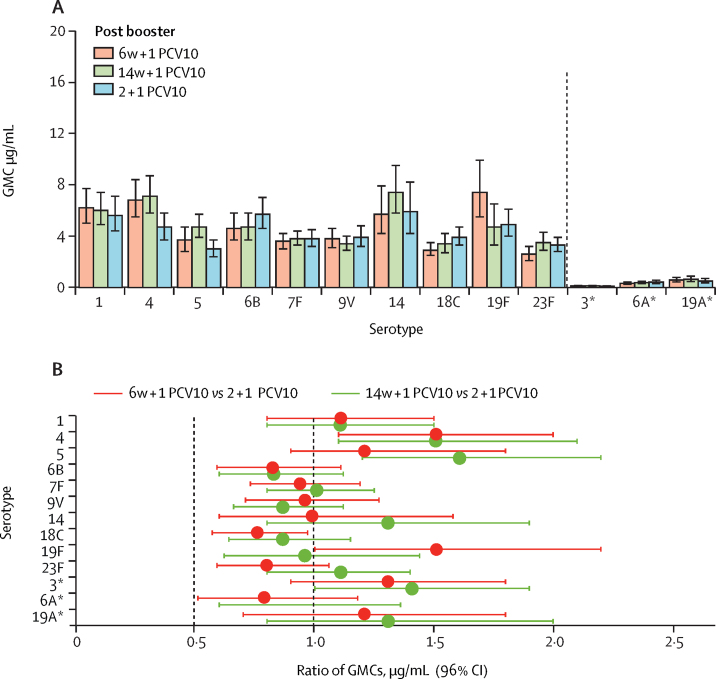
Figure 3.
Serum IgG 1 month post booster with PCV10 following a single-dose or two-dose primary series
(A) GMCs of serotype-specific IgG antibodies (error bars indicate 96% CIs). (B) Ratio of serotype-specific GMCs. The vertical dashed line at 0·5 indicates the non-inferiority margin; for the 1 + 1 vaccine schedule to be non-inferior to the 2 + 1 schedule, the lower bound of the 96% CI for the ratio of GMCs had to be higher than 0·5 for at least eight of the ten vaccine serotypes. The serotype-specific IgG GMC was higher in the 1 + 1 group than in the 2 + 1 group if the lower bound of the 96% CI was above 1, whereas the serotype-specific IgG GMC was lower in the 1 + 1 group than in the 2 + 1 group if the upper bound of the 96% CI was less than 1 (note that the limits have been rounded in this figure). Infants received one primary dose of PCV10 at age 6 weeks (6w + 1 PCV10) or 14 weeks (14w + 1 PCV10) or two primary doses, one each at ages 6 weeks and 14 weeks (2 + 1 PCV10). All infants received a booster dose of PCV10 at age 40 weeks. PCV10=ten-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. GMC=geometric mean concentration. *Serotypes included in the 13-valent but not the ten-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine.