Fig. 3. Speciation during closed-system cooling of a magma ocean–generated atmosphere.
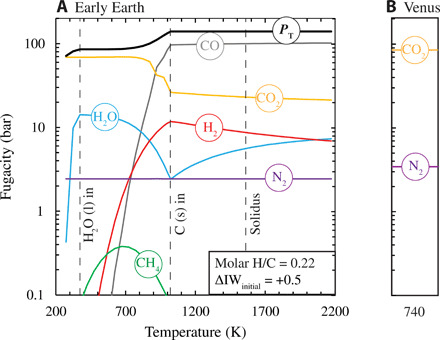
(A) A model atmosphere on the early Earth initially in equilibrium with a magma ocean of BSE composition with H = 0.01 weight % (wt %); C = 0.01 wt %, N = 0.0002 wt % (24, 53) before cooling to 300 K. Molar abundances of H, C, and N in the atmosphere are calculated with existing solubility laws (54–56) yielding H/C = 0.22 and H/N = 5.8, while O is fixed to give an fO2 of ΔIW + 0.5 at 2173 K. The resultant atmosphere of 140 bar is allowed to cool in a closed system. Vertical lines denote the temperatures of condensation of H2O, graphite, and the 1-bar peridotite solidus. Speciation of the real gas is calculated at 50 K intervals using FactSage 7.3 (61) and is reported as fugacity (bar). (B) The present-day partial pressures of CO2 and N2 on Venus are shown for comparison at its surface temperature of 740 K.
