Fig. 3. Light back-scattering from three-dimensional fiber non-wovens.
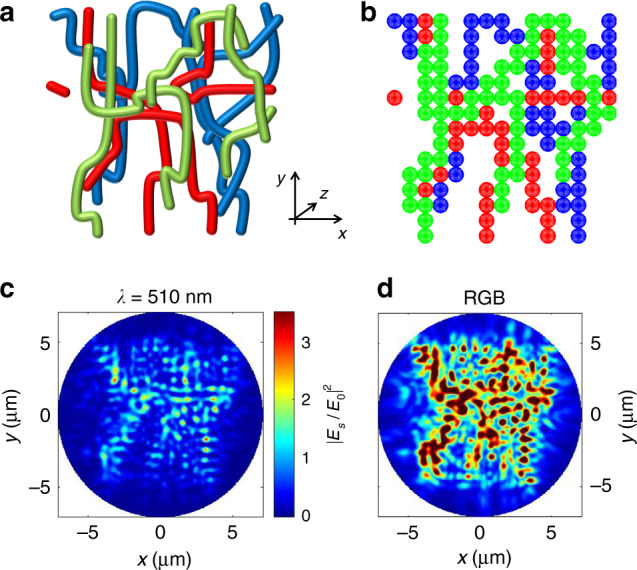
a Scheme of the structure of nanofibers used for the calculations. To mimic the morphological structure of the fibrous non-woven, an area of 10 × 10 µm2 is considered in the x–y plane, and three layers of fibers are positioned along the axial (z) direction with total thickness 2.1 μm (green nanofibers are placed in the first layer, red ones in the second layer, and blue ones in the third layer). The average fiber diameter (700 nm) equals the value measured by SEM (Fig. S2, Supplementary Information). b Planar view (x–y) of cluster discretization used to calculate the light-scattering properties. Each polymer filament is schematized as a linear cluster with 700 nm spherical subunits. c Backscattering intensity map at λ = 510 nm, calculated as the ratio of the backscattered field (Es) and the incident one (E0). The map is obtained by considering a plane wave illumination with unitary amplitude impinging perpendicularly to the fibers (i.e., along the z axis), averaging over polarization, and it is calculated at about 1 μm distance from the first layer of the structure. d RGB intensity map obtained as the sum of the backscattering maps calculated at wavelengths corresponding to red (λ = 600 nm), green (530 nm,) and blue (450 nm) wavelengths.
