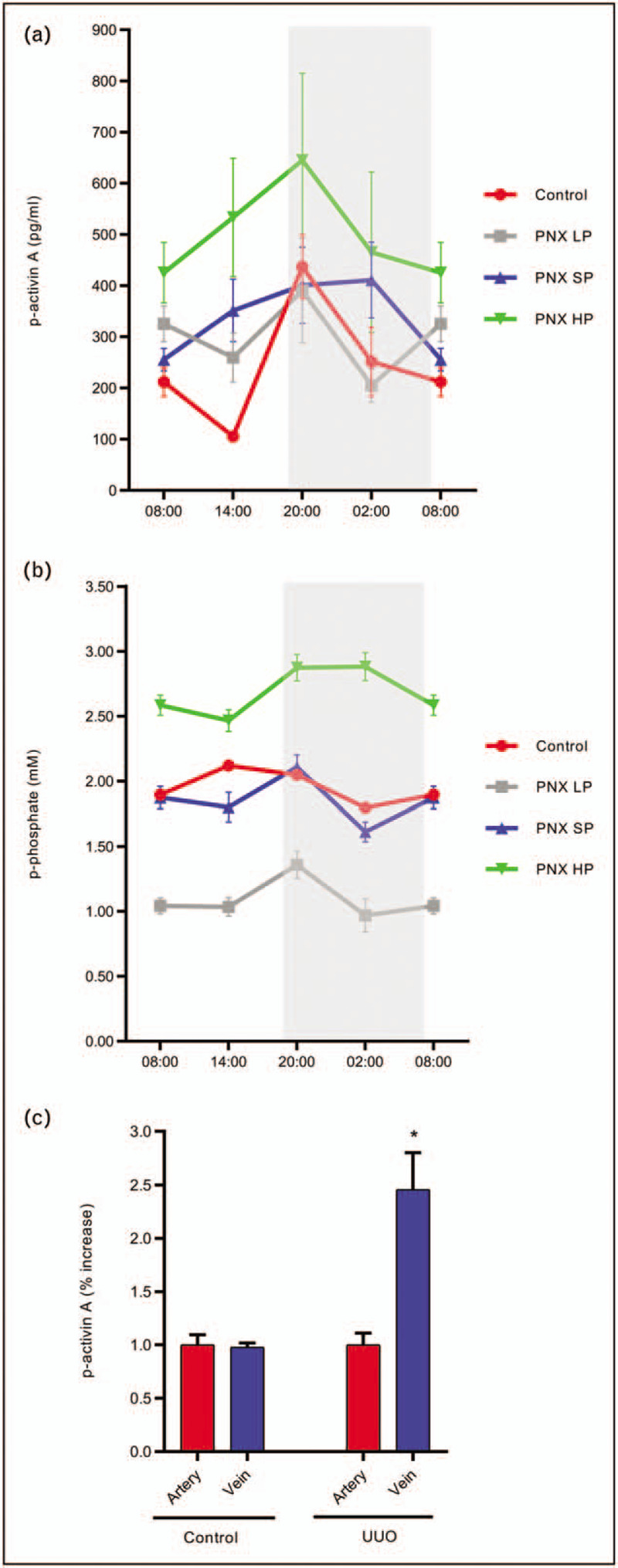
Circadian rhythm of plasma activin A and phosphate in normal and uremic rats on different phosphate diets. Induction and secretion of activin A from the injured kidney. Plasma activin A exhibits circadian rhythmicity in control rats, whereas the rhythm is obliterated by chronic kidney disease. An increase in plasma activin A levels was observed in chronic kidney disease rats, but depending upon the time of the day. In chronic kidney disease rats on a low phosphate diet the increase in plasma activin A was inhibited. However, the circadian rhythm was not restored (a). Similarly, circadian rhythmicity of plasma phosphate was disturbed in chronic kidney disease rats. Furthermore, chronic kidney disease rats on a high phosphate diet developed hyperphosphatemia. This was prevented by the low phosphate diet, which however did not restore the circadian rhythmicity of plasma phosphate in chronic kidney disease (b) [12▪]. Kidney injury was induced by unilateral ureter obstruction for 15 days and blood sampling from the isolated renal artery and vein was performed. Activin A was induced and secreted of from the injured kidney (c). partly nephrectomized: 5/6 partial nephrectomy. HP, high-phosphate diet; LP, low-phosphate diet; SP, standard-phosphate diet. Mean ± SEM.
