Fig. 1. A vulnerable mPFC social circuit in response to juvenile social isolation in mice.
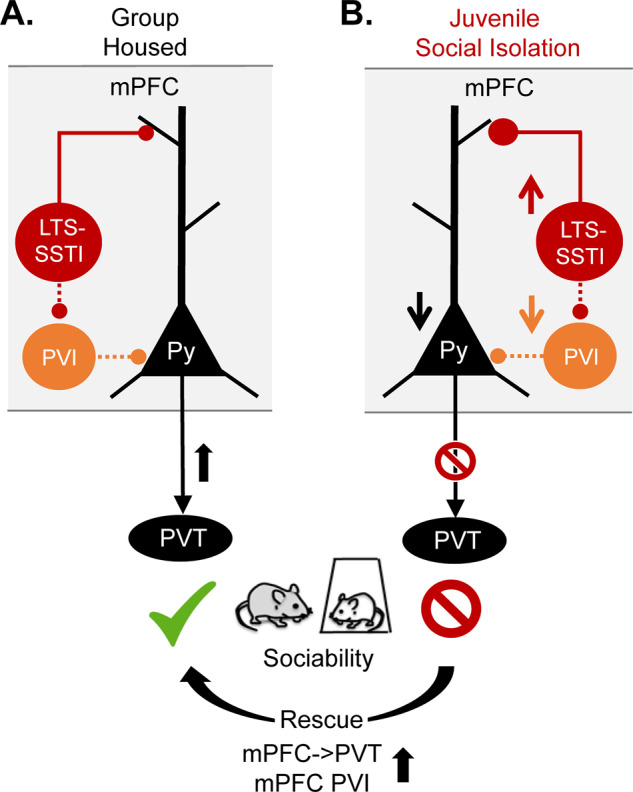
A. Activation of mPFC→PVT projection neurons (black) or mPFC PVIs (orange) is essential for normal sociability in adult group-housed mice. B. However, these neurons show decreased intrinsic excitability and an increased inhibitory input drive from mPFC LTS-SSTIs (red) in juvenile socially isolated (jSI) mice, which show decreased sociability in adulthood. Decreased sociability can be induced in normal animals by inhibiting mPFC→PVT projection/mPFC PVIs or activating mPFC LTS-SSTIs in adulthood. Sociability deficits of jSI mice can be rescued by increasing PFC→PVT projection neuron or mPFC-PVI activity (bottom arrow).
