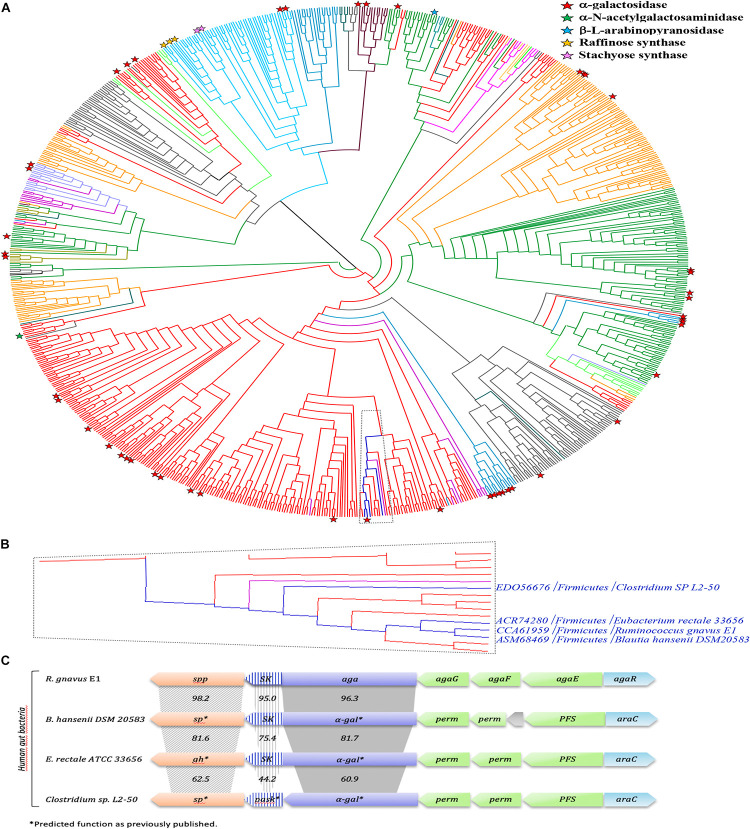
FIGURE 11.
Phylogenetic study of the GH36 family and RgAgaSK genomic environment. (A) A Phylogenic tree of the GH36 family was constructed including all the GH36 referenced in the CAZy database at 11/06/2019. Members sharing full synteny with RgAgaSK are indicated in deep blue. The tree has been colored according to the phylogenetic classification of the organisms. Indeed, Firmicutes appeared in red, Bacteroidetes in gray, Proteobacteria in orange, Actinobacteria in deep green, Acidobacteria in light green, Eukaryota in light blue, Fungi in medium blue, Archaebacteria in deep violet, Spirochaetes in light violet, Thermotogae in light purple, Verrucomicrobia in water-green, Deinococcus in kaki, and Chloroflexi in pink. Characterized enzymes are labeled with a red star for their α-galactosidase activity, a green star for their α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity, a blue star for their β-L-arabinopyranosidase activity, an orange star for their raffinose synthase activity and a pink star for their stachyose synthase activity. (B) Zoom of the clade which includes RgAgaSK and members sharing full synteny with RgAgaSK (in deep blue) and other sequences from human gut bacteria. (C) Genomic environment of the RgAgaSK encoding gene. The values indicate the percentage of identities between the encoding genes according to their modularity i.e., kinase, α-gal and spp or sp.