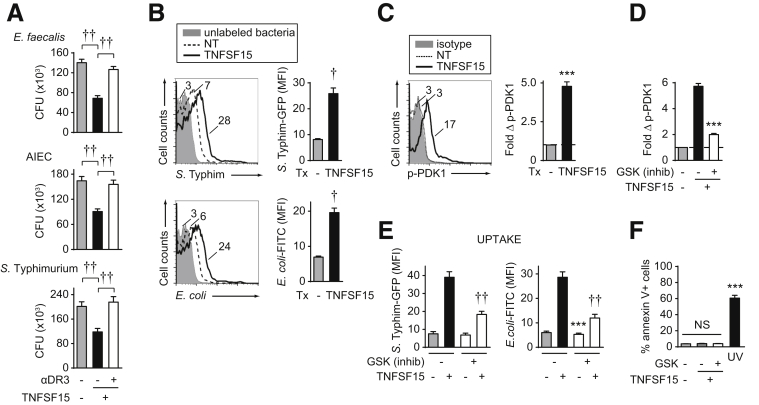
Figure 1.
TNFSF15 treatment of human MDMs increases bacterial uptake and intracellular bacterial clearance. (A) MDMs were left untreated or treated with 10 ng/mL TNFSF15 for 48 hours ± pretreatment for 1 hour with neutralizing anti-DR3 antibodies (or isotype control) (n = 12 donors from 2 independent experiments, repeated in an additional 16 donors in the absence of neutralizing antibodies), and then co-cultured with E faecalis, AIEC, or S Typhimurium and assessed for intracellular bacterial clearance as per the Materials and Methods section. Mean colony forming units (CFU). (B) Human MDMs were left untreated or treated with 10 ng/mL TNFSF15 for 48 hours and then co-cultured with S Typhimurium-GFP or E coli–fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) bioparticles and uptake was assessed 20 minutes later by flow cytometry. Left: Representative flow cytometry with mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Right: Summary graph of MFI (n = 8 donors from 2 independent experiments). (C) Human MDMs were left untreated or treated with 10 ng/mL TNFSF15 for 20 minutes. PDK1 activation was assessed by flow cytometry. Left: Representative flow cytometry. Right: Summary graph of fold PDK1 activation (n = 4 donors, similar results in an additional n = 4 over a time course). (D–F) Human MDMs were left untreated or treated with 10 ng/mL TNFSF15 ± GSK 233470 (PDK1 inhibitor; 1-hour pretreatment). (D) Fold PDK1 activation at 20 minutes (n = 4). (E) After 48 hours, cells were co-cultured with S Typhimurium–GFP or E coli–FITC bioparticles and uptake was assessed 20 minutes later (MFI) (n = 8 from 2 independent experiments). (F) Cell death was assessed at 48 hours by annexin V staining (n = 4). UV stimulation at 50–100 J/m2 was used as a positive control. Means + SEM. Significance comparison is between inhibitor to the vehicle control for the corresponding TNFSF15 treatment condition for panels D–E. ∗∗∗P < .001; †P < 1 × 10-4; ††P < 1 × 10-5. NT, no treatment; Tx, treatment.