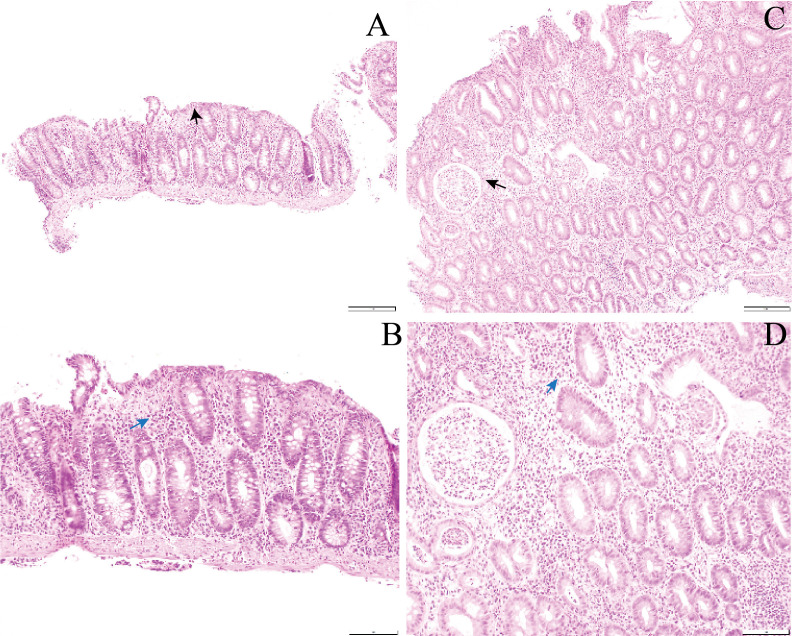
Figure 2.
Representative H&E stained sections demonstrating increased different cellular infiltrates in colitis patients treated with monotherapy and combined immunotherapy (IPI+PD1). Representative H&E sections demonstrating increased different cellular infiltrates in colitis patients treated with monotherapy and combined immunotherapy. (A and B) Histopathology image of colonic biopsy of patient treated with anti-PD1 showing a diffuse chronic inflammatory infiltrate within the lamina propria (blue arrow) and an increase in lymphocytes with the surface epithelium (black arrow). A. H&E ×10; B. H&E ×20. (C and D) Histopathology image of colonic biopsy of patient treated with anti-PD1 and anti-CTLA-4 showing a diffuse infiltration of neutrophils within the lamina propria with numerous neutrophilic crypt abscesses (black arrow) and foci of cryptitis (blue arrow). C. H&E ×10; D. H&E ×20. CTLA-4, cytotoxicT-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; PD1, programmed cell death protein 1, IPI, ipilimumab