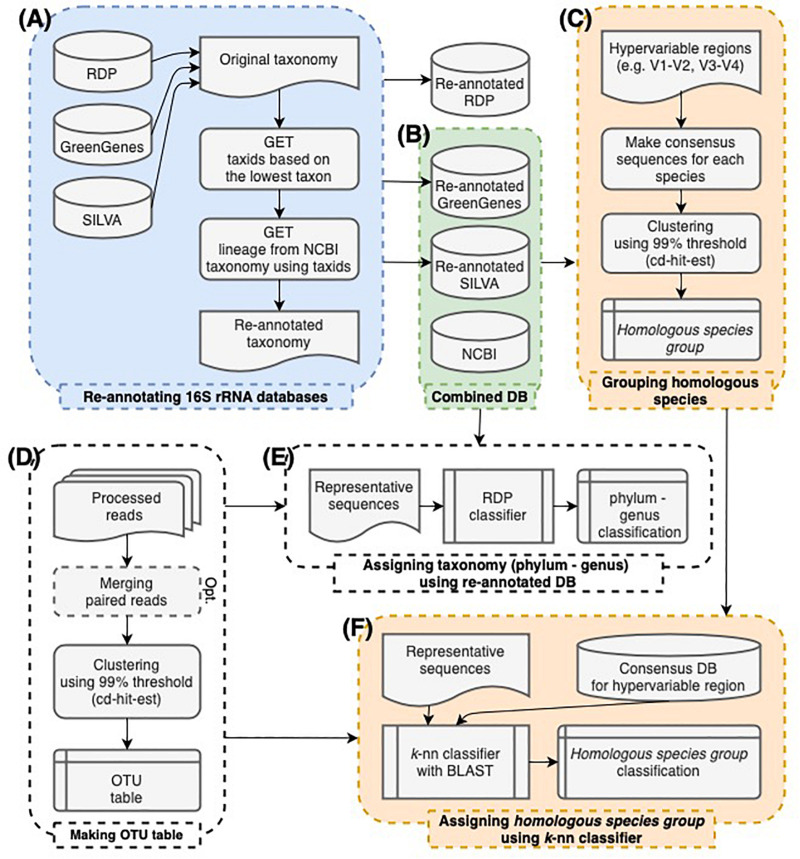
FIGURE 1.
The workflow of this study. (A) The taxonomy of 16S rRNA sequences in GreenGenes, SILVA, and RDP databases was re-annotated according to the NCBI taxonomy. (B) GreenGenes, SILVA, and NCBI databases were combined. RDP database was excluded since they have no species annotation. (C) Consensus sequences of each species were made by hypervariable region sequences extracted from the combined databases. By clustering consensus sequences within 99% sequence similarity, homologous species groups were established. (D) OTU tables were made in a conventional manner. (E) The taxonomy assignment from phylum to genus-level was processed by the RDP naïve Bayesian classifier re-trained using the combined database. (F) The species-level classification was processed by searching sequences against the consensus database. Sequences were labeled as the representative species of the homologous species group that includes the best hit of the sequence.