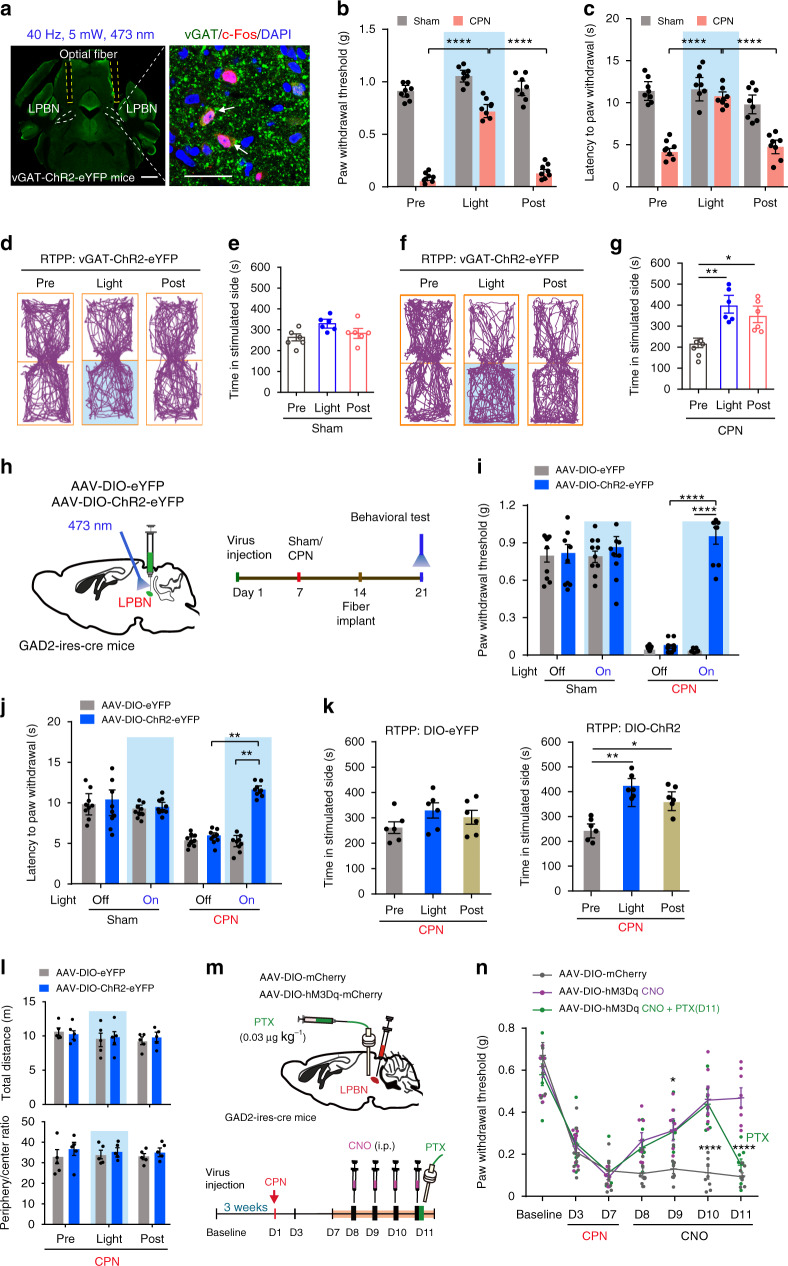
Fig. 6. Optogenetic stimulation of LPBN GABAergic neurons suppresses neuropathic pain-like hypersensitivity, but not basal nociception.
a Image showing optic fibers position in the LPBN (left; scale bar, 1 mm) and c-Fos (red) co-labeled with vGAT-positive neurons (green) in the LPBN after optogenetic stimulation (right; arrows, double-labeled neurons; scale bar, 30 μm). b, c Photoactivation of GABAergic LPBN neurons elevate the PWT (b) and thermal paw-withdrawal latency (c) in CPN-ligated, but not in Sham-operated vGAT-ChR2-eYFP mice. d, f Tracking maps of RTPP from a Sham (d) and a CPN-ligated mouse (f) before, during, and after optogenetic stimulation of GABAergic LPBN neurons. e, g Quantification of time spent in stimulated side as shown in d and f. h Schematic of virus delivery (left) and timeline of the behavioral experiments (right). i, j Optogenetic activation of the GABAergic LPBN neurons increased the PWT (i) and thermal paw-withdrawal latency (j) in CPN-ligated mice, but not in Sham-operated mice or in mice transfected with DIO-eYFP. k Quantification of time spent in the non-preferred RTPP chamber before (Pre), during (Light), and after (Post) laser stimulation of CPN-ligated GAD2-ires-Cre mice transfected with AAV-DIO-eYFP (left) or AAV-DIO-ChR2-eYFP (right). l Quantification of total distance moved (upper) and ratio of time spent in the periphery and center (lower) in the OFT before (Pre), during (Light), and after (Post) light stimulation of GABAergic LPBN neurons in GAD2-ires-Cre mice. m Experimental design for pharmacogenetic activation of GABAergic LPBN neurons. n Time-course of the CPN ligation-induced decrease in PWT and the effect of pharmacogenetic activation of GABAergic LPBN neurons which was reversed by administration of PTX (0.03 μg kg−1) via a cannula into the LPBN at day 11. All data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. and error bars represent s.e.m. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001. See also Supplementary Table 1 for further statistical information. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.