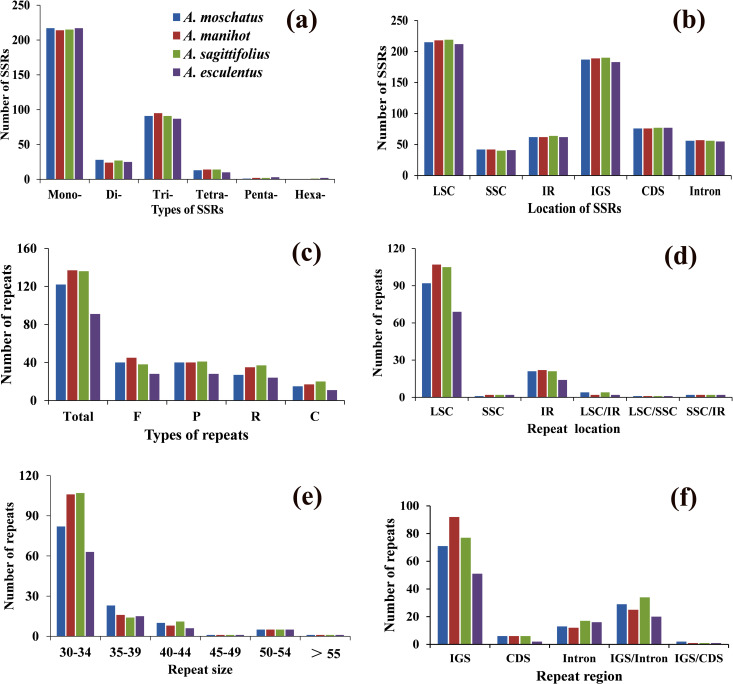
Fig 2. Comparison of SSRs and repeat sequences among four Abelmoschus species.
(a) Numbers of different types of SSRs; Mono-: mononucleotide, Di-: dinucleotide, Tri-: trinucleotide, Tetra-: tetranucleotide, Penta-: pentanucleotide, Hexa-: hexanucleotide; (b) Location of SSRs in different chloroplast genome regions. LSC: large single copy, SSC: small single copy, IR: inverted-repeat region. IGS: Intergenic spacer regions, CDS: coding DNA sequences, Intron: intronic regions; (c) Different types of repeat sequences. Total: total numbers of all repeats. F: forward repeats, P: palindromic repeats, R: reverse repeats, C: complementary repeats; (d) Number of repeats present in different locations of chloroplast genomes. LSC/IR: one copy of repeat present in LSC and another in IR, LSC/SSC: one copy of repeat present in LSC and another in SSC, SSC/IR: one copy present in SSC and another in IR; (e) Number of repeats in different size. For example, 30–34 represent the numbers of repeats with the size from 30 to 34 bp; (f) Number of repeats in different regions of chloroplast genomes. IGS/Intron: one copy of repeat present in intergenic spacer regions and another in intronic regions. IGS/CDS: one copy of repeat present in intergenic spacer regions and another in coding regions.