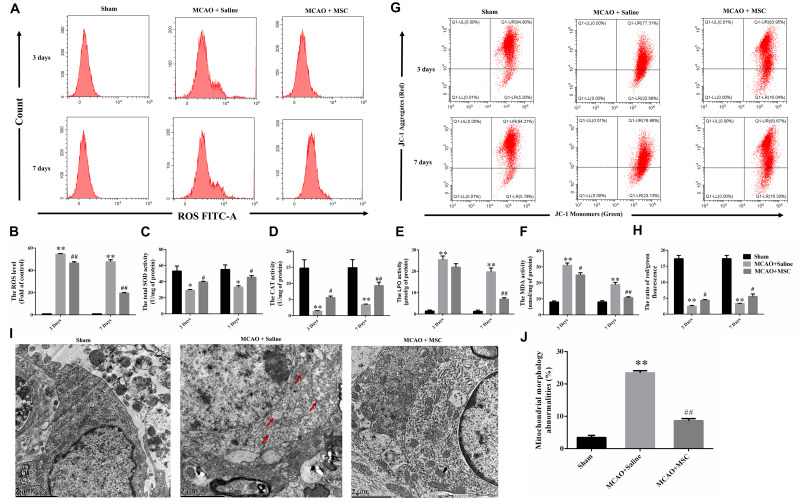
FIGURE 2.
OM-MSC administratio reduced oxidative stress level and alleviated mitochondrial dysfunction in an MCAO animal model. (A,B) ROS levels in the peri-infarct cortex were detected, and the determination was carried out using a flow cytometer. The levels were normalized by the fluorescence intensity of the control group (the value of control cells was presented as 1.0). (C–F) Measurement of antioxidative enzyme activities of CAT and SOD, and oxidative enzyme activities of LPO and MDA. (G–H) Mitochondrial membrane potential was measured using a JC-1 probe determined by flow cytometry. (I) Representative photographs of the transmission electron microscope showed ultrastructural changes in mitochondria morphology in the peri-infarct cortex and its reversal after OM-MSC treatment. In the MCAO + saline group, mitochondria with abnormal shapes, such as focal enlargement of the intermembrane space and loss of a normal cristae pattern (red arrows), were observed. (J) Based on representative photographs, quantification of aberrant mitochondria (membrane ruptures, vacuole formation) was performed. All data are displayed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 vs. sham-operated, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. MCAO + saline).